Figure 1 shows the use of EVPN for VXLAN tunnels on the 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, or 7950 XRS, when the DC provides distributed Layer 3 connectivity to the DC tenants and the VPRN instances are connected through EVPN tunnels.
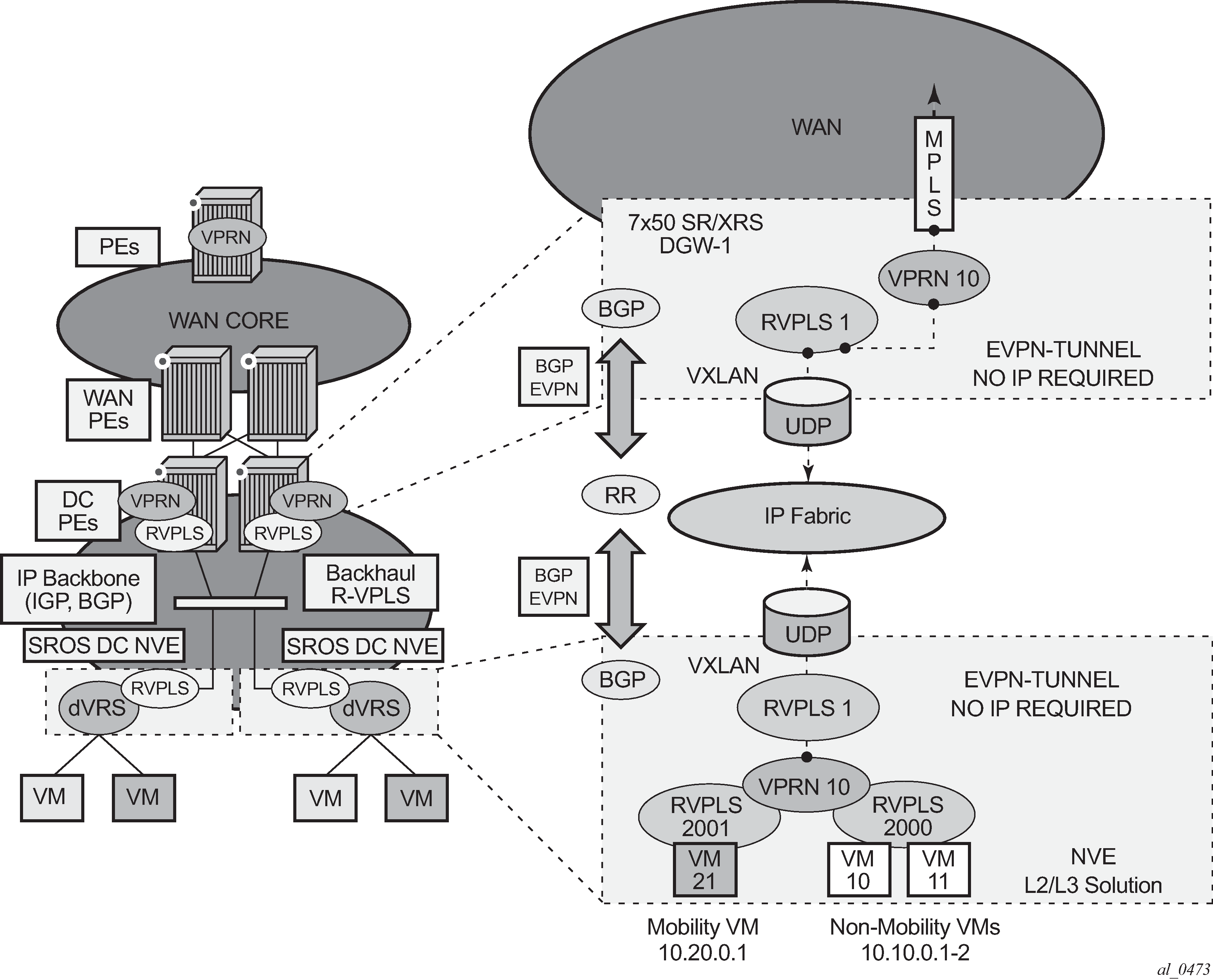
The solution described in section EVPN for VXLAN Tunnels in a Layer 3 DC with Integrated Routing Bridging Connectivity among VPRNs provides a scalable IRB backhaul R-VPLS service where all the VPRN instances for a specified tenant can be connected by using IRB interfaces. When this IRB backhaul R-VPLS is exclusively used as a backhaul and does not have any SAPs or SDP bindings directly attached, the solution can be optimized by using EVPN tunnels.
EVPN tunnels are enabled using the evpn-tunnel command under the R-VPLS interface configured on the VPRN. EVPN tunnels provide the following benefits to EVPN-VXLAN IRB backhaul R-VPLS services:
Easier provisioning of the tenant service. If an EVPN tunnel is configured in an IRB backhaul R-VPLS, there is no need to provision the IRB IPv4 addresses on the VPRN. This makes the provisioning easier to automate and saves IP addresses from the tenant space.
Note:IPv6 interfaces do not require the provisioning of an IPv6 Global Address; a Link Local Address is automatically assigned to the IRB interface.
Higher scalability of the IRB backhaul R-VPLS. If EVPN tunnels are enabled, multicast traffic is suppressed in the EVPN-VXLAN IRB backhaul R-VPLS service (it is not required). As a result, the number of VXLAN binds in IRB backhaul R-VPLS services with EVPN-tunnels can be much higher.
This optimization is fully supported by the 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, and 7950 XRS.