A VPRN can receive and install routes for a specific BGP for a specific BGP owner. The routes may be re-exported in the context of the same VPRN and to the same BGP owner or a different one. For example, an EVPN-IFL route can be received from peer N, installed in VPRN 1, and re-exported to peer M using family VPN-IPv4.
When re-exporting BGP routes, the original BGP path attributes are preserved without any configuration in the following cases:
EVPN-IFL route re-exported into an IPVPN route, and the other way around
EVPN-IFL route re-exported into a BGP IP route (PE-CE), and the other way around
IPVPN route re-exported into a BGP IP route (PE-CE), and the other way around
EVPN-IFL, IPVPN or BGP IP routes re-exported into a route of the same owner. For example, EVPN-IFL to EVPN-IFL, when the allow-export-bgp-vpn command is configured.
BGP path attributes to or from EVPN-IFF are not preserved by default. If BGP Path Attribute propagation is required, the configure service system bgp-evpn ip-prefix-routes iff-attribute-uniform-propagation command must be configured. Figure 1 shows an example of BGP Path Attribute propagation from EVPN-IFF to the other BGP owners in the VPRN when the iff-attribute-uniform-propagation command is configured.
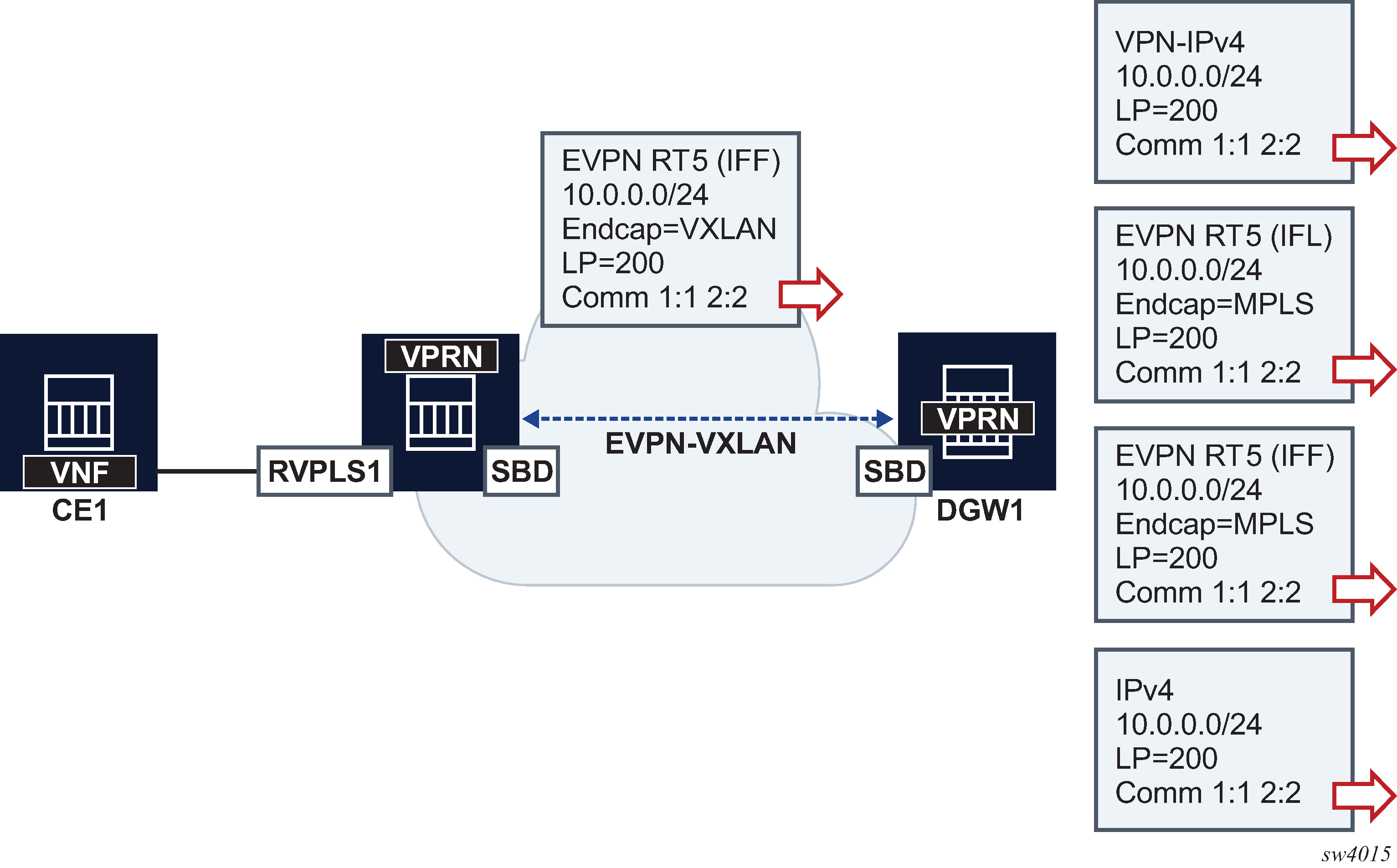
In the example in Figure 1, DGW1 propagates the received LP and communities on an EVPN-IFF route, when advertising the same prefix into any type of BGP owner route, including VPN-IPv4/6, EVPN-IFL, EVPN-IFF, IPv4, or IPv6. If the iff-attribute-uniform-propagation command is not configured on DCW1, no BGP path attributes are propagated, but are re-originated instead. The propagation in the opposite direction follows the same rules; configuration of the iff-attribute-uniform-propagation command is required.
When propagating BGP path attributes, the following criteria are considered.
The propagation is compliant with the uniform propagation described in draft-ietf-bess-evpn-ipvpn-interworking.
The following extended communities are filtered or excluded when propagating attributes:
all extended communities of type 0x06 (EVPN type). In particular, all those that are supported by routes type 5:
MAC Mobility extended community (sub-type 0x00)
EVPN Router's MAC extended community (sub-type 0x03)
BGP encapsulation extended community
all Route Target extended communities
The BGP Path Attribute propagation within the same owner is supported in the following cases:
EVPN-IFF to EVPN-IFF (route received on R-VPLS and advertised in a different R-VPLS context), assuming the iff-attribute-uniform-propagation command is configured
EVPN-IFL to EVPN-IFL (route received on a VPRN and re-advertised based on the configuration of vprn>allow-export-bgp-vpn)
VPN-IPv4/6 to VPN-IPv4/6 (route received on a VPRN and re-advertised based on the configuration of vprn>allow-export-bgp-vpn)
The propagation is supported for iBGP and eBGP as follows:
iBGP-only attributes can only be propagated to iBGP peers
non-transitive attributes are propagated based on existing rules
when peering an eBGP neighbor, the AS_PATH is prepended by the VPRN ASN
If ECMP is enabled in the VPRN and multiple routes of the same BGP owner with different Route Distinguishers are installed in the route table, only the BGP path attributes of the best route are subject for propagation.