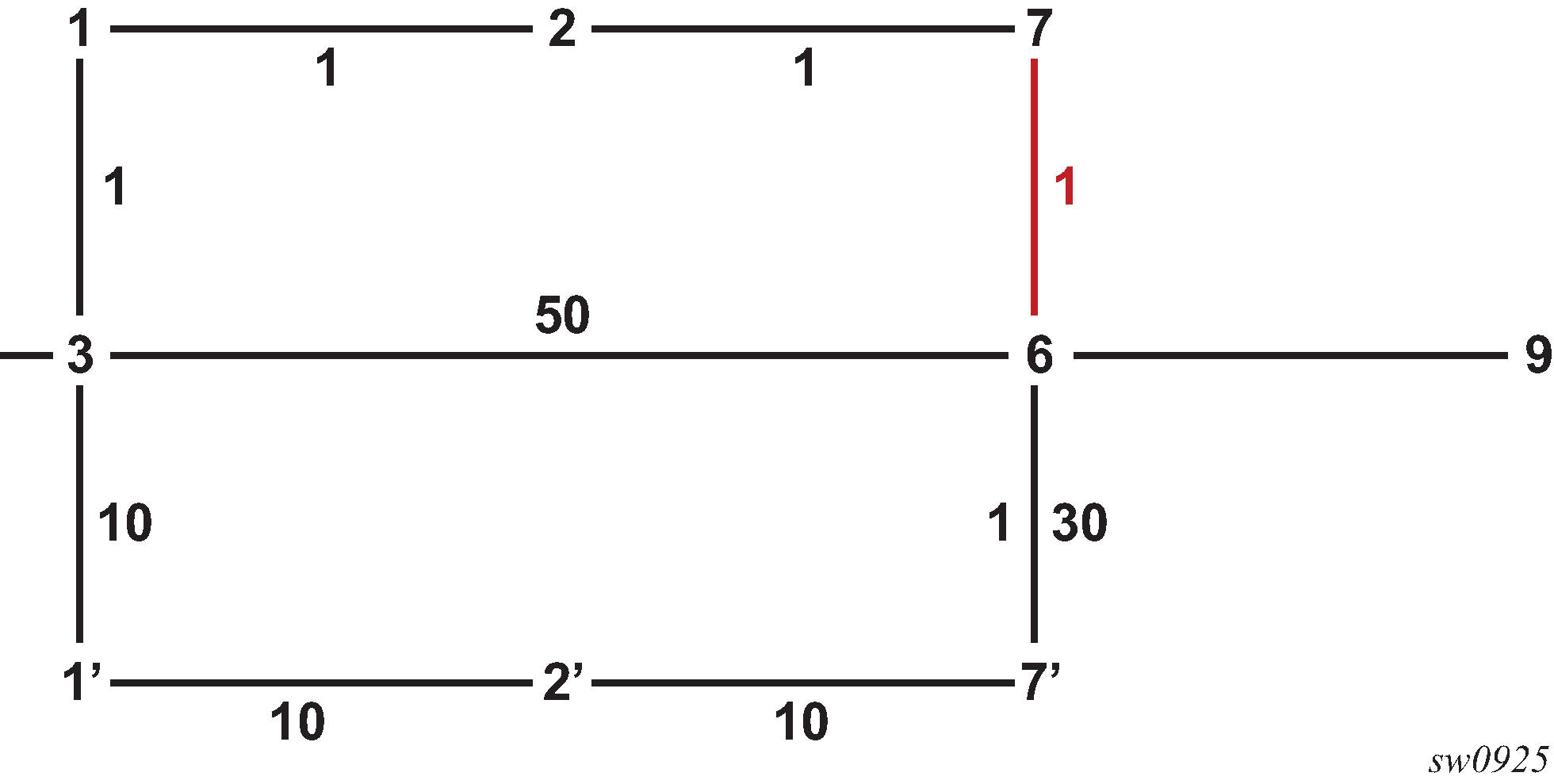
The network topology in Figure 1 depicts an example of link addition or restoration.
The micro-loop avoidance algorithm performs the following steps in the network topology example in Figure 1.
Link 7-6 is added to the topology.
Router 3 detects a single link addition between remote nodes 7 and 6.
Router 3 runs main and LFA SPFs.
all nodes downstream of the added link in Dijkstra tree see a next-hop change: nodes 6 and 9
all nodes upstream of the added link see no route change: nodes 1, 2, and 7
nodes 1', 2', and 7' are not using node 6 or 7 as parent node and are not impacted by the link addition event
For all nodes downstream from the added link, the algorithm computes and activates an SR tunnel that forces traffic to remote endpoint 6 of the added link.
The algorithm pushes node SID 7 and adjacency SID of link 7-6 in SR IS-IS tunnel for these nodes
The use of the adjacency SID of link 7-6 skips the FIB state on node 7 and traffic to all nodes downstream of 6 are not impacted by micro-loop convergence.
The same method applies to metric decrease of link 7-6 that causes traffic to be attracted to that link.