Known unicast traffic forwarding is based on ingress PE filtering. Figure: EVPN E-Tree known unicast ingress filtering shows an example of EVPN-E-Tree forwarding behavior for known unicast.
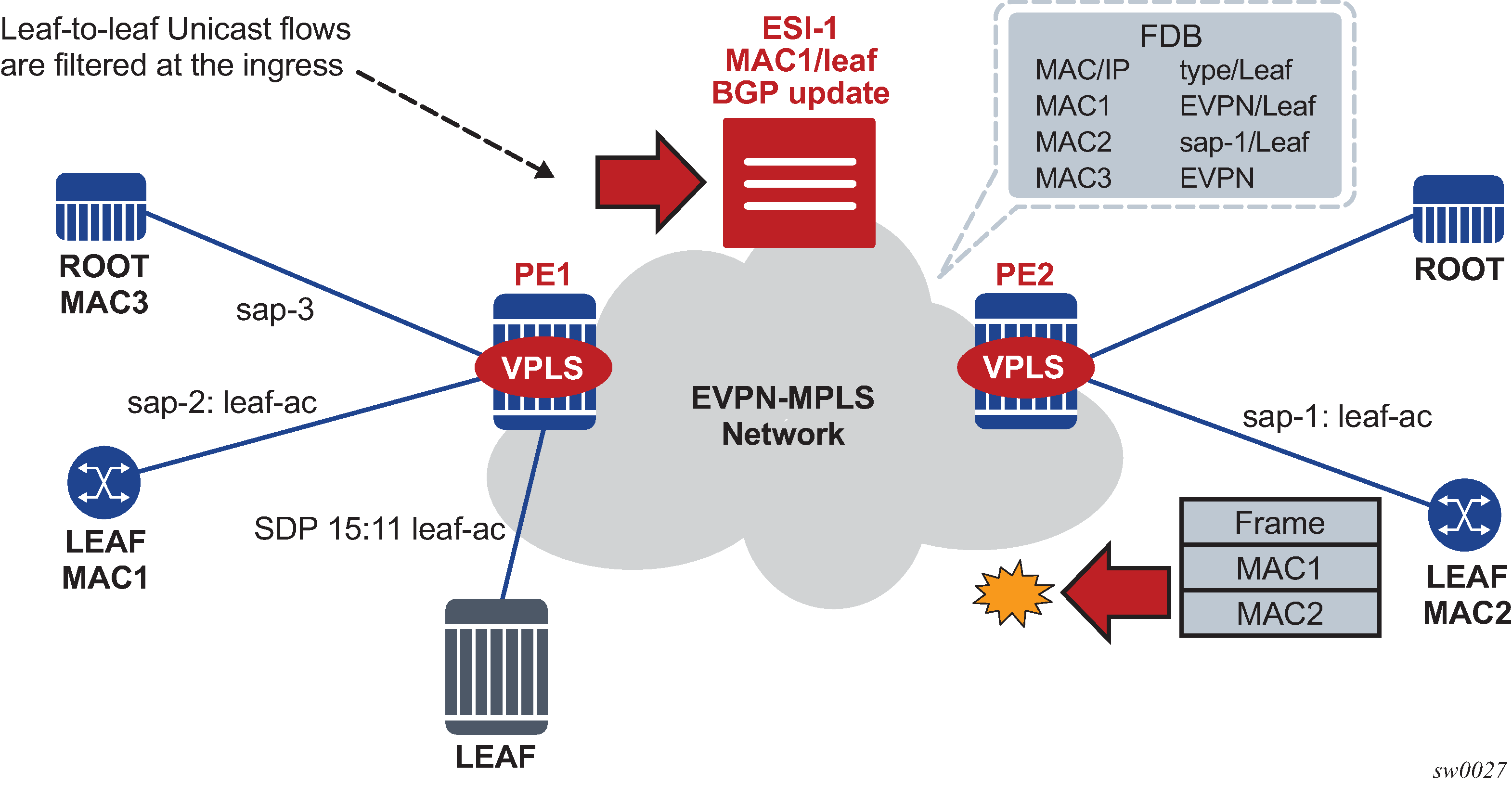
MAC addresses learned on leaf-ac objects are advertised in EVPN with their corresponding leaf indication.
In Figure: EVPN E-Tree known unicast ingress filtering , PE1 advertises MAC1 using the E-Tree EC and leaf indication, and PE2 installs MAC1 with a leaf flag in the FDB.
Assuming MAC DA is present in the local FDB (MAC1 in the FDB of PE2) when PE2 receives a frame, it is handled as follows:
If the unicast frame enters a root-ac, the frame follows regular data plane procedures; that is, it is sent to the owner of the MAC DA (local SAP or SDP binding or remote BGP EVPN PE) without any filtering.
If the unicast frame enters a leaf-ac, it is handled as follows:
-
A MAC DA lookup is performed on the FDB.
-
If there is a hit and the MAC was learned as an EVPN leaf (or from a leaf-ac), then the frame is dropped at ingress.
-
The source MAC (MAC2) is learned and marked as a leaf-learned MAC. It is advertised by the EVPN with the corresponding leaf indication.
-
A MAC received with a root and leaf indication from different PEs in the same ES is installed as root.
The ingress filtering for E-Tree leaf-to-leaf traffic requires the implementation of an extra leaf EVPN MPLS destination per remote PE (containing leaf objects) per E-Tree service. The ingress filtering for E-Tree leaf-to-leaf traffic is as follows:
A separate EVPN MPLS bind is created for unicast leaf traffic in the service. The internal EVPN MPLS destination is created for each remote PE that contains a leaf and advertises at least one leaf MAC.
The creation of the internal EVPN MPLS destination is triggered when a MAC route with L=1 in the E-Tree EC is received. Any EVPN E-Tree service can potentially use one extra EVPN MPLS destination for leaf unicast traffic per remote PE.
The extra destination in the EVPN E-Tree service is for unicast only and it is not part of the flooding list. It is resource-accounted and displayed in the tools dump service evpn usage command, as shown in the following example output.
A:PE-4# tools dump service evpn usage vxlan-evpn-mpls usage statistics at 01/23/2017 00:53:14: MPLS-TEP : 3 VXLAN-TEP : 0 Total-TEP : 3/ 16383 Mpls Dests (TEP, Egress Label + ES + ES-BMAC) : 10 Mpls Etree Leaf Dests : 1 Vxlan Dests (TEP, Egress VNI) : 0 Total-Dest : 10/196607 Sdp Bind + Evpn Dests : 13/245759 ES L2/L3 PBR : 0/ 32767 Evpn Etree Remote BUM Leaf Labels : 3MACs received with L=1 point to the EVPN MPLS destination, whereas root MACs point to the ‟root” destination.