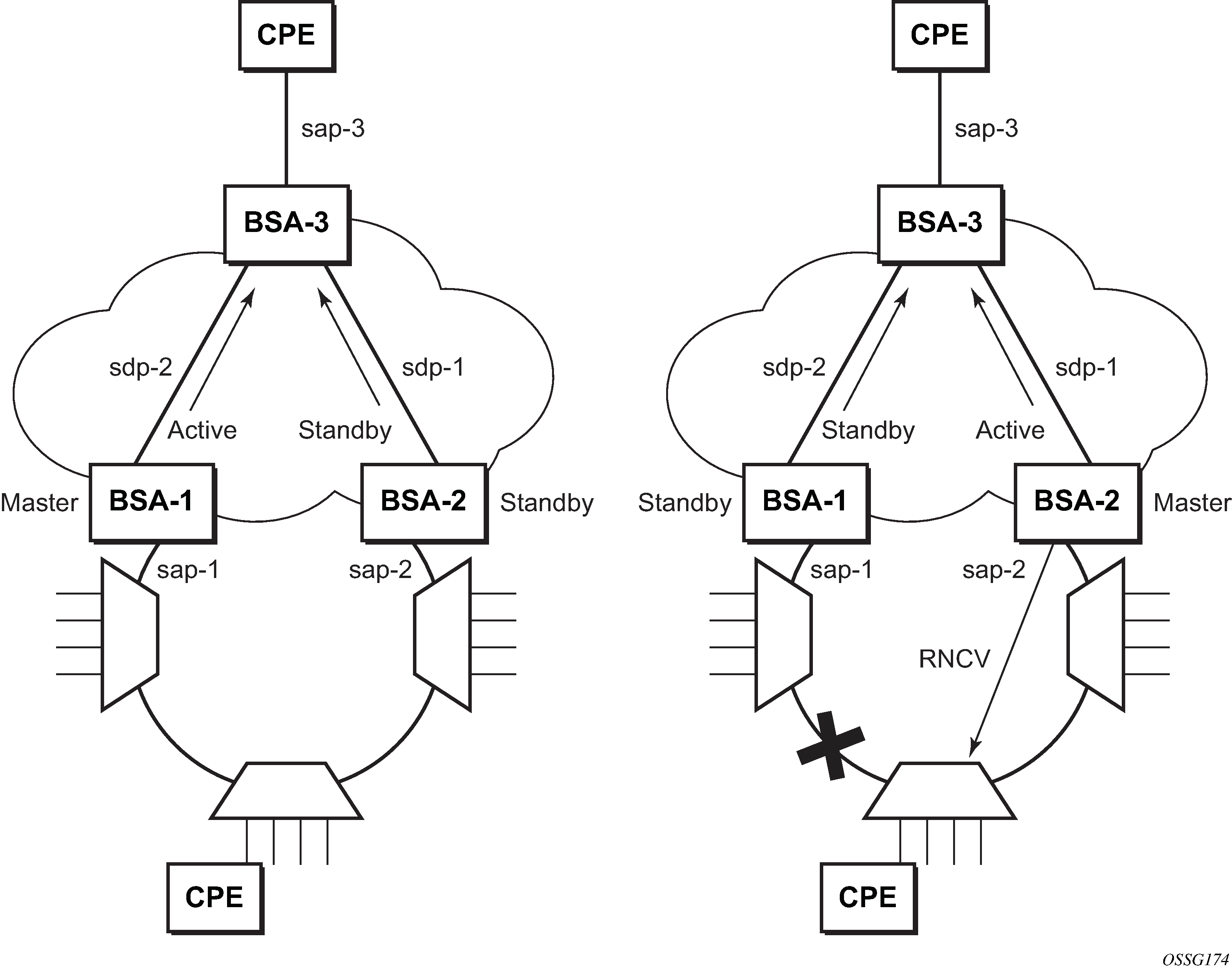
To support redundant VLL access in ring configurations, the multi-chassis ring (MC-Ring) feature is applicable to VLL SAPs. A conceptual drawing of the operation is shown in Figure 1. The specific CPE that is connected behind the ring node has access to both BSAs through the same VLAN provisioned in all ring nodes. There are two SAPs (with the same VLAN) provisioned on both nodes.
If a closed ring status occurs, one of the BSAs becomes the master and signals an active status bit on the corresponding VLL pseudowire. Similarly, the standby BSA signals a standby status. With this information, the remote node can choose the correct path to reach the CPE. In case of a broken ring, the node that can reach the ring node, to which the CPE is connected by RNCV check, becomes master and signals corresponding status on its pseudowire.
The mapping of individual SAPs to the ring nodes is done statically through CLI provisioning. To keep the convergence time to a minimum, MAC learning must be disabled on the ring node so all CPE originated traffic is sent in both directions. If the status is operationally down on the SAP on the standby BSA, that part of the traffic is blocked and not forwarded to the remote site.
For further information about Multi-Chassis Ring Layer 2 (with ESM), see the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, and 7950 XRS Advanced Configuration Guide.