Pseudowire redundancy is supported on dynamic MS-PWs used for VLLs. It is configured in a similar manner to pseudowire redundancy on VLLs using FEC128, whereby each spoke-sdp-fec within an endpoint is configured with a unique SAII/TAII.
Figure: Pseudowire redundancy shows the use of pseudowire redundancy.
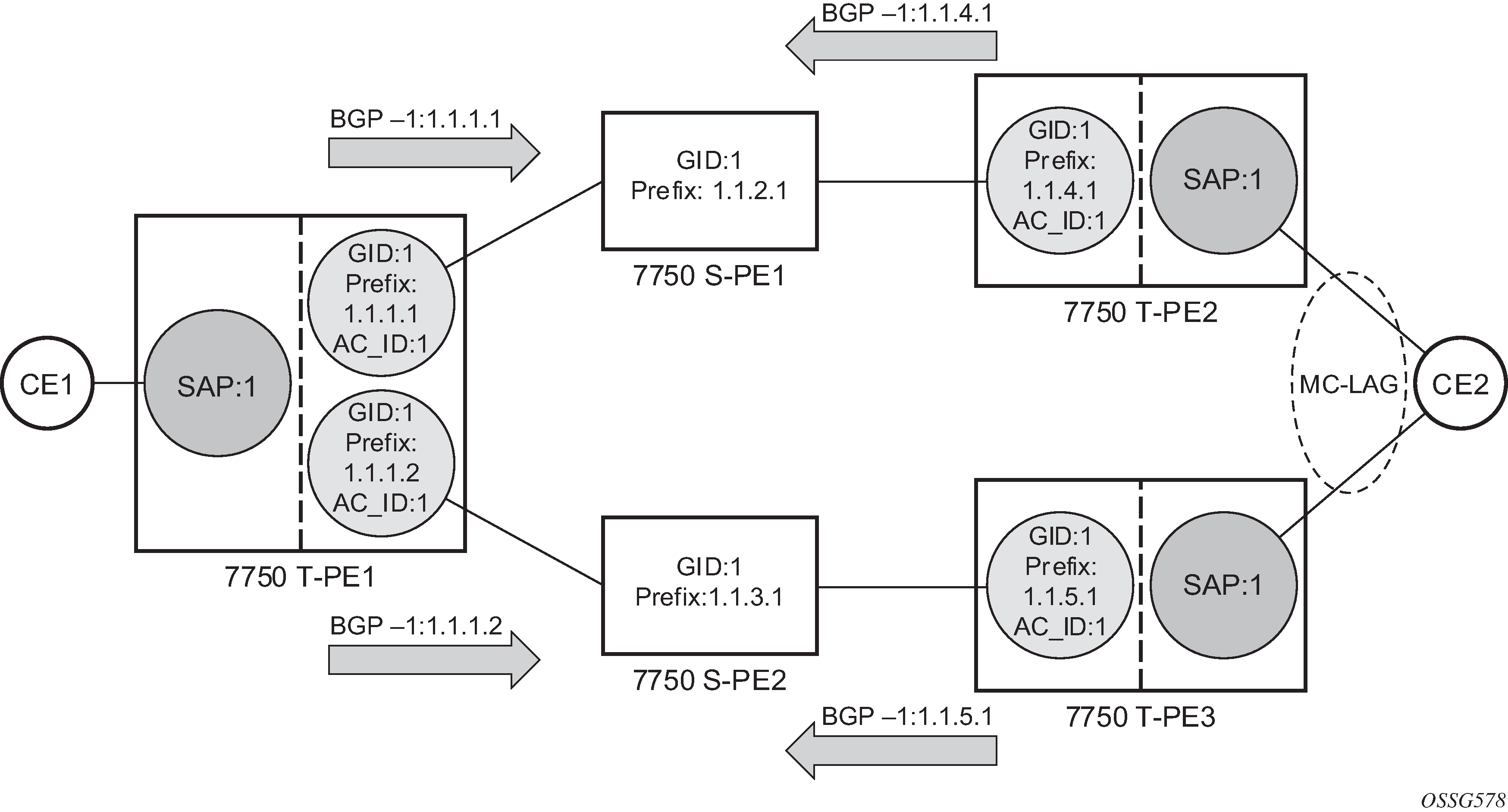
The following is a summary of the key points to consider in using pseudowire redundancy with dynamic MS-PWs:
Each MS-PW in the redundant set must have a unique SAII/TAII set and is signaled separately. The primary pseudowire is configured in the spoke-sdp-fec>primary context.
Each MS-PW in the redundant set should use a diverse path (from the point of view of the S-PEs traversed) from every other MS-PW in that set if path diversity is possible in a specific network topology. There are a number of possible ways to achieve this:
Configure an explicit path for each MS-PW.
Allow BGP routing to automatically determine diverse paths using BGP policies applied to different local prefixes assigned to the primary and standby MS-PWs.
Path diversity can be further provided for each primary pseudowire through the use of a BGP RD.
If the primary MS-PW fails, fail-over to a standby MS-PW occurs, as per the normal pseudowire redundancy procedures. A configurable retry timer for the failed primary MS-PW is then started. When the timer expires, attempts to reestablish the primary MS-PW using its original path occur, up to a maximum number of attempts as per the retry count parameter. On successful reestablishment, the T-PE may then optionally revert to the primary MS-PW.
Because the SDP ID is determined dynamically at signaling time, it cannot be used as a tie breaker to choose the primary MS-PW between multiple MS-PWs of the same precedence. The user should, therefore, explicitly configure the precedence values to determine which MS-PW is active in the final selection.