Figure 1 shows the use of all-active multihoming in the 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, and 7950 XRS SR OS PBB-EVPN implementation.
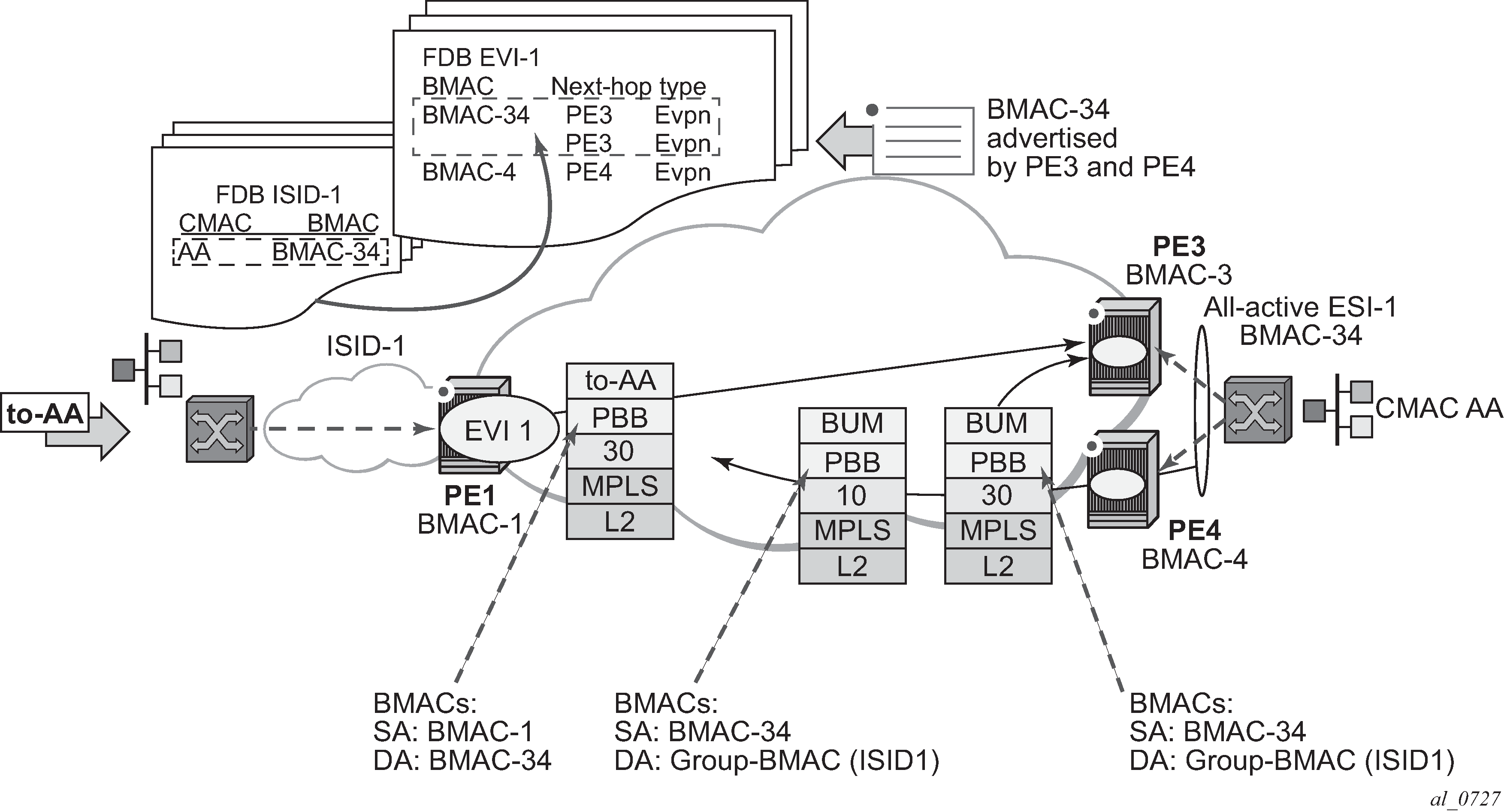
For example, the following shows the ESI-1 and all-active configuration in PE3 and PE4. As in EVPN-MPLS, all-active multihoming is only possible if a LAG is used at the CE. All-active multihoming uses es-bmacs, that is, each ESI is assigned a dedicated B-MAC. All the PEs part of the ES source traffic using the same es-bmac.
In Figure 1 and the following configuration, the es-bmac used by PE3 and PE4 is B-MAC-34 (for example, 00:00:00:00:00:34). The es-bmac for a specified ethernet-segment is configured by the source-bmac-lsb along with the (b-)vpls>pbb>use-es-bmac command.
Configuration in PE3:
*A:PE3>config>lag(1)# info
----------------------------------------------
mode access
encap-type dot1q
port 1/1/1
lacp active administrative-key 32768
no shutdown
*A:PE3>config>service>system>bgp-evpn# info
----------------------------------------------
route-distinguisher 10.3.3.3:0
ethernet-segment ESI-1 create
esi 00:34:34:34:34:34:34:34:34:34
multi-homing all-active
service-carving auto
lag 1
source-bmac-lsb 00:34 es-bmac-table-size 8
no shutdown
*A:PE3>config>service>vpls 1(b-vpls)# info
----------------------------------------------
bgp
exit
bgp-evpn
evi 1
mpls bgp 1
no shutdown
ecmp 2
auto-bind-tunnel resolution any
exit
pbb
source-bmac 00:00:00:00:00:03
use-es-bmac
*A:PE3>config>service>vpls (i-vpls)# info
----------------------------------------------
pbb
backbone-vpls 1
sap lag-1:101 create
*A:PE1>config>service>epipe (pbb)# info
----------------------------------------------
pbb
tunnel 1 backbone-dest-mac 00:00:00:00:00:01 isid 102
sap lag-1:102 create
Configuration in PE4:
*A:PE4>config>lag(1)# info
----------------------------------------------
mode access
encap-type dot1q
port 1/1/1
lacp active administrative-key 32768
no shutdown
*A:PE4>config>service>system>bgp-evpn# info
----------------------------------------------
route-distinguisher 10.4.4.4:0
ethernet-segment ESI-1 create
esi 00:34:34:34:34:34:34:34:34:34
multi-homing all-active
service-carving auto
lag 1
source-bmac-lsb 00:34 es-bmac-table-size 8
no shutdown
*A:PE4>config>service>vpls 1(b-vpls)# info
----------------------------------------------
bgp
exit
bgp-evpn
evi 1
mpls bgp 1
no shutdown
ecmp 2
auto-bind-tunnel resolution any
exit
pbb
source-bmac 00:00:00:00:00:04
use-es-bmac
*A:PE4>config>service>vpls (i-vpls)# info
----------------------------------------------
pbb
backbone-vpls 1
sap lag-1:101 create
*A:PE4>config>service>epipe (pbb)# info
----------------------------------------------
pbb
tunnel 1 backbone-dest-mac 00:00:00:00:00:01 isid 102
sap lag-1:102 create
The above configuration enables the all-active multihoming procedures for PBB-EVPN.
The following considerations apply when the ESI is used for PBB-EVPN.
ESI association: Only LAG is supported for all-active multihoming. The following commands are used for the LAG to ESI association:
config>service>system>bgp-evpn>ethernet-segment# lag <id>
config>service>system>bgp-evpnethernet-segment# source-bmaclsb <MAC-lsb> [es-bmac-table-size <size>]
Where:
The same ESI may be used for EVPN and PBB-EVPN services.
For PBB-EVPN services, the source-bmac-lsb attribute is mandatory and ignored for EVPN-MPLS services.
The source-bmac-lsb attribute must be set to a specific 2-byte value. The value must match on all the PEs part of the same ESI, for example, PE3 and PE4 for ESI-1. This means that the configured pbb>source-bmac on the two PEs for B-VPLS 1 must have the same 4 most significant bytes.
The es-bmac-table-size parameter modifies the default value (8) for the maximum number of virtual B-MACs that can be associated with the ethernet-segment (for example, es-bmacs). When the source-bmac-lsb is configured, the associated es-bmac-table-size is reserved out of the total FDB space.
When multi-homing all-active is configured within the ethernet-segment, only a LAG can be associated with it. The association of a port or an sdp is restricted by the CLI.
If service-carving is configured in the ESI, the DF election algorithm is a modulo function of the ISID and the number of PEs part of the ESI, as opposed to a modulo function of evi and number of PEs (used for EVPN-MPLS).
A service-carving mode manual option is added so that the user can control what PE is DF for a specified ISID. The PE is DF for the configured ISIDs and non-DF for the non-configured ISIDs.
DF election: an all-active Designated Forwarder (DF) election is also carried out for PBB-EVPN. In this case, the DF election defines which of the PEs of the ESI for a specified I-VPLS is the one able to send the downstream BUM traffic to the CE. Only one DF per ESI is allowed in the I-VPLS service, and the non-DF only blocks BUM traffic and in the downstream direction.
Split-horizon function: in PBB-EVPN, the split-horizon function to avoid echoed packets on the CE is based on an ingress lookup of the ES B-MAC (as opposed to the ESI label in EVPN-MPLS). In Figure 1 PE3 sends packets using B-MAC SA = BMAC-34. PE4 does not send those packets back to the CE because BMAC-34 is identified as the es-bmac for ESI-1.
Aliasing: in PBB-EVPN, aliasing is based on the ES B-MAC sent by all the PEs part of the same ESI. See the following section for more information. In Figure 1 PE1 performs load balancing between PE3 and PE4 when sending unicast flows to BMAC-34 (es-bmac for ESI-1).
In the configuration above, a PBB-Epipe is configured in PE3 and PE4, both pointing at the same remote pbb tunnel backbone-dest-mac. On the remote PE, for example PE1, the configuration of the PBB-Epipe points at the es-bmac:
*A:PE1>config>service>epipe (pbb)# info
----------------------------------------------
pbb
tunnel 1 backbone-dest-mac 00:00:00:00:00:34 isid 102
sap 1/1/1:102 create
When PBB-Epipes are used in combination with all-active multihoming, Nokia recommends using bgp-evpn mpls ingress-replication-bum-label in the PEs where the ethernet-segment is created, that is in PE3 and PE4. This guarantees that in case of flooding in the B-VPLS service for the PBB Epipe, only the DF forwards the traffic to the CE.
Aliasing for PBB-Epipes with all-active multihoming only works if shared-queuing or ingress policing is enabled on the ingress PE Epipe. In any other case, the IOM sends the traffic to a single destination (no ECMP is used in spite of the bgp-evpn mpls ecmp setting).
All-active multihomed es-bmacs are treated by the remote PEs as eES:MAX-ESI BMACs. The following example shows the FDB in B-VPLS 1 in PE1 as shown in Figure 1:
*A:PE1# show service id 1 fdb detail
===============================================================================
Forwarding Database, Service 1
===============================================================================
ServId MAC Source-Identifier Type Last Change
Age
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 00:00:00:00:00:03 eMpls: EvpnS 06/12/15 15:35:39
192.0.2.3:262138
1 00:00:00:00:00:04 eMpls: EvpnS 06/12/15 15:42:52
192.0.2.4:262130
1 00:00:00:00:00:34 eES: EvpnS 06/12/15 15:35:57
MAX-ESI
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
No. of MAC Entries: 3
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Legend: L=Learned O=Oam P=Protected-MAC C=Conditional S=Static
===============================================================================
The show service id evpn-mpls on PE1 shows that the remote es-bmac (that is, 00:00:00:00:00:34) has two associated next-hops (for example, PE3 and PE4):
*A:PE1# show service id 1 evpn-mpls
===============================================================================
BGP EVPN-MPLS Dest
===============================================================================
TEP Address Egr Label Num. MACs Mcast Last Change
Transport
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
192.0.2.3 262138 1 Yes 06/12/2015 15:34:48
ldp
192.0.2.4 262130 1 Yes 06/12/2015 15:34:48
ldp
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of entries : 2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
===============================================================================
===============================================================================
BGP EVPN-MPLS Ethernet Segment Dest
===============================================================================
Eth SegId TEP Address Egr Label Last Change
Transport
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
No Matching Entries
===============================================================================
===============================================================================
BGP EVPN-MPLS ES BMAC Dest
===============================================================================
VBMacAddr TEP Address Egr Label Last Change
Transport
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
00:00:00:00:00:34 192.0.2.3 262138 06/12/2015 15:34:48
ldp
00:00:00:00:00:34 192.0.2.4 262130 06/12/2015 15:34:48
ldp
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of entries : 2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
===============================================================================