When single-active multihoming is used, the IGMP snooping state is learned on the active multihoming object. If a failover occurs, the system with the newly active multihoming object must wait for IGMP messages to be received to instantiate the IGMP snooping state after the ES activation timer expires; this could result in an increased outage.
The outage can be reduced by using MCS synchronization, which is supported for IGMP snooping in both EVPN-MPLS and PBB-EVPN services (see Multi-Chassis Synchronization for Layer 2 Snooping States). However, MCS only supports synchronization between two PEs, whereas EVPN multihoming is supported between a maximum of four PEs. Also, IGMP snooping state can be synchronized only on a SAP.
An increased outage would also occur when using all-active EVPN multihoming. The IGMP snooping state on an ES LAG SAP or virtual ES to the attached CE must be synchronized between all the ES PEs, as the LAG link used by the DF PE may not be the same as that used by the attached CE. MCS synchronization is not applicable to all-active multihoming as MCS only supports active/standby synchronization.
To eliminate any additional outage on a multihoming failover, IGMP snooping messages can be synchronized between the PEs on an ES using data-driven IGMP snooping state synchronization, which is supported in EVPN-MPLS services, PBB-EVPN services, EVPN-MPLS VPRN and IES R-VPLS services. The IGMP messages received on an ES SAP or spoke SDP are sent to the peer ES PEs with an ESI label (for EVPN-MPLS) or ES B-MAC (for PBB-EVPN) and these are used to synchronize the IGMP snooping state on the ES SAP or spoke SDP on the receiving PE.
Data-driven IGMP snooping state synchronization is supported for both all-active multihoming and single-active with an ESI label multihoming in EVPN-MPLS, EVPN-MPLS VPRN and IES R-VPLS services, and for all-active multihoming in PBB-EVPN services. All PEs participating in a multihomed ES must be running an SR OS version supporting this capability. PBB-EVPN with IGMP snooping using single-active multihoming is not supported.
Data-driven IGMP snooping state synchronization is also supported with P2MP mLDP LSPs in both EVPN-MPLS and PBB-EVPN services. When P2MP mLDP LSPs are used in EVPN-MPLS services, all PEs (including the PEs not connected to a multihomed ES) in the EVPN-MPLS service must be running an SR OS version supporting this capability with IGMP snooping enabled and all network interfaces must be configured on FP3 or higher-based line cards.
Figure 1 shows the processing of an IGMP message for EVPN-MPLS. In PBB-EVPN services, the ES B-MAC is used instead of the ESI label to synchronize the state.
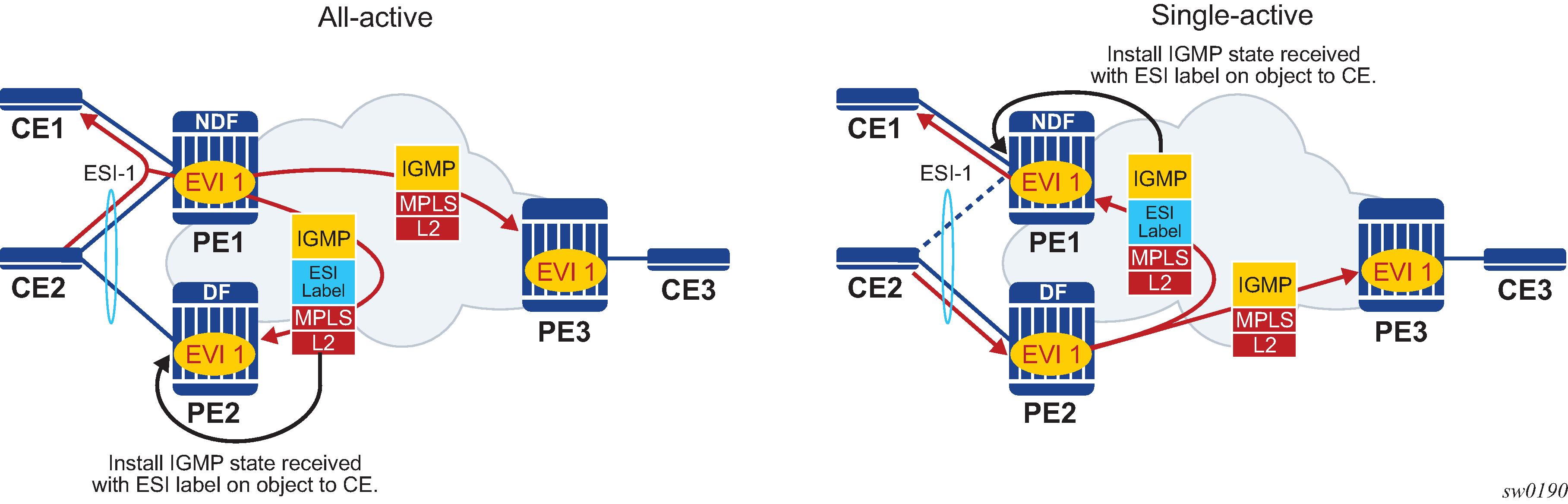
Data-driven synchronization is enabled by default when IGMP snooping is enabled within an EVPN-MPLS service using all-active multihoming or single-active with an ESI label multihoming, or in a PBB-EVPN service using all-active multihoming. If IGMP snooping MCS synchronization is enabled on an EVPN-MPLS or PBB-EVPN (I-VPLS) multihoming SAP then MCS synchronization takes precedence over the data-driven synchronization and the MCS information is used. Mixing data-driven and MCS IGMP synchronization within the same ES is not supported.
When using EVPN-MPLS, the ES should be configured as non-revertive to avoid an outage when a PE takes over the DF role. The Ethernet A-D per ESI route update is withdrawn when the ES is down which prevents state synchronization to the PE with the ES down, as it does not advertise an ESI label. The lack of state synchronization means that if the ES comes up and that PE becomes DF after the ES activation timer expires, it may not have any IGMP snooping state until the next IGMP messages are received, potentially resulting in an additional outage. Configuring the ES as non-revertive can avoid this potential outage. Configuring the ES to be non-revertive would also avoid an outage when PBB-EVPN is used, but there is no outage related to the lack of the ESI label as it is not used in PBB-EVPN.
The following steps can be used when enabling IGMP snooping in EVPN-MPLS and PBB-EVPN services.
Upgrade SR OS on all ES PEs to a version supporting data-driven IGMP snooping synchronization with EVPN multihoming.
Enable IGMP snooping in the required services on all ES PEs. Traffic loss occurs until all ES PEs have IGMP snooping enabled and the first set of join/query messages are processed by the ES PEs.
There is no action required on the non-ES PEs.
If P2MP mLDP LSPs are also configured, the following steps can be used when enabling IGMP snooping in EVPN-MPLS and PBB-EVPN services.
Upgrade SR OS on all PEs (both ES and non-ES) to a version supporting data-driven IGMP snooping synchronization with EVPN multihoming.
For EVPN-MPLS:
Enable IGMP snooping on all non-ES PEs. Traffic loss occurs until the first set of join/query messages are processed by the non-ES PEs.
Then enable IGMP snooping on all ES PEs. Traffic loss occurs until all PEs have IGMP snooping enabled and the first set of join/query messages are processed by the ES PEs.
For PBB-EVPN:
Enable IGMP snooping on all ES PEs. Traffic loss occurs until all PEs have IGMP snooping enabled and the first set of join/query messages are processed by the ES PEs.
There is no action required on the non-ES PEs.
To aid with troubleshooting, the debug packet output displays the IGMP packets used for the snooping state synchronization. An example of a join sent on ES esi-1 from one ES PE and the same join received on another ES PE follows.
6 2017/06/16 18:00:07.819 PDT MINOR: DEBUG #2001 Base IGMP
"IGMP: TX packet on svc 1
from chaddr 5e:00:00:16:d8:2e
send towards ES:esi-1
Port : evpn-mpls
SrcIp : 0.0.0.0
DstIp : 239.0.0.22
Type : V3 REPORT
Num Group Records: 1
Group Record Type: MODE_IS_EXCL (2), AuxDataLen 0, Num Sources 0
Group Addr: 239.0.0.1
4 2017/06/16 18:00:07.820 PDT MINOR: DEBUG #2001 Base IGMP
"IGMP: RX packet on svc 1
from chaddr d8:2e:ff:00:01:41
received via evpn-mpls on ES:esi-1
Port : sap lag-1:1
SrcIp : 0.0.0.0
DstIp : 239.0.0.22
Type : V3 REPORT
Num Group Records: 1
Group Record Type: MODE_IS_EXCL (2), AuxDataLen 0, Num Sources 0
Group Addr: 239.0.0.1