In general, PBB technologies in the 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, or 7950 XRS SR OS support a way to contain the flooding for a specified I-VPLS ISID, so that BUM traffic for that ISID only reaches the PEs where the ISID is locally defined. Each PE creates an MFIB per I-VPLS ISID on the B-VPLS instance. That MFIB supports SAP or SDP bindings endpoints that can be populated by:
MMRP in regular PBB-VPLS
IS-IS in SPBM
In PBB-EVPN, B-VPLS EVPN endpoints can be added to the MFIBs using EVPN Inclusive Multicast Ethernet Tag routes.
The example in Figure 1 shows how the MFIBs are populated in PBB-EVPN.
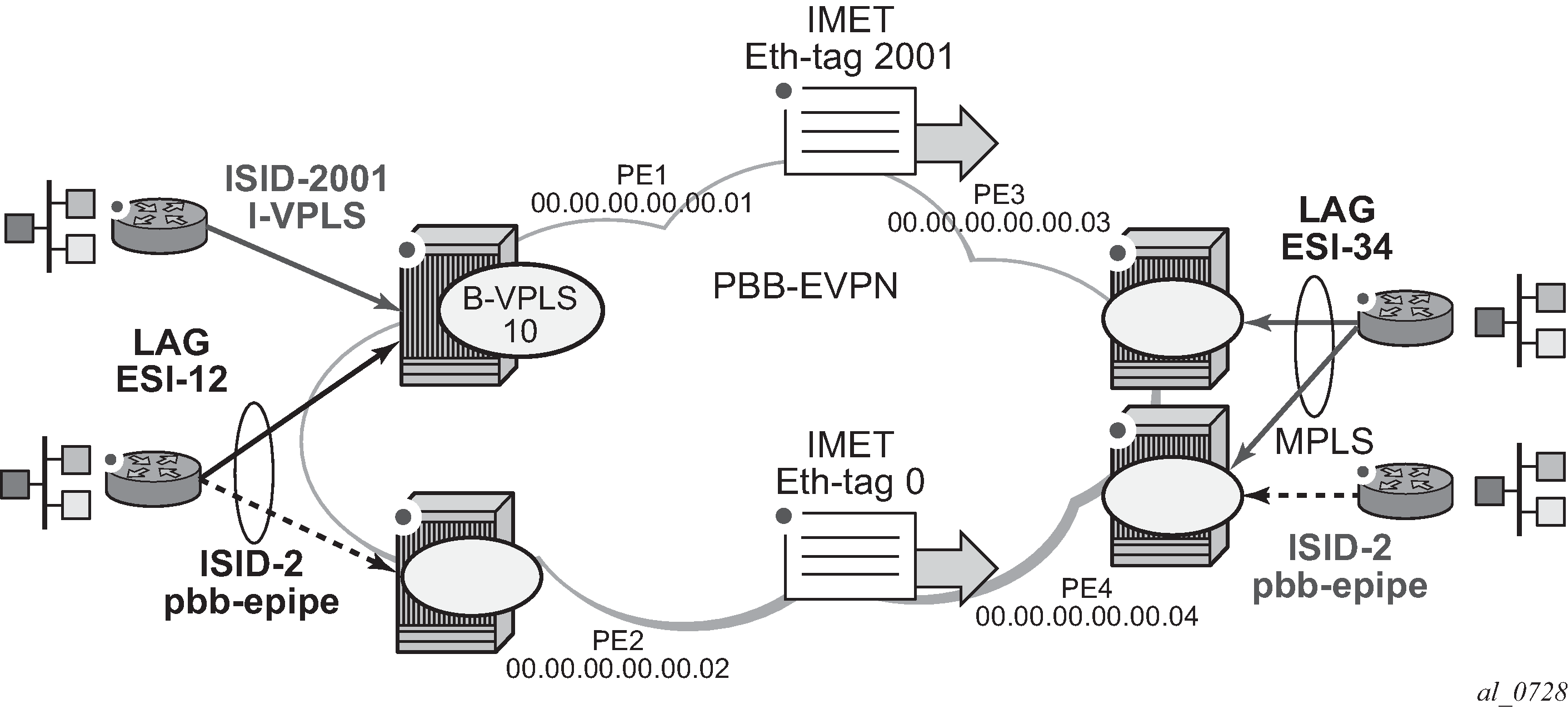
When the B-VPLS 10 is enabled, PE1 advertises as follows:
A B-MAC route containing PE1's system B-MAC (00:01 as configured in pbb>source-bmac) along with an MPLS label.
An Inclusive Multicast Ethernet Tag route (IMET route) with Ethernet-tag = 0 that allows the remote B-VPLS 10 instances to add an entry for PE1 in the default multicast list.
When I-VPLS 2001 (ISID 2001) is enabled as per the CLI in the preceding section, PE1 advertises as follows:
An additional inclusive multicast route with Ethernet-tag = 2001. This allows the remote PEs to create an MFIB for the corresponding ISID 2001 and add the corresponding EVPN binding entry to the MFIB.
This default behavior can be modified by the configured isid-policy. For instance, for ISIDs 1-2000, configure as follows:
isid-policy
entry 10 create
no advertise-local
range 1 to 2000
use-def-mcast
This configuration has the following effect for the ISID range:
no advertise-local instructs the system to not advertise the local active ISIDs contained in the 1 to 2001 range.
use-def-mcast instructs the system to use the default flooding list as opposed to the MFIB.
The ISID flooding behavior on B-VPLS SAPs and SDP bindings is as follows:
B-VPLS SAPs and SDP bindings are only added to the TLS-multicast list and not to the MFIB list (unless static-isids are configured, which is only possible for SAPs/SDP bindings and not BGP-AD spoke SDPs).
As a result, if the system needs to flood ISID BUM traffic and the ISID is also defined in remote PEs connected through SAPs or spoke SDPs without static-isids, then an isid-policy must be configured for the ISID so that the ISID uses the default multicast list.
When an isid-policy is configured and a range of ISIDs use the default multicast list, the remote PBB-EVPN PEs are added to the default multicast list as long as they advertise an IMET route with an ISID included in the policy's ISID range. PEs advertising IMET routes with Ethernet-tag = 0 are also added to the default multicast list (7750 SR, 7450 ESS, or 7950 XRS SR OS behavior).
The B-VPLS 10 also allows the ISID flooding to legacy PBB networks via B-SAPs or B-SDPs. The legacy PBB network B-MACs are dynamically learned on those SAPs/binds or statically configured through the use of conditional static-macs. The use of static-isids is required so that non-local ISIDs are advertised.
sap 1/1/1:1 create
exit
spoke-sdp 1:1 create
static-mac
mac 00:fe:ca:fe:ca:fe create sap 1/1/1:1 monitor fwd-status
static-isid
range 1 isid 3000 to 5000 create