Some use cases for MPLS-TP require an MPLS-TP based aggregation network and an IP-based core network to interoperate, so providing the seamless transport of packet services across static MPLS-TP and dynamically signaled domains using an MS-PW. In this environment, end-to-end VCCV Ping and VCCV Trace may be used on the MS-PW, as shown in Figure 1.
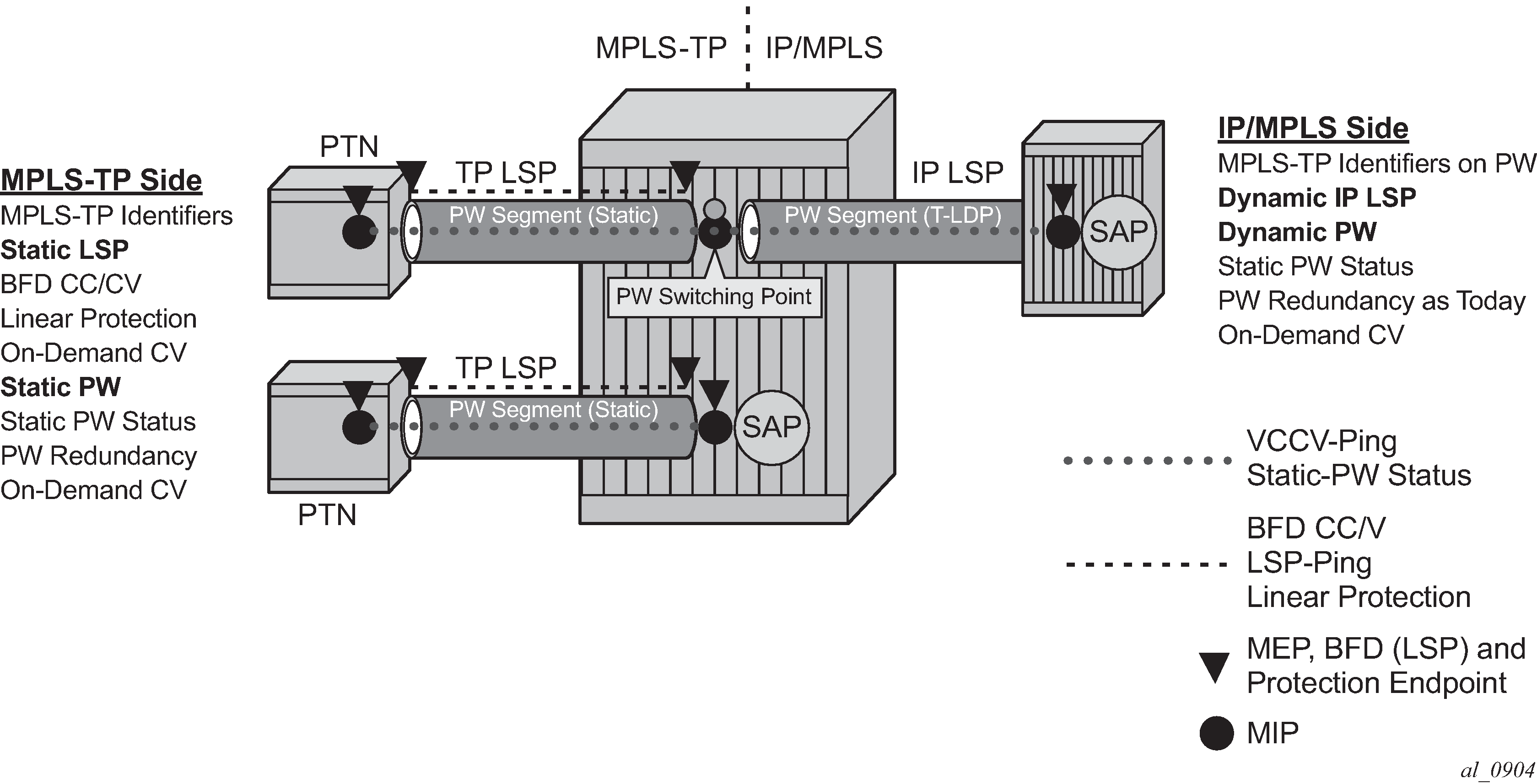
Services are backhauled from the static MPLS-TP network on the left to the dynamic IP/MPLS network on the right. The router acts as an S-PE interconnecting the static and dynamic domains.
The router implementation supports such use cases through the ability to mate a static MPLS-TP spoke SDP, with a defined pw-path-id, to a FEC128 spoke SDP. The dynamically signaled spoke SDP must be MPLS; GRE PWs are not supported, but the T-LDP signaled PW can use any supported MPLS tunnel type (for example, LDP, RSVP-TE, static, BGP). The control-word must be enabled on both mate spoke SDPs.
Mapping of control channel status signaling to and from T-LDP status signaling at the router S-PE is also supported.
The use of VCCV Ping and VCCV Trace on an MS-PW composed of a mix of static MPLS-TP and dynamic FEC128 segments is described in more detail in the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR OAM and Diagnostics Guide.