Consider a link configured with two class types CT0 and CT1 and making use of the RDM admission control model as shown in Figure 1.
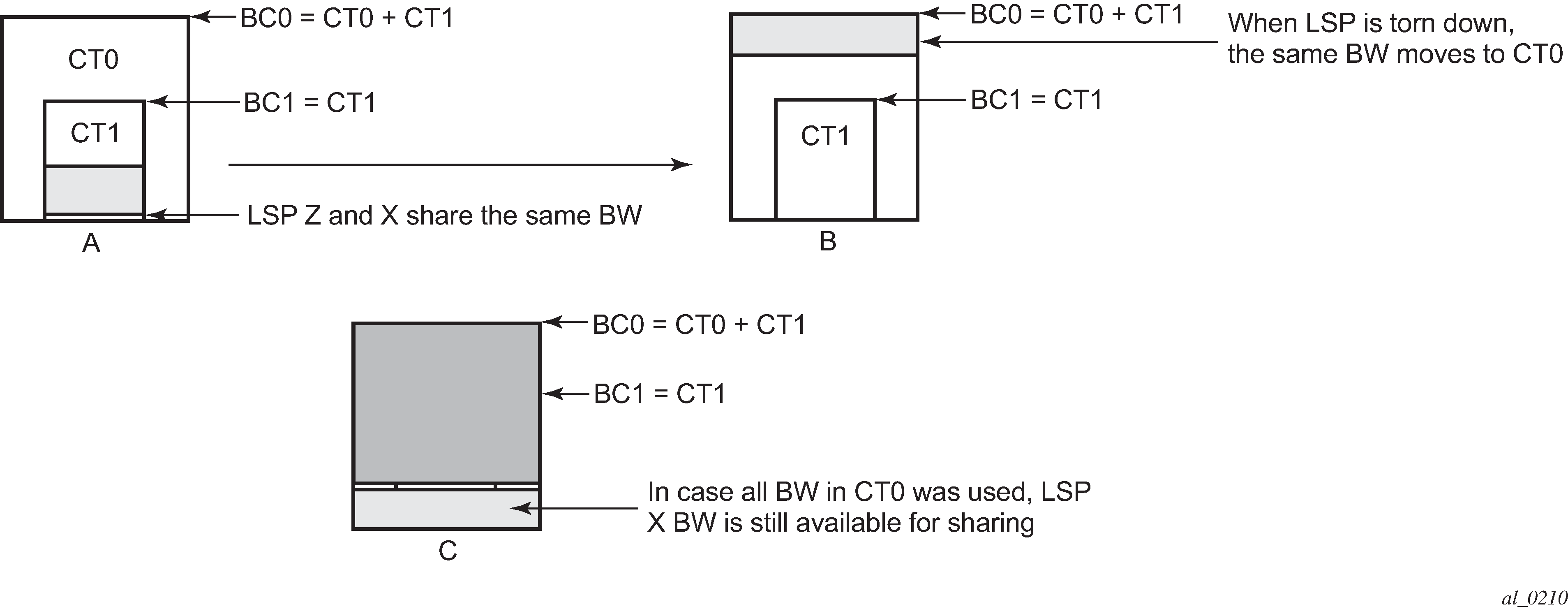
Consider an LSP path Z occupying bandwidth B at CT1. BC0 being the sum of all CTs below it, the bandwidth occupied in CT1 is guaranteed to be available in CT0. When new path X of the same LSP for CT0 is setup, it uses the same bandwidth B as used by path Z as shown in Figure 1 (a). When path Z is torn down the same bandwidth now occupies CT0 as shown in Figure 1 (b). Even if there were no new BW available in CT0 as can be seen in Figure 1 (c), path X can always share the bandwidth with path Z.
CSPF at the head-end node and CAC at the transit LSR node shares bandwidth of an existing path when its CT is downgraded in the new path of the same LSP.