RFC 8365 describes EVPN as the control plane for overlay-based networks. The 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, and 7950 XRS support all routes and features described in RFC 7432 that are required for the DGW function. EVPN multihoming and BGP multihoming based on the L2VPN BGP address family are both supported if redundancy is needed.
Figure: EVPN-VXLAN required routes and communities shows the EVPN MP-BGP NLRI, required attributes and extended communities, and two route types supported for the DGW Layer 2 applications:
- route type 3
- Inclusive Multicast Ethernet Tag route
- route type 2
- MAC/IP advertisement route
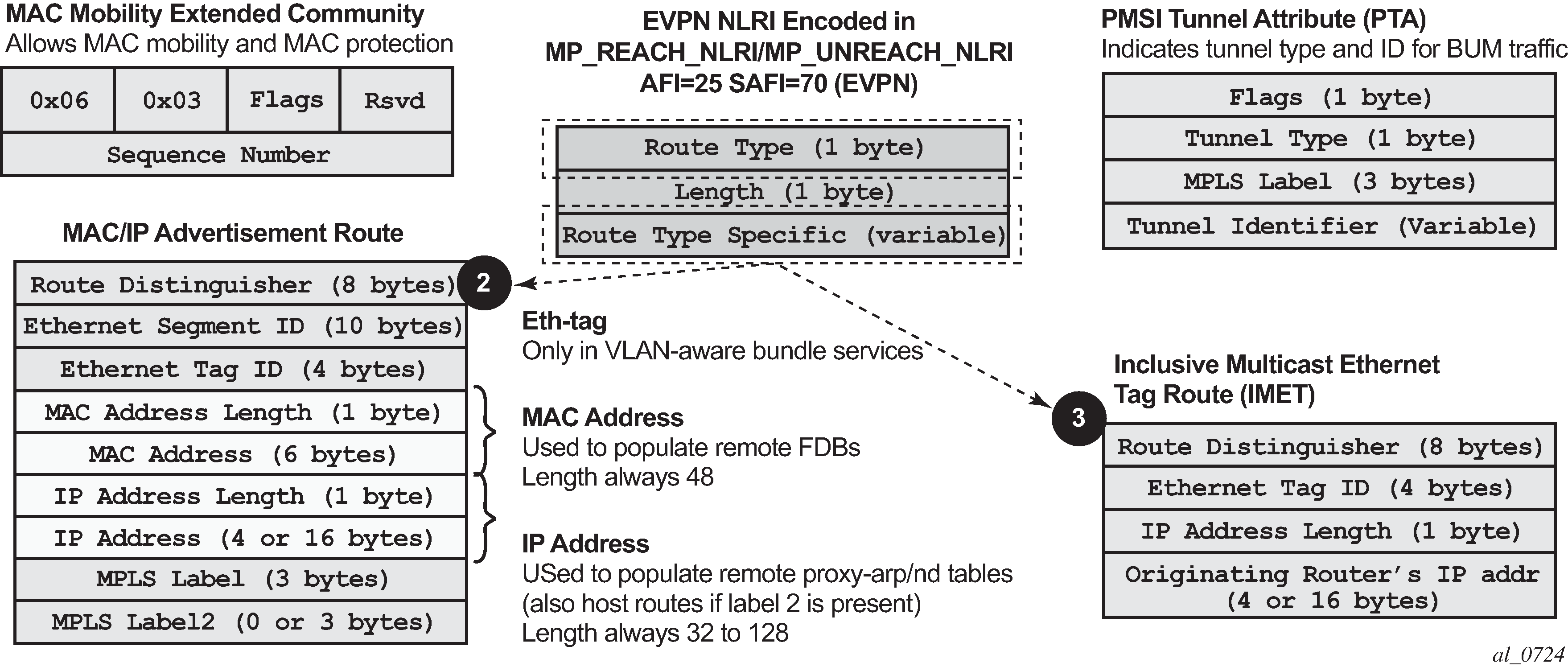
EVPN route type 3 – inclusive multicast Ethernet tag route
Route type 3 is used to set up the flooding tree (BUM flooding) for a specified VPLS service in the data center. The received inclusive multicast routes add entries to the VPLS flood list in the 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, and 7950 XRS. The tunnel types supported in an EVPN route type 3 when BGP-EVPN MPLS is enabled are ingress replication, P2MP MLDP, and composite tunnels.
Ingress Replication (IR) and Assisted Replication (AR) are supported for VXLAN tunnels. See Layer 2 multicast optimization for VXLAN (Assisted-Replication) for more information about the AR.
If ingress-repl-inc-mcast-advertisement is enabled, a route type 3 is generated by the router per VPLS service as soon as the service is in an operationally up state. The following fields and values are used:
-
Route Distinguisher is taken from the RD of the VPLS service within the BGP context.
Note: The RD can be configured or derived from the bgp-evpn evi value. -
Ethernet Tag ID is 0.
-
IP address length is always 32.
-
Originating router’s IP address carries an IPv4 or IPv6 address.
Note: By default, the IP address of the Originating router is derived from the system IP address. However, this can be overridden by the configure service vpls bgp-evpn incl-mcast-orig-ip ip-address command for the Ingress Replication (and mLDP if MPLS is used) tunnel type. -
For PMSI Tunnel Attribute (PTA), tunnel type = Ingress replication (6) or Assisted Replication (10)
-
Leaf not required for Flags.
-
MPLS label carries the VNI configured in the VPLS service. Only one VNI can be configured per VPLS service.
-
Tunnel endpoint is equal to the system IP address.
As shown in Figure: PMSI attribute flags field for AR, additional flags are used in the PTA when the service is configured for AR.
Figure: PMSI attribute flags field for AR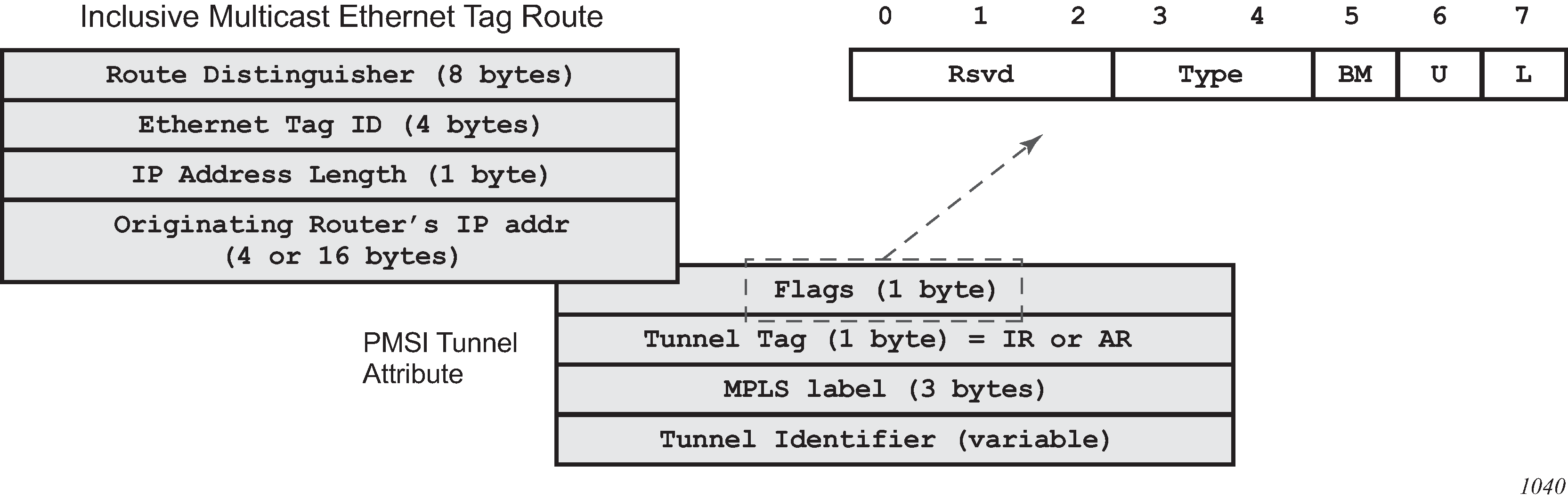
The Flags field is defined as a Type field (for AR) with two new flags that are defined as follows:
-
T is the AR Type field (2 bits):
-
00 (decimal 0) = RNVE (non-AR support)
-
01 (decimal 1) = AR REPLICATOR
-
10 (decimal 2) = AR LEAF
-
-
The U and BM flags defined in IETF Draft draft-ietf-bess-evpn-optimized-ir are not used in the SR OS.
Table: AR-R and AR-L routes and usage describes the inclusive multicast route information sent per VPLS service when the router is configured as assisted-replication replicator (AR-R) or assisted-replication leaf (AR-L). A Regular Network Virtualization Edge device (RNVE) is defined as an EVPN-VXLAN router that does not support (or is not configured for) Assisted-Replication.
Note: For AR-R, two inclusive multicast routes may be advertised if ingress-repl-inc-mcast-advertisement is enabled: a route with tunnel-type IR, tunnel-id = IR IP (generally system-ip) and a route with tunnel-type AR, tunnel-id = AR IP (the address configured in the assisted-replication-ip command).Table: AR-R and AR-L routes and usage AR role Function Inclusive Mcast routes advertisement AR-R
Assists AR-LEAFs
-
IR included in the Mcast route (uses IR IP) if ingress-repl-inc-mcast-advertisement is enabled
-
AR included in the Mcast route (uses AR IP, tunnel type=AR, T=1)
AR-LEAF
Sends BM only to AR-Rs
IR inclusive multicast route (IR IP, T=2) if ingress-repl-inc-mcast-advertisement is enabled
RNVE
Non-AR support
IR inclusive multicast route (IR IP) if ingress-repl-inc-mcast-advertisement is enabled
-
EVPN route type 2 – MAC/IP advertisement route
The 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, and 7950 XRS generates this route type for advertising MAC addresses. If mac-advertisement is enabled, the router generates MAC advertisement routes for the following:
-
learned MACs on SAPs or SDP bindings
-
conditional static MACs
The route type 2 generated by a router uses the following fields and values:
-
Route Distinguisher is taken from the RD of the VPLS service within the BGP context.
Note: The RD can be configured or derived from the bgp-evpn evi value. -
Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI) value = 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 or non-zero, depending on whether the MAC addresses are learned on an Ethernet Segment.
-
Ethernet Tag ID is 0.
-
MAC address length is always 48.
-
MAC Address:
-
is 00:00:00:00:00:00 for the Unknown MAC route address.
-
is different from 00:…:00 for the rest of the advertised MACs.
-
-
IP address and IP address length:
-
The length of the IP address associated with the MAC being advertised is either 32 for IPv4 or 128 for IPv6.
-
If the MAC address is the Unknown MAC route, the IP address length is zero and the IP omitted.
-
In general, any MAC route without IP has IPL=0 (IP length) and the IP is omitted.
-
When received, any IPL value not equal to zero, 32, or 128 discards the route.
-
-
MPLS Label 1 carries the VNI configured in the VPLS service. Only one VNI can be configured per VPLS.
-
MPLS Label 2 is 0.
-
MAC Mobility extended community is used for signaling the sequence number in case of MAC moves and the sticky bit in case of advertising conditional static MACs. If a MAC route is received with a MAC mobility ext-community, the sequence number and the sticky bit are considered for the route selection.
When EVPN-VXLAN multihoming is enabled, type 1 routes (Auto-Discovery per-ES and per-EVI routes) and type 4 routes (ES routes) are also generated and processed. See BGP-EVPN control plane for MPLS tunnels for more information about route types 1 and 4.
EVPN route type 5 – IP prefix route
Figure: EVPN route-type 5 shows the IP prefix route or route-type 5.
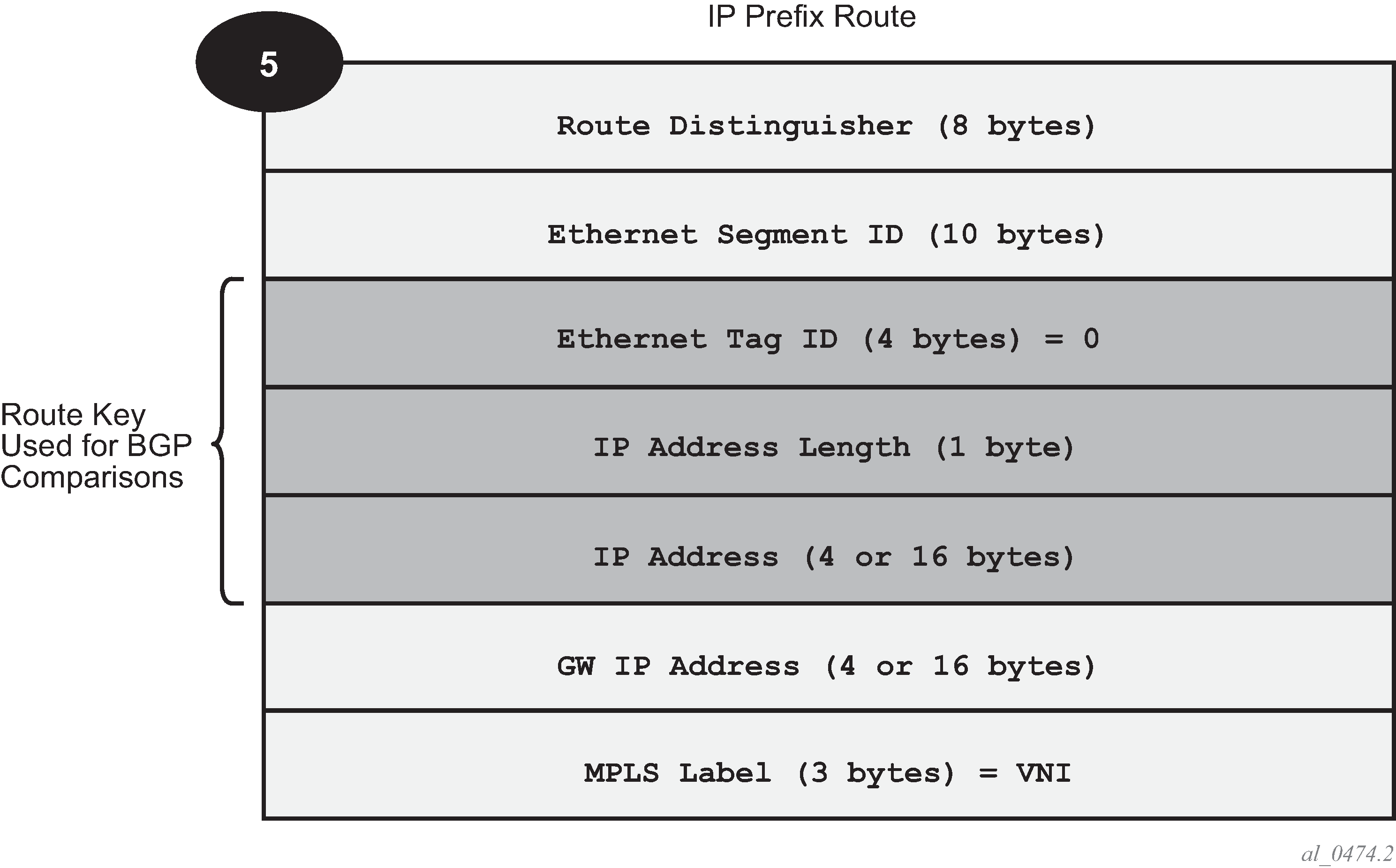
The router generates this route type for advertising IP prefixes in EVPN. The router generates IP prefix advertisement routes for IP prefixes existing in a VPRN linked to the IRB backhaul R-VPLS service.
The route-type 5 generated by a router uses the following fields and values:
-
Route Distinguisher: taken from the RD configured in the IRB backhaul R-VPLS service within the BGP context
-
Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI): value = 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
-
Ethernet Tag ID: 0
-
IP address length: any value in the 0 to 128 range
-
IP address: any valid IPv4 or IPv6 address
-
Gateway IP address: can carry two different values:
-
if different from zero, the route-type 5 carries the primary IP interface address of the VPRN behind which the IP prefix is known. This is the case for the regular IRB backhaul R-VPLS model.
-
if 0.0.0.0, the route-type 5 is sent with a MAC next-hop extended community that carries the VPRN interface MAC address. This is the case for the EVPN tunnel R-VPLS model.
-
-
MPLS Label: carries the VNI configured in the VPLS service. Only one VNI can be configured per VPLS service.
All the routes in EVPN-VXLAN is sent with the RFC 5512 tunnel encapsulation extended community, with the tunnel type value set to VXLAN.