This section provides a description of the QoS model used for ATM-based services on the router ATM MDA. Although slight variations of this model are applied on other ATM-capable MDAs, the principles remain the same. An example of a VPLS Service with ATM SAP is shown in Figure 1.
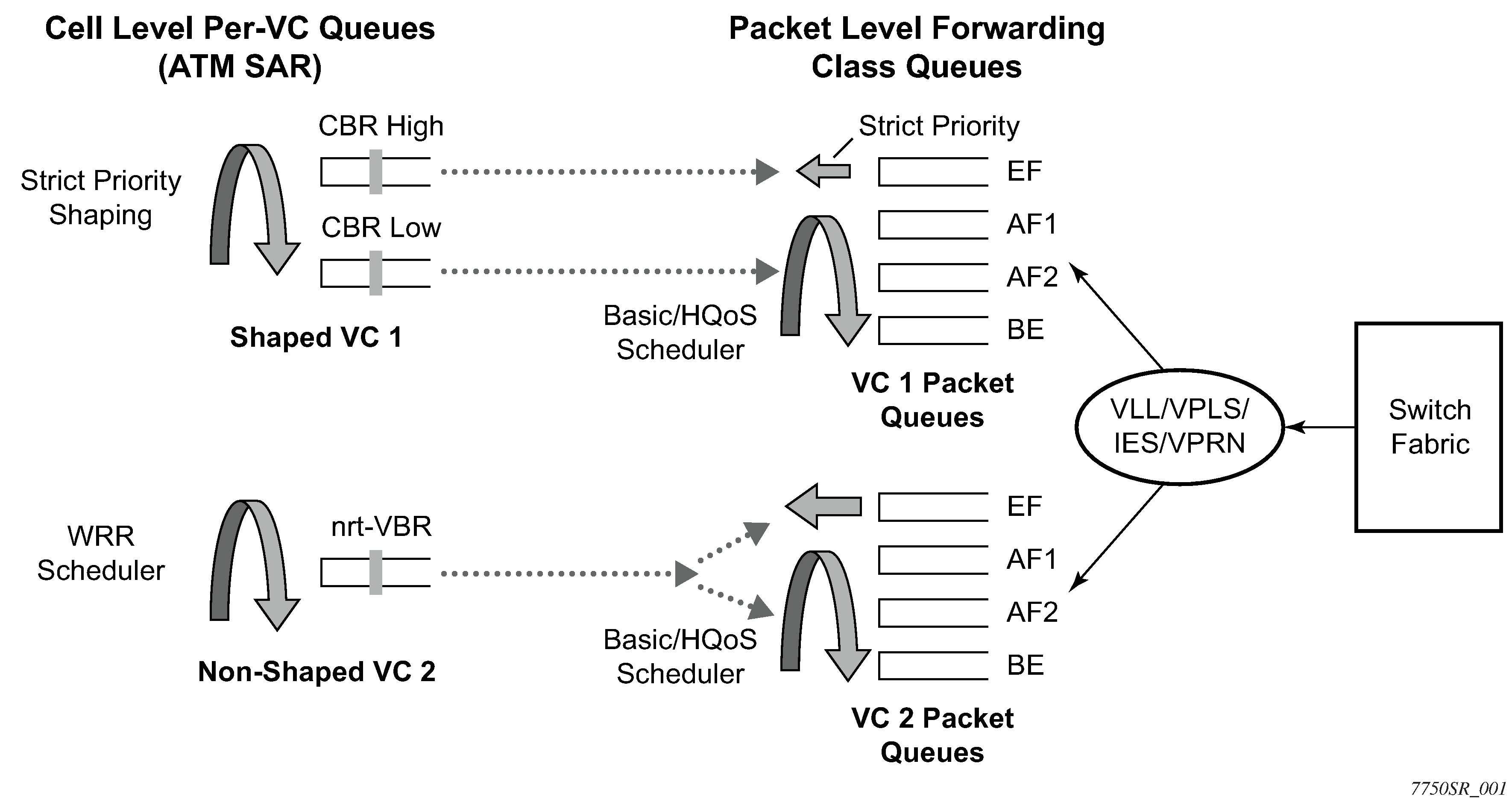
When Ethernet frames are sent over an ATM VC, the scheduling of data becomes hierarchical with two main levels: packet level scheduling and per-VC cell level scheduling.
At the first level, frames are queued on a per-CoS (or forwarding class), per-VC basis in order to achieve the correct class of service differentiation for the frames in the same VC. Each Ethernet frame is queued based on the VC dedicated forwarding class queue, as configured in the service egress QoS policy. The packet level scheduling can use HQoS scheduler policy to enforce aggregate bandwidth among a group of queues feeding an ATM VC or to enforce aggregation of bandwidth across all queues of all VCs at a specific customer site.
The frame level scheduling is the same for other types of SAP (Ethernet, FR, and PPP) and all the features available on the service ingress and egress QoS policies can be applied.
At the second level, the segmented cells are queued in per-VC queues according to the service category of the ATM traffic descriptor profile applied to the ATM SAP. Scheduling at the ATM level enforces the priority and bandwidth sharing needed at the cell level.
Any discard decision is performed exclusively at the packet level where the context for the frame forwarding class and for the 802.1p bit mapping to a forwarding class is known. When a per-VC queue backs up, a back-pressure scheme is applied such that the frames are held in the per-forwarding class packet queues dedicated to this VC.
This hierarchical scheduling of frames and cells of a specific VC terminating on a VPLS instance provides the flexibility to apply policing and shaping on a per-forwarding class basis for the Ethernet frames of each VC as well as the option to shape the aggregate cell flow into the ATM VC back into the customer site.
This QoS model is applied to all router services that include an ATM SAP (VLL, VPLS, IES, and VPRN).