The MPLS Fast Re-Route (FRR) feature implements a background task to evaluate Path State Block (PSB) associations with bypass LSP. The following is the task evaluation behavior.
For PSBs that have facility FRR enabled but no bypass association, the task triggers a FRR protection request.
For PSBs that have requested node-protect bypass LSP but are currently associated with a link-protect bypass LSP, the task triggers a node-protect FRR request.
For PSBs that have LSP statistics enabled but the statistic index allocation failed, the task re-attempts index allocation.
The MPLS FRR background task enables PLRs to be aware of the missing node protection and allows them to probe regularly for a node-bypass. Figure 1 shows an example of FRR node protection.
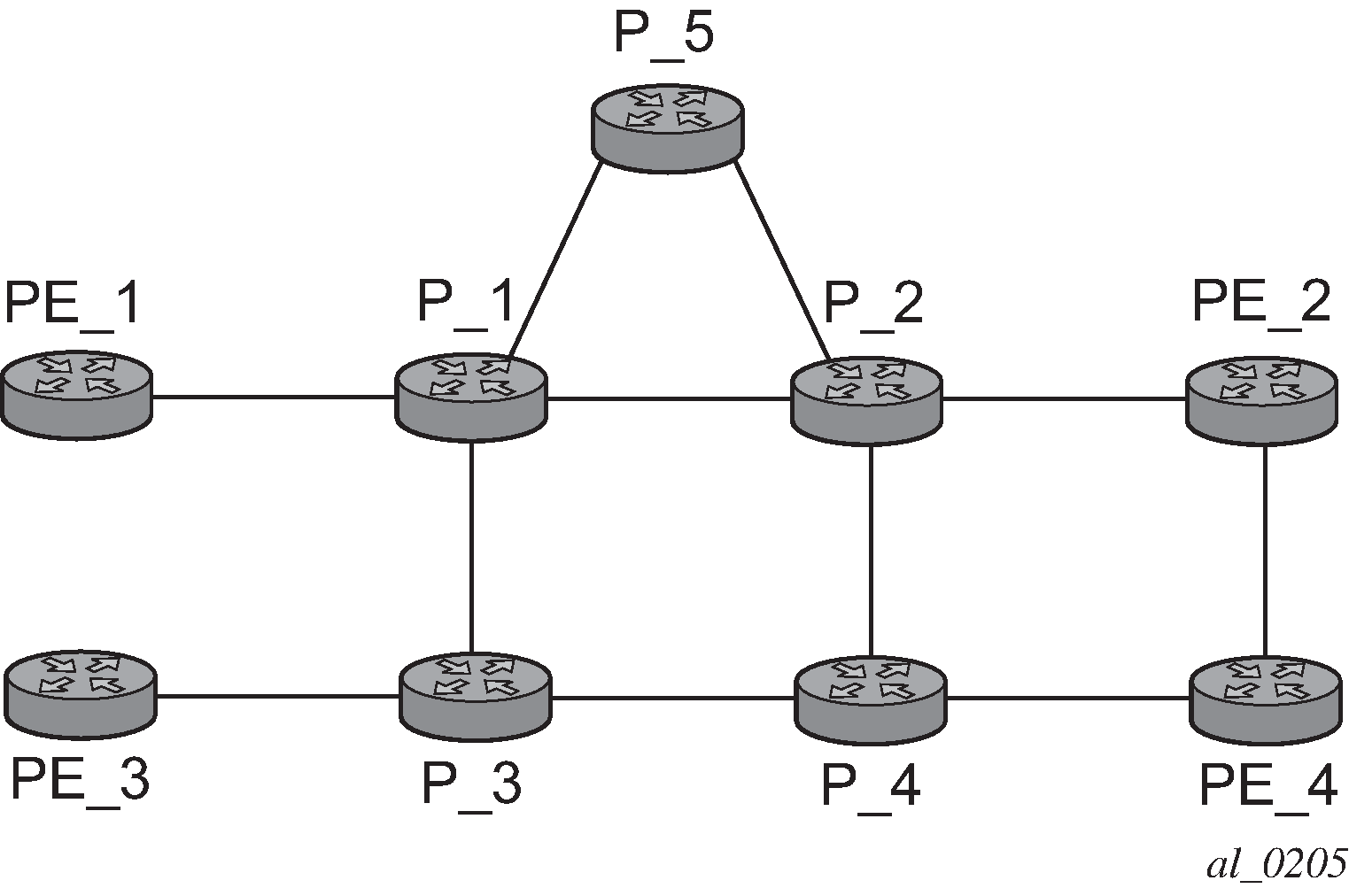
The following describes an LSP scenario where:
LSP 1: from PE_1 to PE_2, with CSPF, FRR facility node-protect enabled
P_1 protects P_2 with bypass-nodes P_1 -P_3 - P_4 - PE_4 -PE_2
If P_4 fails, P_1 tries to establish the bypass-node three times
When the bypass-node creation fails, P_1 protects link P_1-P_2
P_1 protects the link to P_2 through P_1 - P_5 - P_2
P_4 returns online
LSP 1 has requested node protection, but because there is no available path, it can only obtain link protection. Therefore, every 60 seconds the PSB background task triggers the PLR for LSP 1 to search for a new path that can provide node protection. When P_4 is back online and such a path is available, a new bypass tunnel is signaled and LSP 1 gets associated with this new bypass tunnel.