The 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, and 7950 XRS SR OS implementation of PBB-EVPN reuses the existing PBB-VPLS model, where N I-VPLS (or Epipe) services can be linked to a B-VPLS service. BGP-EVPN is enabled in the B-VPLS and the B-VPLS becomes an EVI (EVPN Instance). Figure: PBB-EVPN for I-VPLS and PBB Epipe services shows the PBB-EVPN model in the SR OS.
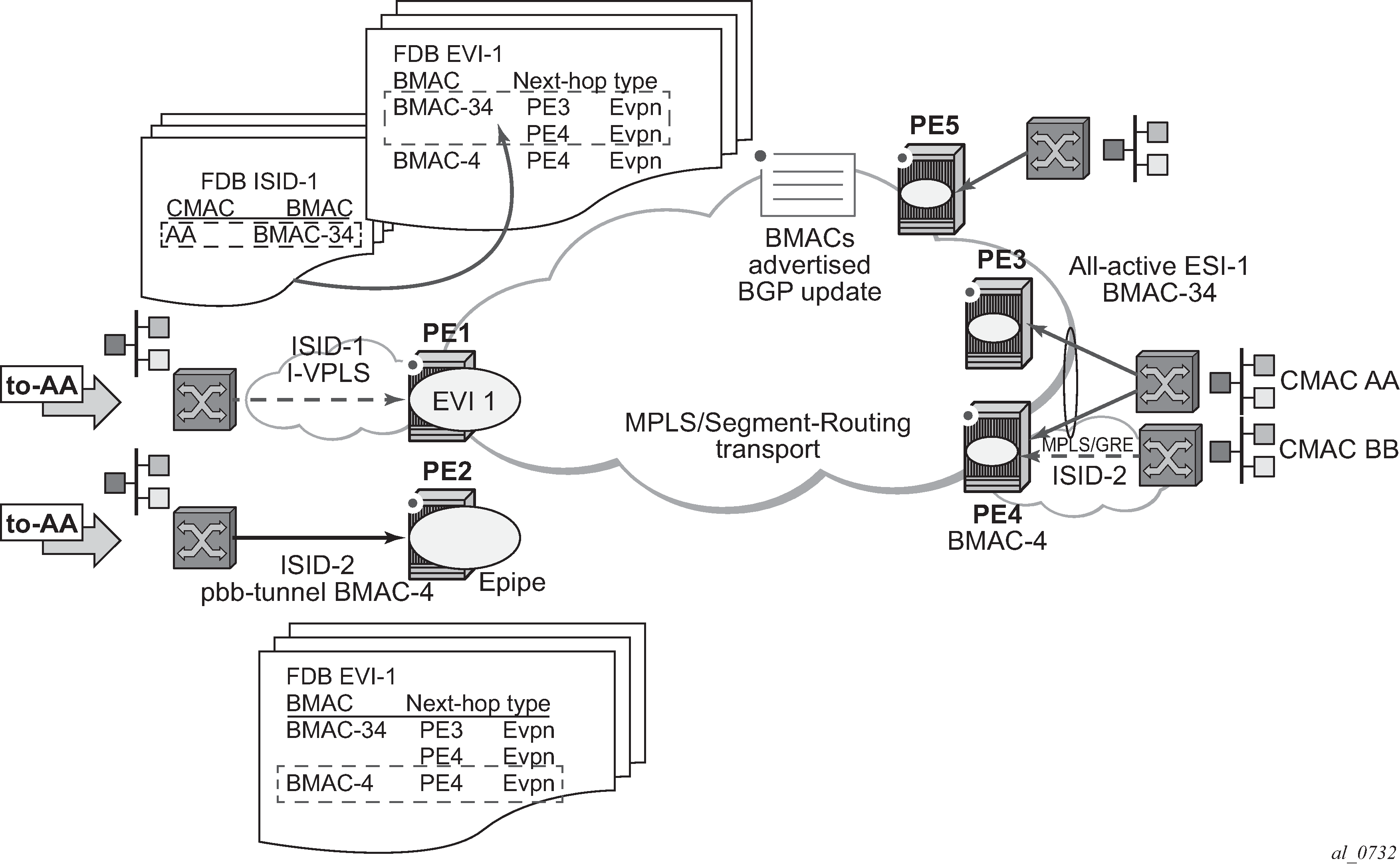
Each PE in the B-VPLS domain advertises its source-bmac as either configured in vpls>pbb>source-bmac or auto-derived from the chassis MAC. The remote PEs install the advertised B-MACs in the B-VPLS FDB. If a specified PE is configured with an ethernet-segment associated with an I-VPLS or PBB Epipe, it may also advertise an es-bmac for the Ethernet-Segment.
In the example shown in Figure: PBB-EVPN for I-VPLS and PBB Epipe services, when a frame with MAC DA = AA gets to PE1, a MAC lookup is performed on the I-VPLS FDB and B-MAC-34 is found. A B-MAC lookup on the B-VPLS FDB yields the next-hop (or next-hops if the destination is in an all-active Ethernet-Segment) to which the frame is sent. As in PBB-VPLS, the frame is encapsulated with the corresponding PBB header. A label specified by EVPN for the B-VPLS and the MPLS transport label are also added.
If the lookup on the I-VPLS FDB fails, the system sends the frame encapsulated into a PBB packet with B-MAC DA = Group B-MAC for the ISID. That packet is distributed to all the PEs where the ISID is defined and contains the EVPN label distributed by the Inclusive Multicast routes for that ISID, as well as the transport label.
For PBB-Epipes, all the traffic is sent in a unicast PBB packet to the B-MAC configured in the pbb-tunnel.
The following CLI output shows an example of the configuration of an I-VPLS, PBB-Epipe, and their corresponding B-VPLS.
*A:PE-1>config#
service vpls 1 name "b-vpls1" b-vpls create
description "pbb-evpn-service"
service-mtu 2000
pbb
source-bmac 00:00:00:00:00:03
bgp
bgp-evpn
evi 1
mpls bgp 1
no shutdown
auto-bind-tunnel resolution any
sap 1/1/1:1 create
exit
spoke-sdp 1:1 create
*A:PE-1>config#
service vpls 101 name "vpls101" i-vpls create
pbb
backbone-vpls 1
sap 1/2/1:101 create
spoke-sdp 1:102 create
*A:PE-1>config#
service epipe 102 name "epipe102" create
pbb
tunnel 1 backbone-dest-mac 00:00:00:00:00:01 isid 102
sap 1/2/1:102 create
Configure the bgp-evpn context as described in section EVPN for MPLS tunnels in VPLS services (EVPN-MPLS).
Some EVPN configuration options are not relevant to PBB-EVPN and are not supported when BGP-EVPN is configured in a B-VPLS; these are as follows:
bgp-evpn> [no] ip-route-advertisement
bgp-evpn> [no] unknown-mac-route
bgp-evpn> vxlan [no] shutdown
bgp-evpn>mpls>force-vlan-vc-forwarding
When bgp-evpn>mpls no shutdown is added to a specified B-VPLS instance, the following considerations apply:
BGP-AD is supported along with EVPN in the same B-VPLS instance.
The following B-VPLS and BGP-EVPN commands are fully supported:
vpls>backbone-vpls
vpls>backbone-vpls>send-flush-on-bvpls-failure
vpls>backbone-vpls>source-bmac
vpls>backbone-vpls>use-sap-bmac
vpls>backbone-vpls>use-es-bmac (For more infomration, see PBB-EVPN multihoming in I-VPLS and PBB Epipe services)
vpls>isid-policies
vpls>static-mac
vpls>SAP or SDP-binding>static-isid
bgp-evpn>mac-advertisement - this command affects the 'learned' B-MACs on SAPs or SDP bindings and not on the system B-MAC or SAP/es-bmacs being advertised.
bgp-evpn>mac-duplication and settings.
bgp-evpn>mpls>auto-bind-tunnel and options.
bgp-evpn>mpls>ecmp
bgp-evpn>mpls>control-word
bgp-evpn>evi
bgp-evpn>mpls>ingress-replication-bum-label