Multicast source geo-redundancy is targeted primarily for MVPN deployments for multicast delivery services like IPTV. The solutions allows operators to configure a list of geographically dispersed redundant multicast sources (with different source IPs) and then, using configured BGP policies, ensure that each Receiver PE (a PE with receivers in its C-instance) selects only a single, most-preferred multicast source for a given group from the list. Although the data may still be replicated in P-instance (each multicast source sends (C-S, C-G) traffic onto its I-PMSI tree or S-PMSI tree), each Receiver PE only forwards data to its receivers from the preferred multicast source. This allows operators to support multicast source geo-redundancy without the replication of traffic for each (C-S, C-G) in the C-instance while allowing fast recovery of service when an active multicast source fails.
Figure 1 shows an operational example of multicast source geo-redundancy:
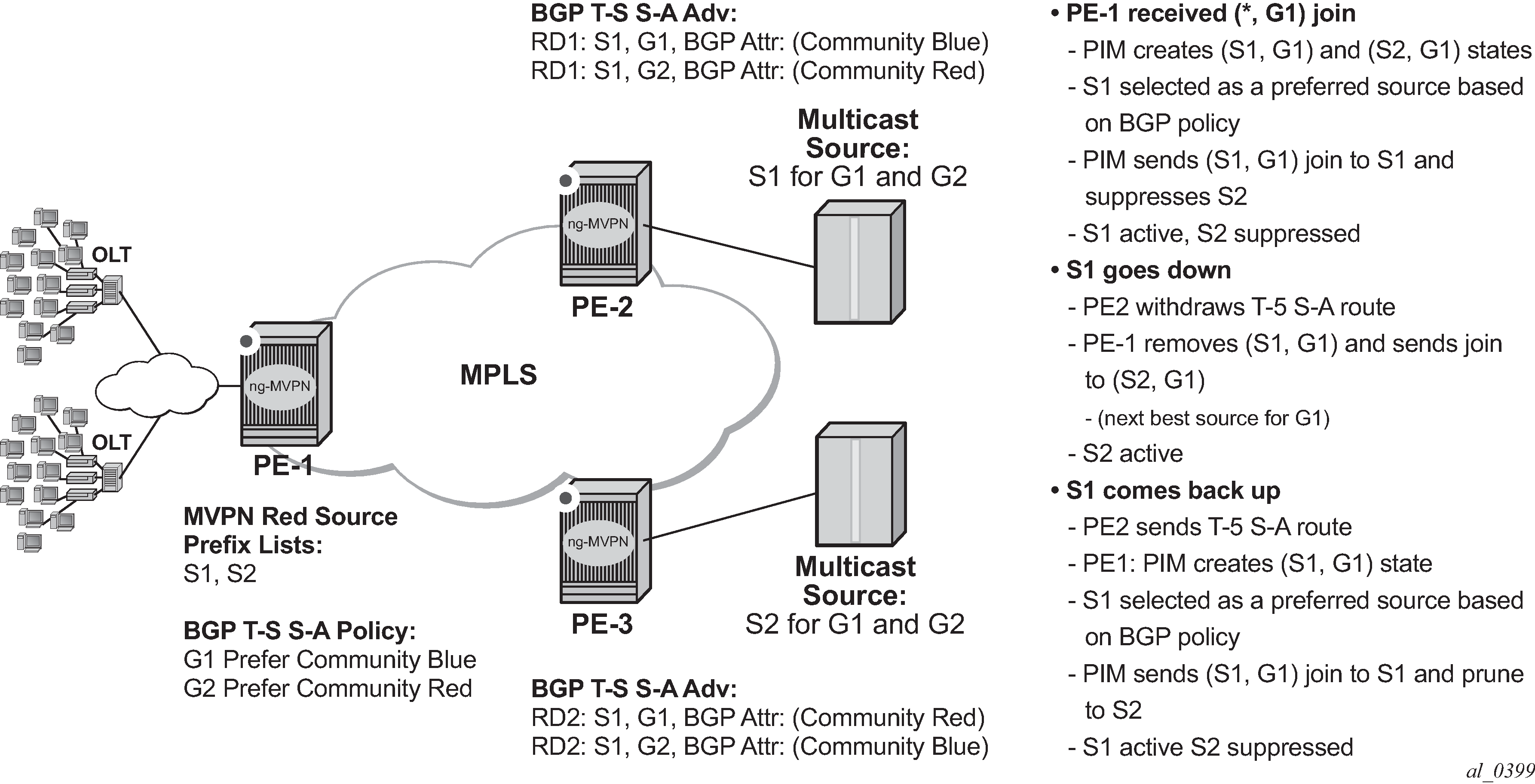
Operators can configure a list of prefixes for multicast source redundancy per MVPN on Receiver PEs:
Up to 8 multicast source prefixes per VPRN are supported.
Any multicast source that is not part of the source prefix list is treated as a unique source and automatically joined in addition to joining the most preferred source from the redundant multicast source list.
A Receiver PE selects a single, most-preferred multicast source from the list of pre-configured sources for a given MVPN during (C-*, C-G) processing as follows:
A single join for the group is sent to the most preferred multicast source from the operator-configured multicast source list. Joins to other multicast sources for a given group are suppressed. Operator can see active and suppressed joins on a Receiver PE. Although a join is sent to a single multicast source only, (C-S, C-G) state is created for every source advertising Type-5 S-A route on the Receiver PE.
The most preferred multicast source is a reachable source with the highest local preference for Type-5 SA route based on the BGP policy, as described later in this section.
On a failure of the preferred multicast source or when a new multicast source with a better local preference is discovered, Receiver PE will join the new most-preferred multicast source. The outage experienced will depend on how quickly Receiver PE receives Type-5 S-A route withdrawal or loses unicast route to multicast source, and how quickly the network can process joins to the newly selected preferred multicast source(s).
Local multicast sources on a Receiver PE are not subject to the most-preferred source selection, regardless of whether they are part of redundant source list or not.
BGP policy on Type-5 SA advertisements is used to determine the most preferred multicast source based on the best local preference as following:
Each Source PE (a PE with multicast sources in its C-instance) tags Type-5 SA routes with a unique standard community attribute using global BGP policy or MVPN vrf-export policy. Depending on multicast topology, the policy may require source-aware tagging in the policy. Either all MVPN routes or Type 5 SA routes only can be tagged in the policy (new attribute mvpn-type 5).
Each receiver PE has a BGP VRF import policy that sets local preference using match on Type-5 SA routes (new attribute mvpn-type 5) and standard community attribute value (as tagged by the Source PEs). Using policy statements that also include group address match, allows receiver PEs to select the best multicast source per group. The BGP VRF import policy must be applied as vrf-import under config>service>vprn>mvpn context. It must have default-action accept specified, or all MVPN routes other than those matched by specified entries will be rejected. In addition, it must have vrf-target as a community match condition, because vrf-target mvpn configuration is ignored when vrf-import policy is defined.
Operators can change redundant source list or BGP policy affecting source selection in service. If such a change of the list/policy results in a new preferred multicast source election, make-before-break is used to join the new source and prune the previously best source.
For the proper operations, MVPN multicast source geo-redundancy requires the router:
To maintain the list of eligible multicast sources on Receiver PEs, Source PE routers must generate Type-5 S-A route even if the Source PE sees no active joins from any receiver for a given group.
To trigger a switch from a currently active multicast source on a Receiver PE, Source PE routers must withdraw Type-5 S-A route when the multicast source fails or alternatively unicast route to multicast source must be withdrawn or go down on a Receiver PE.
MVPN multicast source redundancy solutions is supported for the following configurations only. Enabling the feature in unsupported configuration must be avoided:
NG-MVPN with RSVP-TE or mLDP or PIM with BGP c-multicast signaling in P-instance. Both I-PMSI and S-PMSI trees are supported.
IPv4 and IPv6 (C-*, C-G) PIM ASM joins in the C-instance.
Both intersite-shared enabled and disabled are supported. For intersite-shared enabled, operators must enable generation of Type-5 S-A routes even in the absence of receivers seen on Source PEs (intersite-shared persistent-type5-adv must be enabled).
The Source PEs must be configured as a sender-receiver, the Receiver PEs can be configured as a sender-receiver or a receiver-only.
The RP(s) must be on the Source PE(s) side. Static RP, anycast-RP, embedded-RP types are supported.
UMH redundancy can be deployed to protect Source PE to any multicast source. When deployed, UMH selection is executed independently of source selection after the most preferred multicast source had been chosen. Supported umh-selection options include: highest-ip, hash-based, tunnel-status (not supported for IPv6), and unicast-rt-pref.