The 7750 SR supports APS on channelized interfaces. This allows the router to be deployed as the radio access network (RAN) aggregation router which connects the base transceiver station (BTS) and the radio network controller (RNC).
Figure 1 shows an example of MLPPP termination on APS protected channelized OC-n/STM-n links. This example illustrates the following:
SC-APS (the APS circuits terminate on the same node aggregation router A).
APS protecting MLPPP bundles (bundles are between the BTS and aggregation router A, but APS operates on the SONET links between the DACS and the aggregation router).
APS on channelized access interfaces (OC-3/OC-12 links).
Figure 1. SC-APS MLPPP on Channelized Access Interfaces Example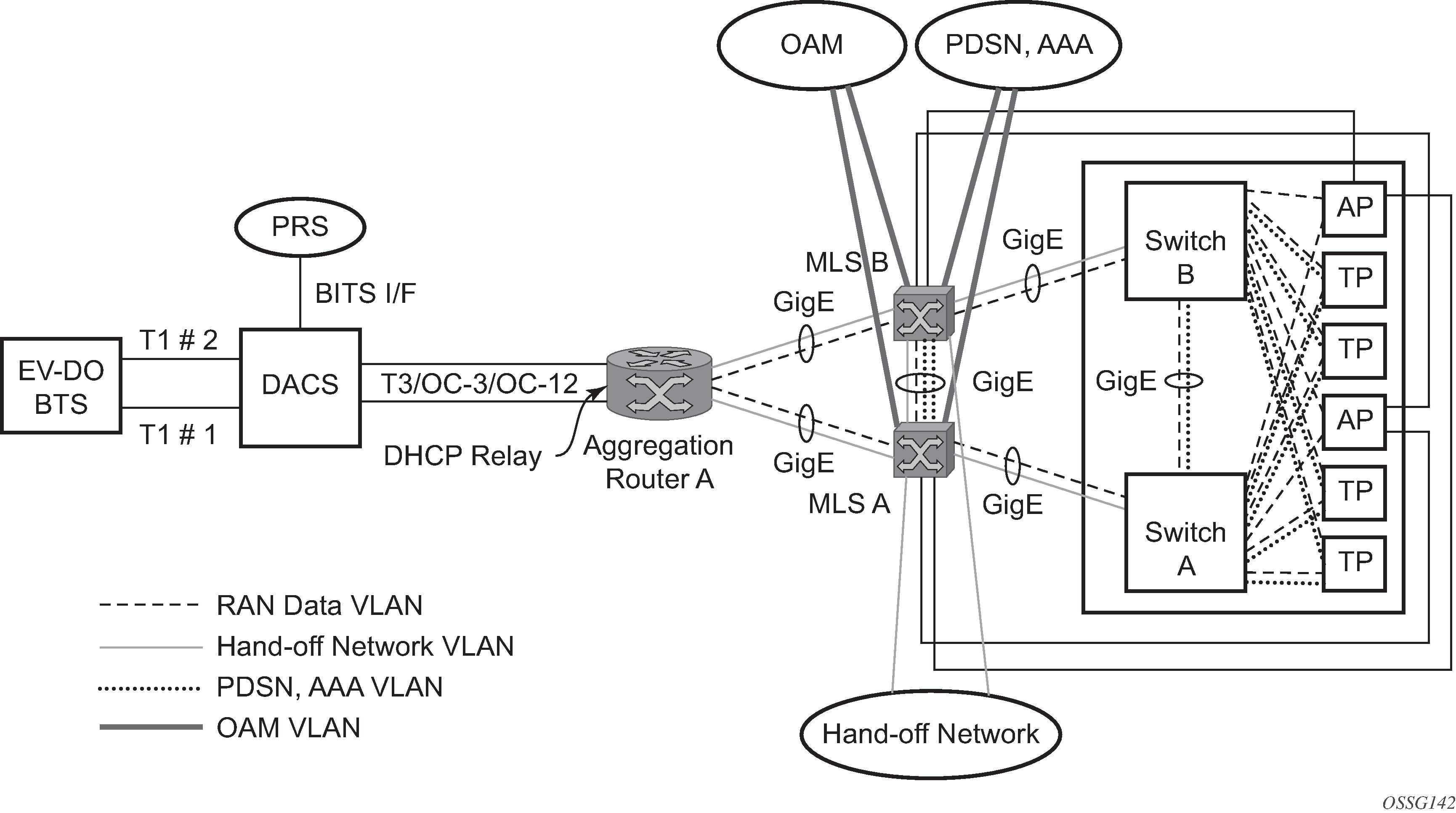
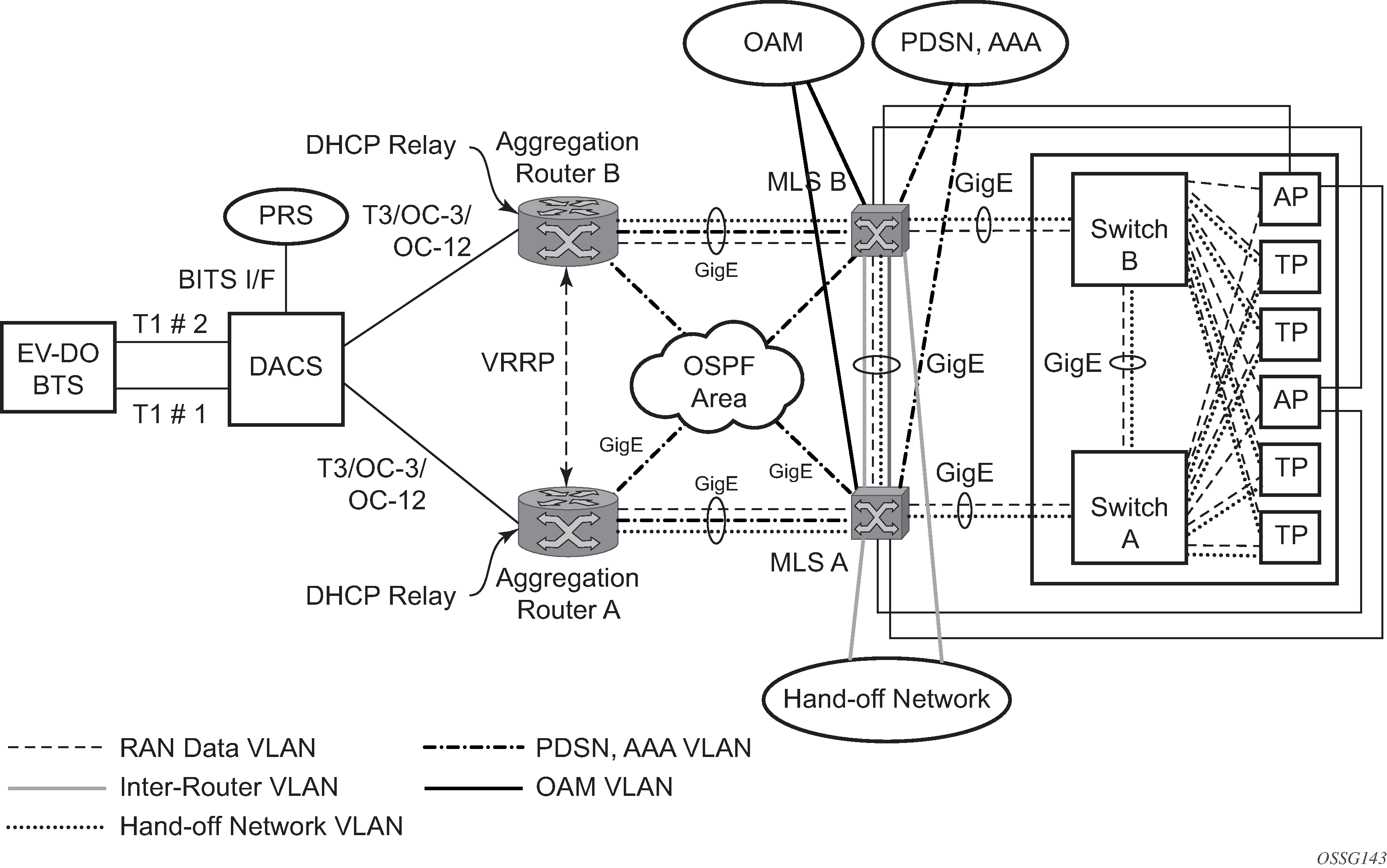
Figure 2 shows an APS group between a digital access cross-connect system (DACS) and a pair of aggregation routers. At one end of the APS group both circuits (OC-3/STM-1 and, or OC-12/STM-4 links) are terminated on the DACS and at the other end each circuit is terminated on a different aggregation routers to provide protection against router failure. The MLPPP bundle operates between the BTS and the aggregation routers. At any one time only one of the two aggregation routers is actually terminating the MLPPP bundle (whichever aggregation router is processing the active APS circuit).
This example shows the following:
MC-APS (the APS circuits terminate on different aggregation routers)
APS protecting MLPPP bundles (bundles are between the BTS and the aggregation routers but APS operates on the SONET links between the DACS and the aggregation routers)
APS on channelized access interfaces (OC-3/OC-12 links)
Figure 2. MC-APS MLPPP on Channelized Access Interfaces Example