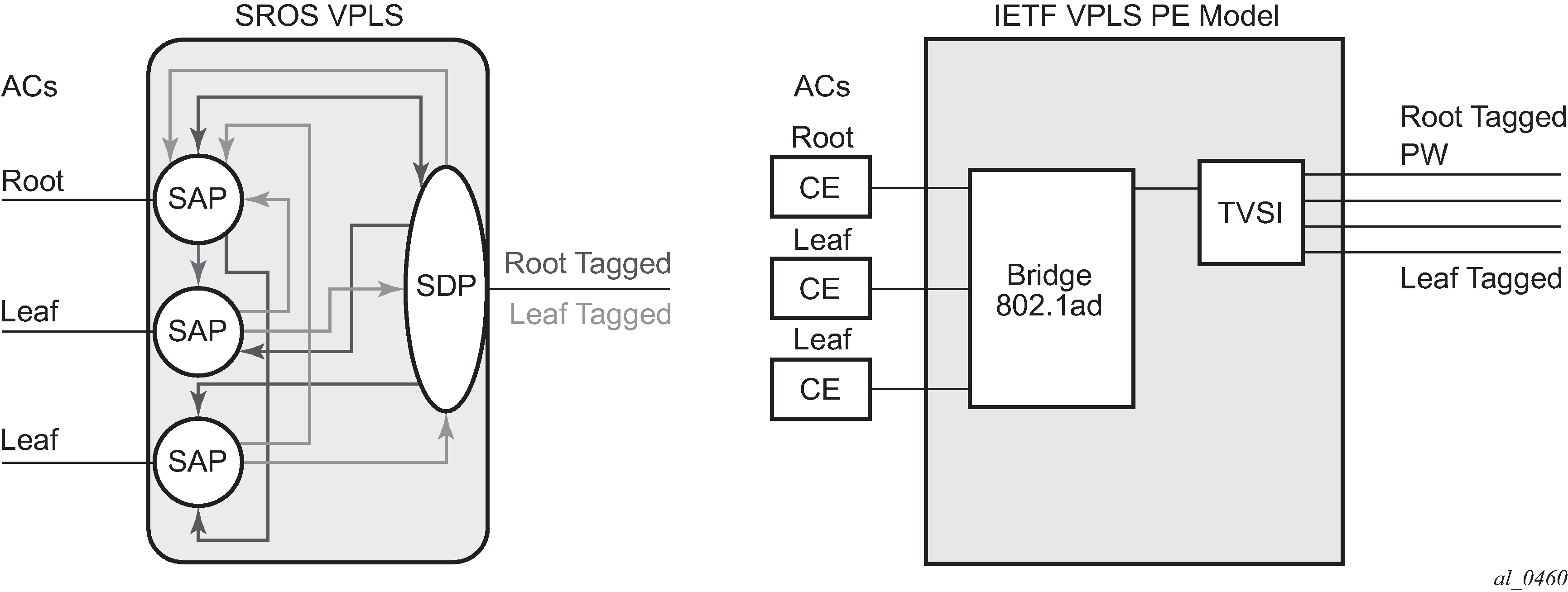
Figure: Mapping PE model to VPLS service shows the terminology used for E-Tree in IETF Draft draft-ietf-l2vpn-vpls-pe-etree and a mapping to SR OS terms.
An Ethernet service access SAP is characterized as either a leaf-ac or a root-ac for a VPLS E-Tree service. As far as SR OS is concerned, these are normal SAPs with either no tag (Null), priority tag, or dot1q or QinQ encapsulation on the frame. Functionally, a root-ac is a normal SAP and does not need to be differentiated from the regular SAPs except that it is associated with a root behavior in a VPLS E-Tree.
Leaf-ac SAPs have restrictions; for example, a SAP configured for a leaf-ac can never send frames to another leaf-ac directly (local) or through a remote node. Leaf-ac SAPs on the same VPLS instance behave as if they are part of a split horizon group (SHG) locally. Leaf-ac SAPs that are on other nodes need to have the traffic marked as originating ‟from a Leaf” in the context of the VPLS service when carried on PWs and SAPs with tags (VLANs).
Root-ac SAPs on the same VPLS can talk to any root-ac or leaf-ac.