The VPLS E-Tree service offers a VPLS service with Root and Leaf designated access SAPs and SDP bindings, which prevent any traffic flow from leaf to leaf directly. With a VPLS E-Tree, the split horizon group capability is inherent for leaf SAPs (or SDP bindings) and extends to all the remote PEs that are part of the same VPLS E-Tree service. This feature is based on IETF Draft draft-ietf-l2vpn-vpls-pe-etree.
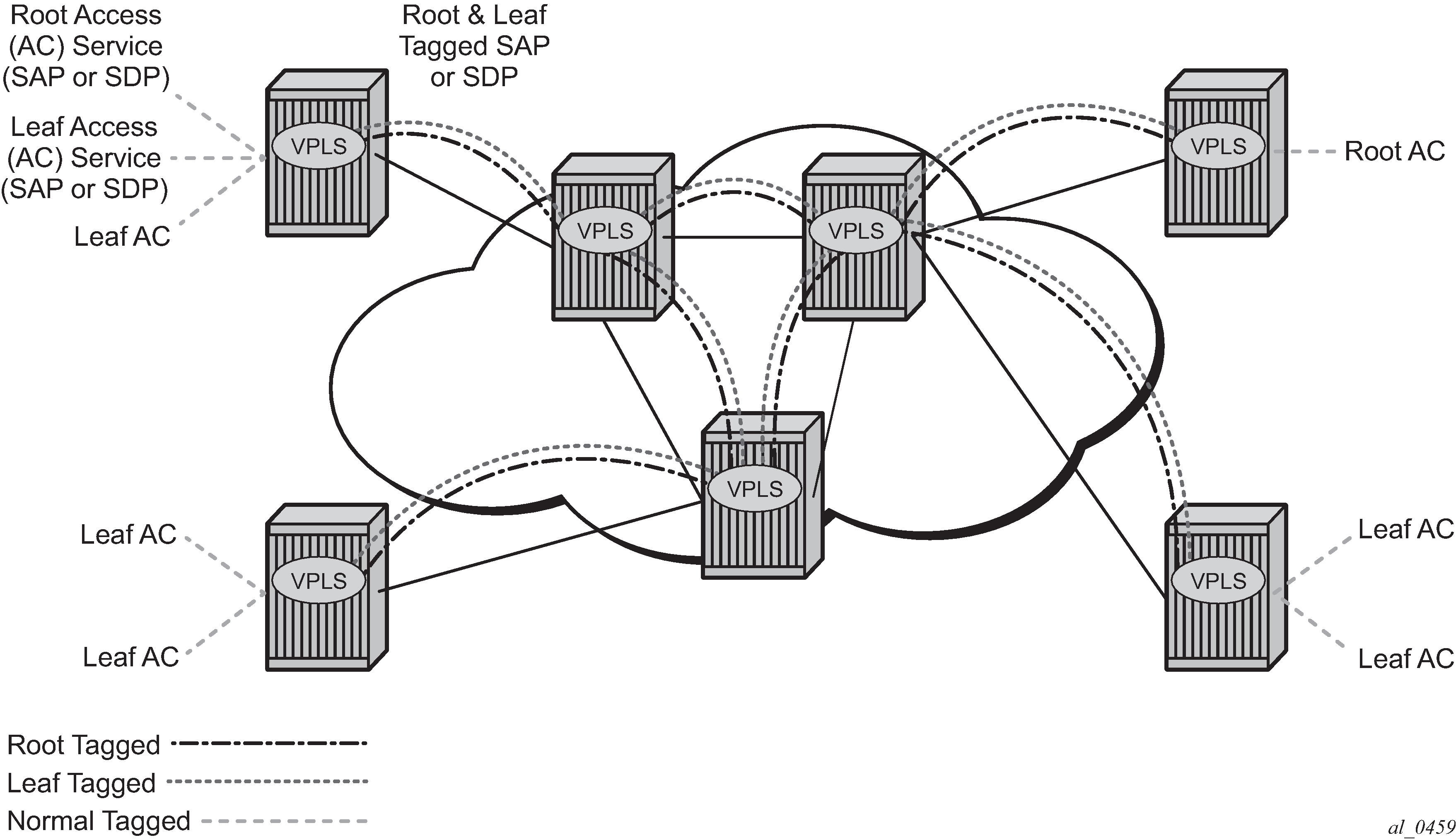
A VPLS E-Tree service may support an arbitrary number of leaf access (leaf-ac) interfaces, root access (root-ac) interfaces, and root-leaf tagged (root-leaf-tag) interfaces. Leaf-ac interfaces are supported on SAPs and SDP binds and can only communicate with root-ac interfaces (also supported on SAPs and SDP binds). Leaf-ac to leaf-ac communication is not allowed. Root-leaf-tag interfaces (supported on SAPs and SDP bindings) are tagged with root and leaf VIDs to allow remote VPLS instances to enforce the E-Tree forwarding.
Figure 1 shows a network with two root-ac interfaces and several leaf-ac SAPs (also could be SDPs). The figure indicates two VIDs in use to each service within the service with no restrictions on the AC interfaces. The service guarantees no leaf-ac to leaf-ac traffic.