The network setup illustrated in Figure: SRv6 OAM network setup shows an example configuration of segment routing using SRv6 that is discussed in this section. See the 7750 SR and 7950 XRS Segment Routing and PCE User Guide for further information about the SRv6 feature.
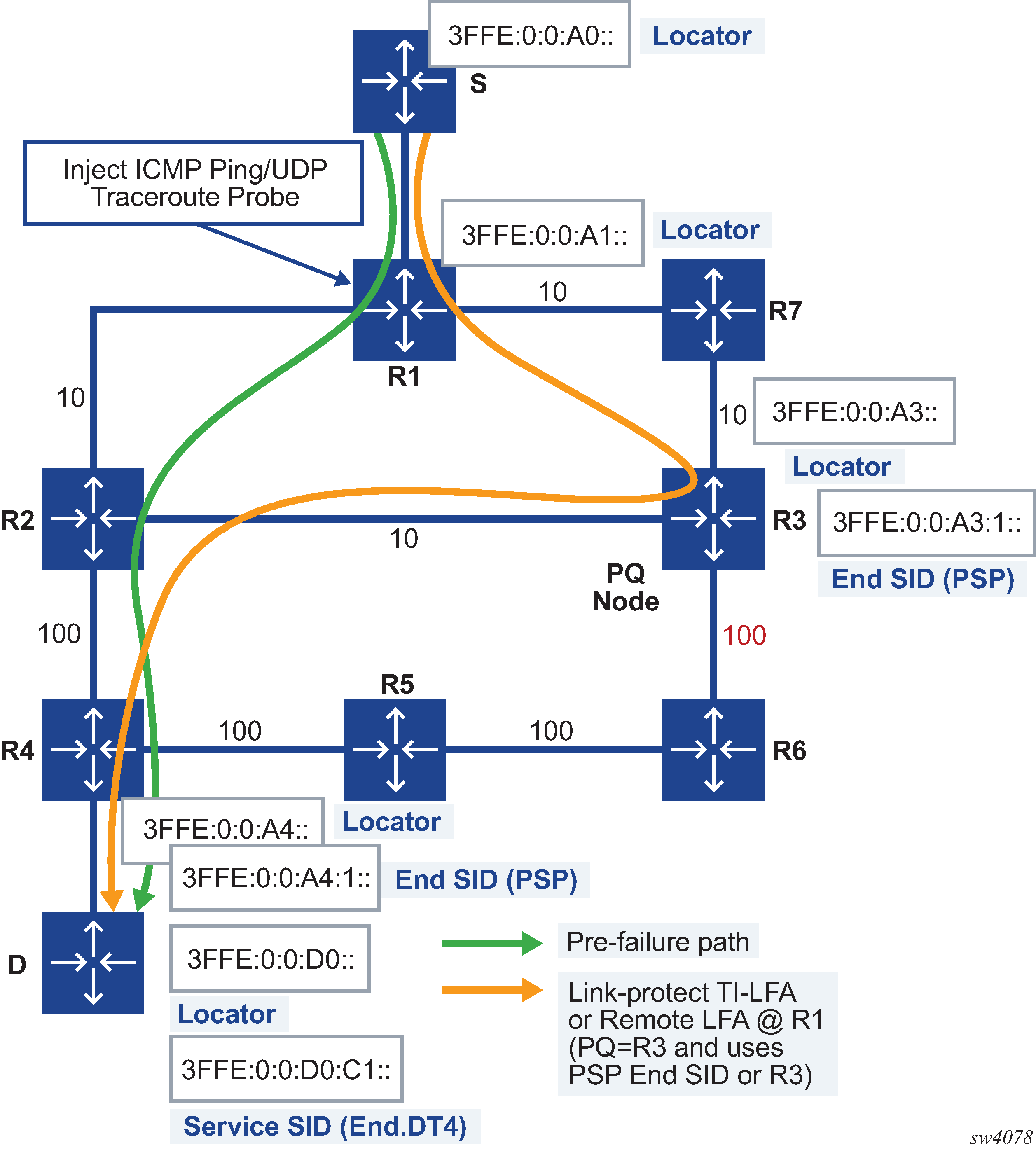
As shown in Figure: SRv6 OAM network setup, the network administrator originates a ping or a traceroute probe on node R1 to test the path of an SRv6 locator of node D, an SRv6 segment identifier (SID) owned by node D, or an IP prefix resolved to an SRv6 tunnel toward node D. R1 is referred to as the sender node. Node D is referred to as the target node because it owns the target locator or SID that is being tested. A target node can be any router in the SRv6 network domain which either owns the target locator or SID, or a router in which the OAM probe was extracted because a local route matches or because of the value of the hop-limit field setting in the packet.
The primary path to D is through R2 and R4. The link-protect TI-LFA backup path is through R3 as a PQ node and then R2 and R4.
The classic ping and traceroute OAM CLI commands are used to test an IPv4 or IPv6 prefix in a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) table or in the base router table when resolved to an SRv6 tunnel, for example:
ping address [detail] [source ip-address]
traceroute address [detail] source ip-address]
The same CLI commands are used to test the address of an SRv6 locator or a SID. In this case, the user enters the IPv6 address of the target locator prefix or the target SID.
The source address encoded in the outer IPv6 header of the ping or traceroute packet is derived from the following steps, in ascending order:
the user-entered source IPv6 address in the ping or traceroute command, which is checked for validity against a local interface address or a local locator prefix or SID
the globally-configured IPv6 source address from the source-address application6 ping or source-address application6 traceroute commands
the preferred primary IPv6 address of the system interface
the IPv6 address of outgoing interface