A simplified topology example for a PBB network offering a carrier of carrier service for wireless service providers is depicted in Figure 1.
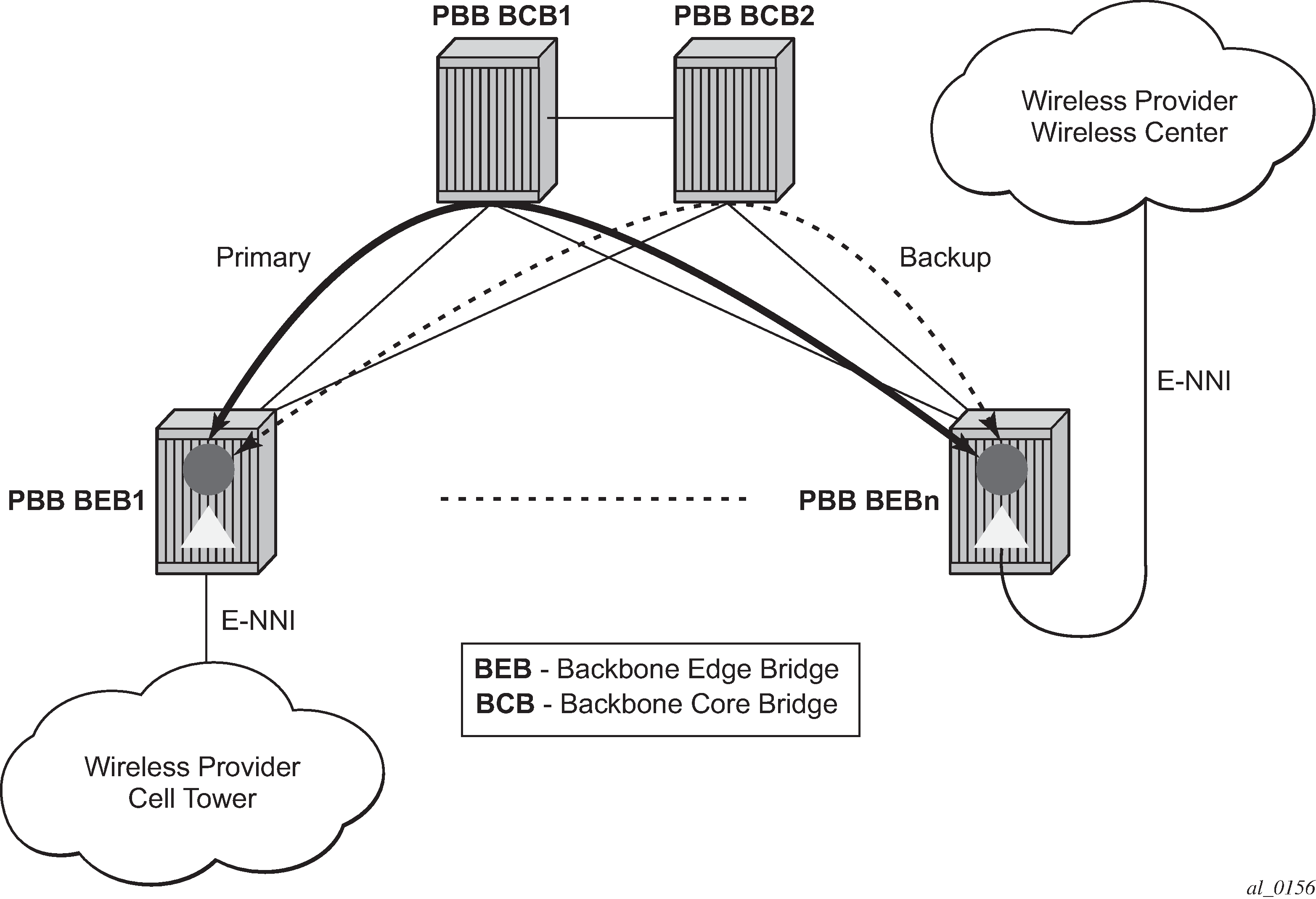
The wireless service provider in this example purchases an E-Line service between the ENNIs on PBB edge nodes, BEB1 and BEBn. PBB services are employing a type of Ethernet tunneling (Eth-tunnels) between BEBs where primary and backup member paths controlled by G.8031 1:1 protection are used to ensure faster backbone convergence. Ethernet CCMs based on IEEE 802.1ag specification may be used to monitor the liveliness for each individual member paths.
The Ethernet paths span a native Ethernet backbone where the BCBs are performing simple Ethernet switching between BEBs using an Epipe or a VPLS service.
Although the network diagram shows just the Epipe case, both PBB E-Line and E-LAN services are supported.