In multicast MVPN, by default, if multiple PE nodes form a peering with a common MVPN instance then each PE node originates a multicast tree locally towards the remaining PE nodes that are member of this MVPN instance. This behavior creates a mesh of I-PMSI across all PE nodes in the MVPN. It is often a case, that a given VPN has many sites that will host multicast receivers, but only few sites that either host both receivers and sources or sources only.
MVPN Sender-only/Receiver-only allows optimization of control and data plane resources by preventing unnecessary I-PMSI mesh when a given PE hosts multicast sources only or multicast receivers only for a given MVPN.
For PE nodes that host only multicast sources for a given VPN, operators can now block those PEs, through configuration, from joining I-PMSIs from other PEs in this MVPN. For PE nodes that host only multicast receivers for a given VPN, operators can now block those PEs, through configuration, to set-up a local I-PMSI to other PEs in this MVPN.
MVPN Sender-only/Receiver-only is supported with ng-MVPN using IPv4 RSVP-TE or IPv4 LDP provider tunnels for both IPv4 and IPv6 customer multicast. Figure 1 depicts 4-site MVPN with sender-only, receiver-only and sender-receiver (default) sites.
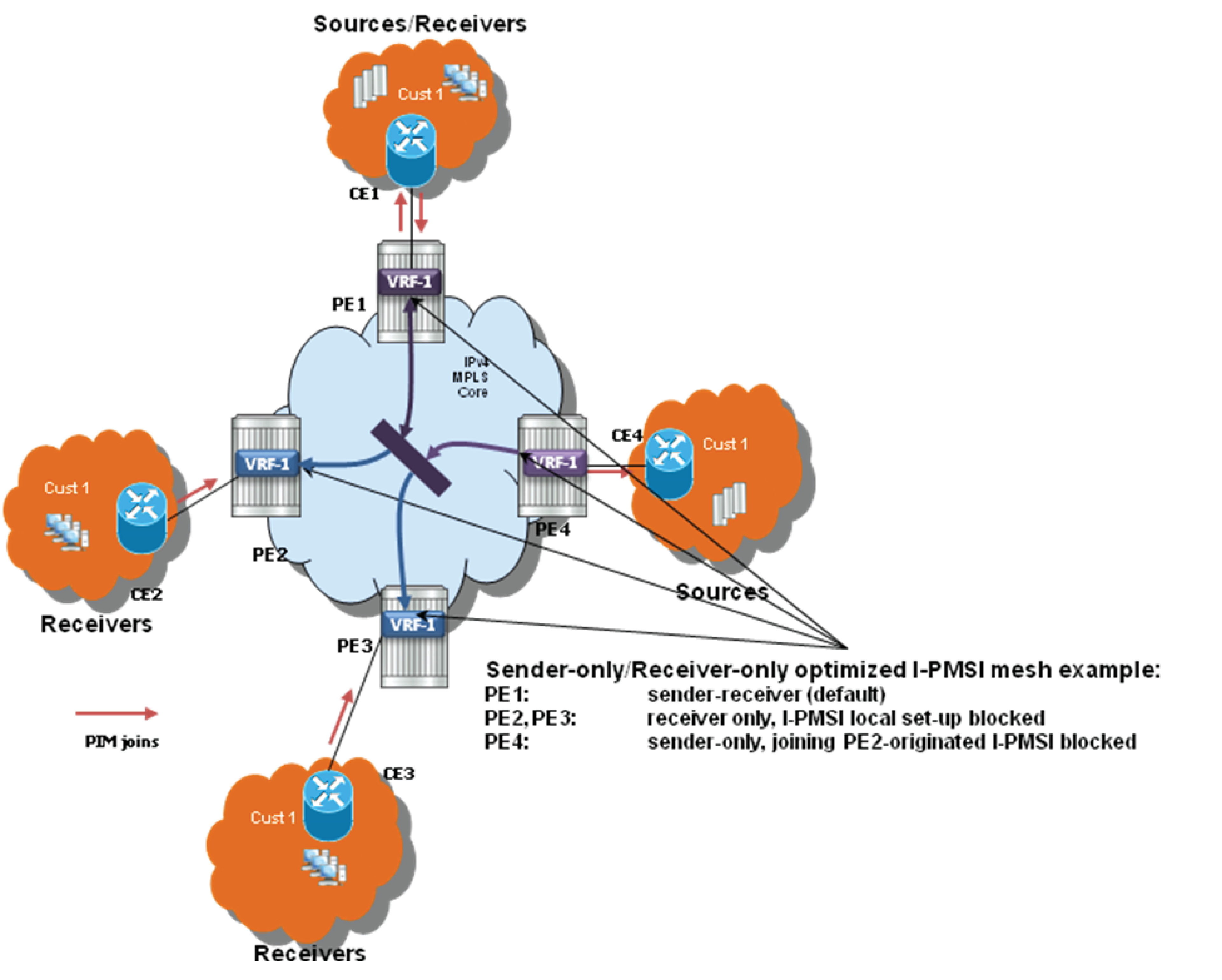
Extra attention needs to be paid to BSR/RP placement when Sender-only/Receiver-only is enabled. Source DR sends unicast encapsulated traffic towards RP, therefore, RP shall be at sender-receiver or sender-only site, so that *G traffic can be sent over the tunnel. BSR shall be deployed at the sender-receiver site. BSR can be at sender-only site if the RPs are at the same site. BSR needs to receive packets from other candidate-BSR and candidate-RPs and also needs to send BSM packets to everyone.