The stitching of an LDP FEC to a BGP labeled route allows the LDP capable PE devices to offer services to PE routers in other areas or domains without the need to support BGP labeled routes.
This feature is used in a large network to provide services across multiple areas or autonomous systems. Figure 1 shows a network with a core area and regional areas.
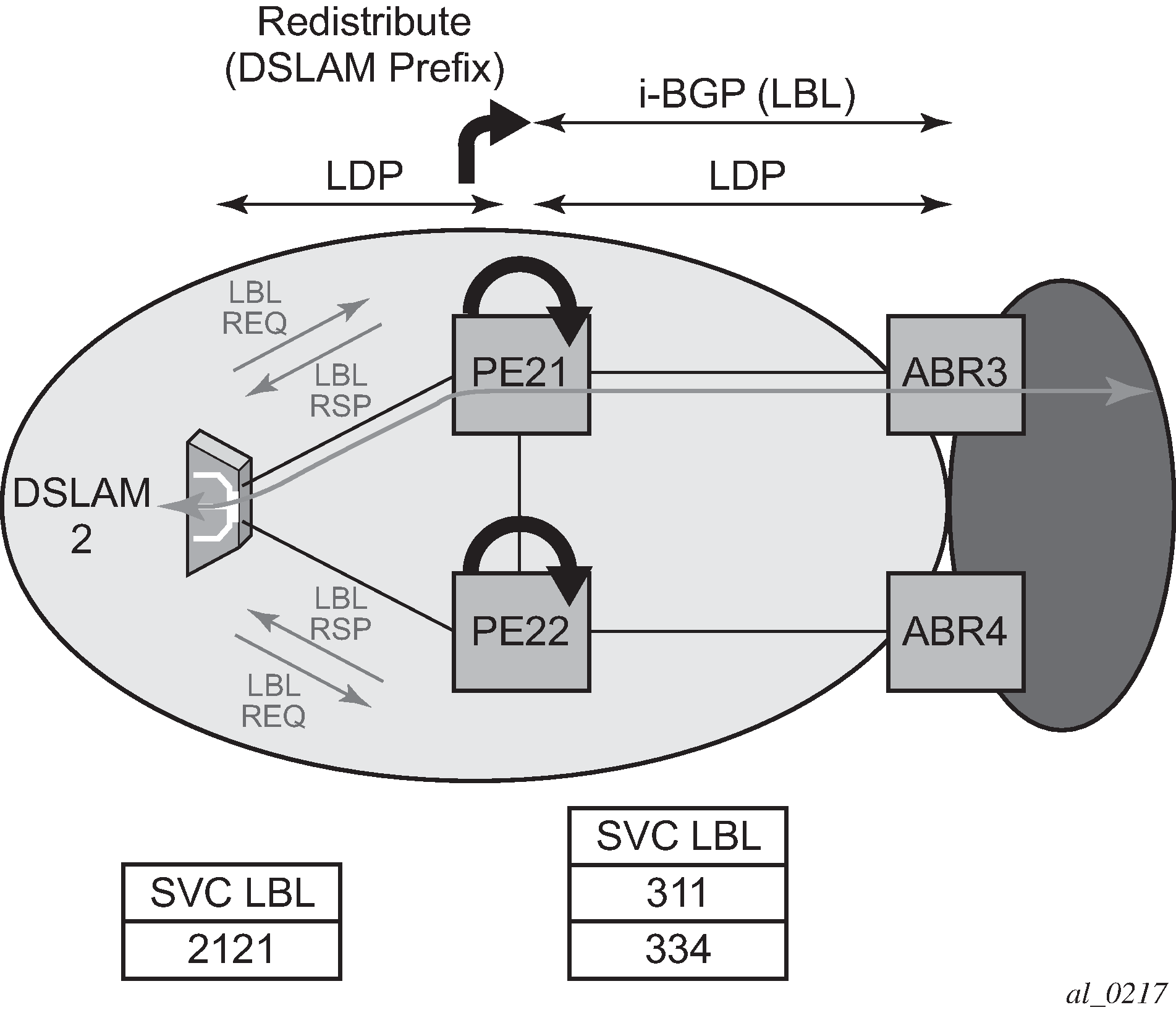
Specific /32 routes in a regional area are not redistributed into the core area. Therefore, only nodes within a regional area and the ABR nodes in the same area exchange LDP FECs. A PE router, for example, PE21, in a regional area learns the reachability of PE routers in other regional areas by way of RFC 3107 BGP labeled routes redistributed by the remote ABR nodes by way of the core area. The remote ABR then sets the next-hop self on the labeled routes before re-distributing them into the core area. The local ABR for PE2, for example, ABR3 may or may not set next-hop self when it re-distributes these labeled BGP routes from the core area to the local regional area.
When forwarding a service packet to the remote PE, PE21 inserts a VC label, the BGP route label to reach the remote PE, and an LDP label to reach either ABR3, if ABR3 sets next-hop self, or ABR1.
In the same network, an MPLS capable DSLAM also acts as PE router for VLL services and needs to establish a PW to a PE in a different regional area by way of router PE21, acting now as an LSR. To achieve that, PE21 is required to perform the following operations:
Translate the LDP FEC it learned from the DSLAM into a BGP labeled route and re-distribute it by way of Interior Border Gateway Protocol (IBGP) within its area. This is in addition to redistributing the FEC to its LDP neighbors in the same area.
Translate the BGP labeled routes it learns through IBGP into an LDP FEC and re-distribute it to its LDP neighbors in the same area. In the application in Figure 1, the DSLAM requests the LDP FEC of the remote PE router using LDP Downstream on Demand (DoD).
When a packet is received from the DSLAM, PE21 swaps the LDP label into a BGP label and pushes the LDP label to reach ABR3 or ABR1. When a packet is received from ABR3, the top label is removed and the BGP label is swapped for the LDP label corresponding to the DSLAM FEC.