Figure 1 shows the use of EVPN for VXLAN overlay tunnels on the 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, or 7950 XRS when it is used as a Layer 2 DGW.
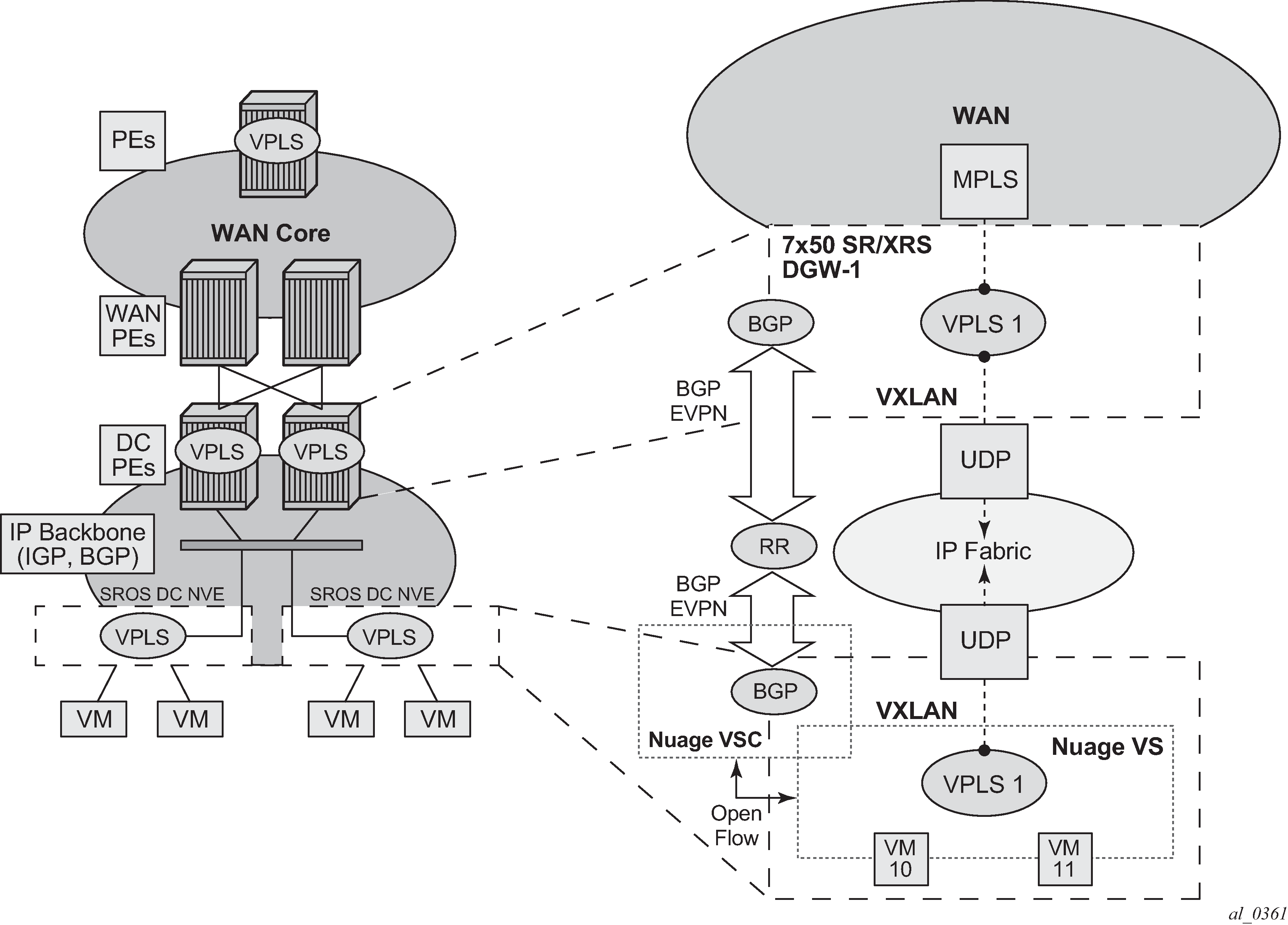
DC providers require a DGW solution that can extend tenant subnets to the WAN. Customers can deploy the NVO3-based solutions in the DC, where EVPN is the standard control plane and VXLAN is a predominant data plane encapsulation. The Nokia DC architecture (Nuage) uses EVPN and VXLAN as the control and data plane solutions for Layer 2 connectivity within the DC and so does the SR OS.
While EVPN VXLAN is used within the DC, most service providers use VPLS and H-VPLS as the solution to extend Layer 2 VPN connectivity. Figure 1 shows the Layer 2 DGW function on the 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, and 7950 XRS routers, providing VXLAN connectivity to the DC and regular VPLS connectivity to the WAN.
The WAN connectivity is based on VPLS where SAPs (null, dot1q, and qinq), spoke SDPs (FEC type 128 and 129), and mesh-SDPs are supported.
The DC GWs can provide multi-homing resiliency through the use of BGP multi-homing.
EVPN-MPLS can also be used in the WAN. In this case, the Layer 2 DGW function provides translation between EVPN-VXLAN and EVPN-MPLS. EVPN multi-homing can be used to provide DGW redundancy.
If point-to-point services are needed in the DC, SR OS supports the use of EVPN-VPWS for VXLAN tunnels, including multi-homing, according to RFC8214.