The SBD is equivalent to an R-VPLS that connects all the PEs that are attached to the same tenant VPRN. Interface-ful refers to the fact that there is a full IRB interface between the VPRN and the SBD (an interface object with MAC and IP addresses, over which interface parameters can be configured).
Figure 1 illustrates this model.
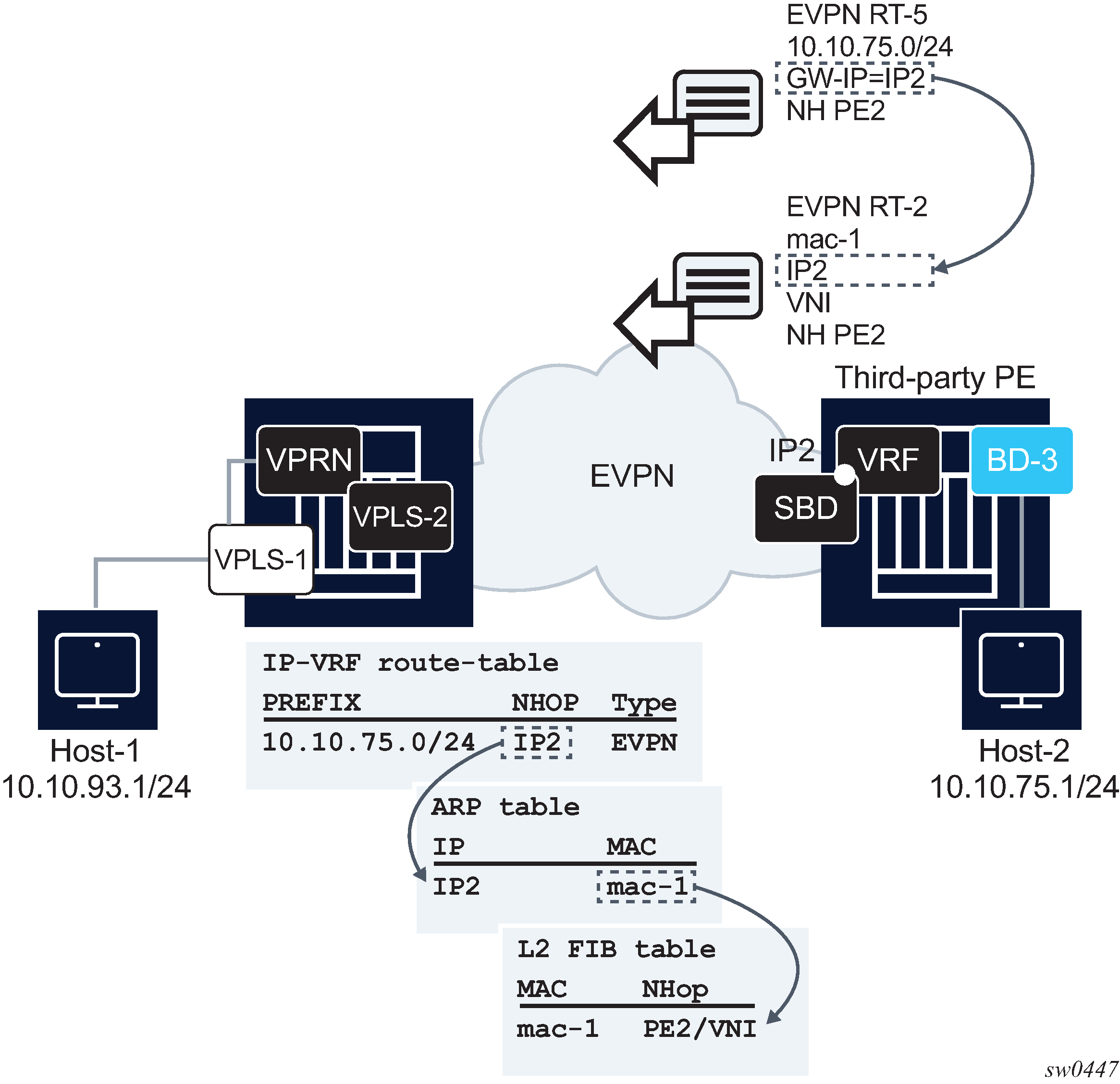
Figure 1 shows a 7750 SR and a third-party router using interface-ful IP-VRF-to-IP-VRF with SBD IRB model. The two routers are attached to a VPRN for the same tenant, and those VPRNs are connected by R-VPLS-2, or SBD. Both routers exchange IP prefix routes with a non-zero gateway IP (this is the IP address of the SBD IRB). The SBD IRB MAC and IP are advertised in a MAC/IP route. On reception, the IP prefix route creates a route-table entry in the VPRN, where the gateway IP must be recursively resolved to the information provided by the MAC/IP route and installed in the ARP and FDB tables.
This model is described in detail in EVPN for VXLAN in IRB backhaul R-VPLS services and IP prefixes. As an example, and based on Figure 1 above, the following CLI output shows the configuration of a 7750 SR SBD and VPRN, using on this interface-ful with SBD IRB mode:
7750SR#config>service#
vpls 2 customer 1 name "sbd" create
allow-ip-int-bind
exit
bgp
exit
bgp-evpn
evi 2
ip-route-advertisement
mpls bgp 1
auto-bind-tunnel resolution any
no shutdown
vprn 1 customer 1 name "vprn1" create
route-distinguisher auto-rd
interface "sbd" create
address 192.168.0.1/16
ipv6
30::3/64
exit
vpls "sbd"
The model is, also, supported for IPv6 prefixes. There are no configuration differences except the ability to configure an IPv6 address and interface.