This section describes how MPLS OAM models the SR tunnel types.
An SR shortest path tunnel, SR-ISIS, or SR-OSPF tunnel, uses a single FEC element in the Target FEC Stack TLV. The FEC corresponds to the prefix of the node SID in a specific IGP instance.
Figure: IPv4 IGP-prefix segment ID illustrates the format for the IPv4 IGP-prefix segment ID:
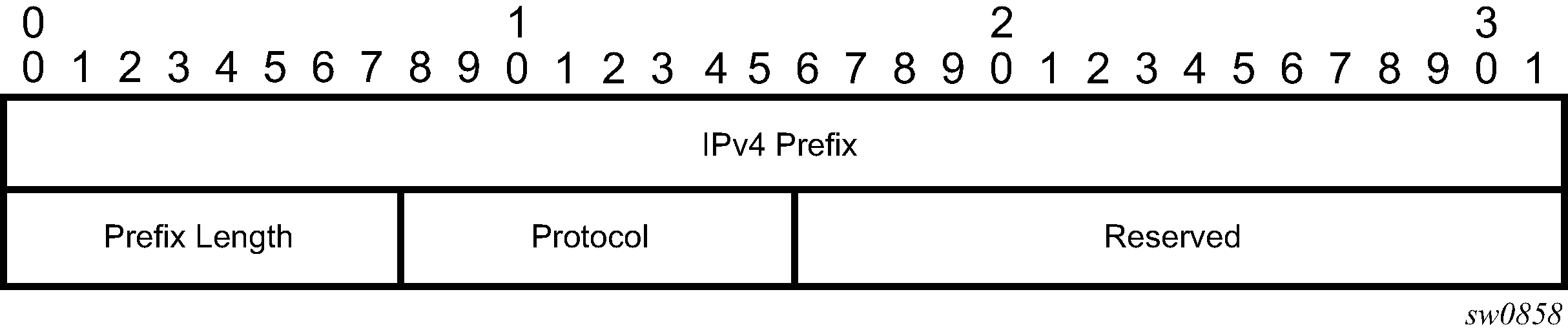
In this format, the fields are as follows:
IPv4 Prefix
This field carries the IPv4 prefix to which the segment ID is assigned. For anycast segment ID, this field carries the IPv4 anycast address. If the prefix is shorter than 32 bits, trailing bits must be set to zero.
Prefix Length
The Prefix Length field is one octet. It gives the length of the prefix in bits (values can be 1 to 32).
Protocol
This field is set to 1 if the IGP protocol is OSPF and is set to 2 if the IGP protocol is IS-IS.
Figure: IPv6 IGP prefix segment ID illustrates the format for the IPv6 IGP prefix segment ID:
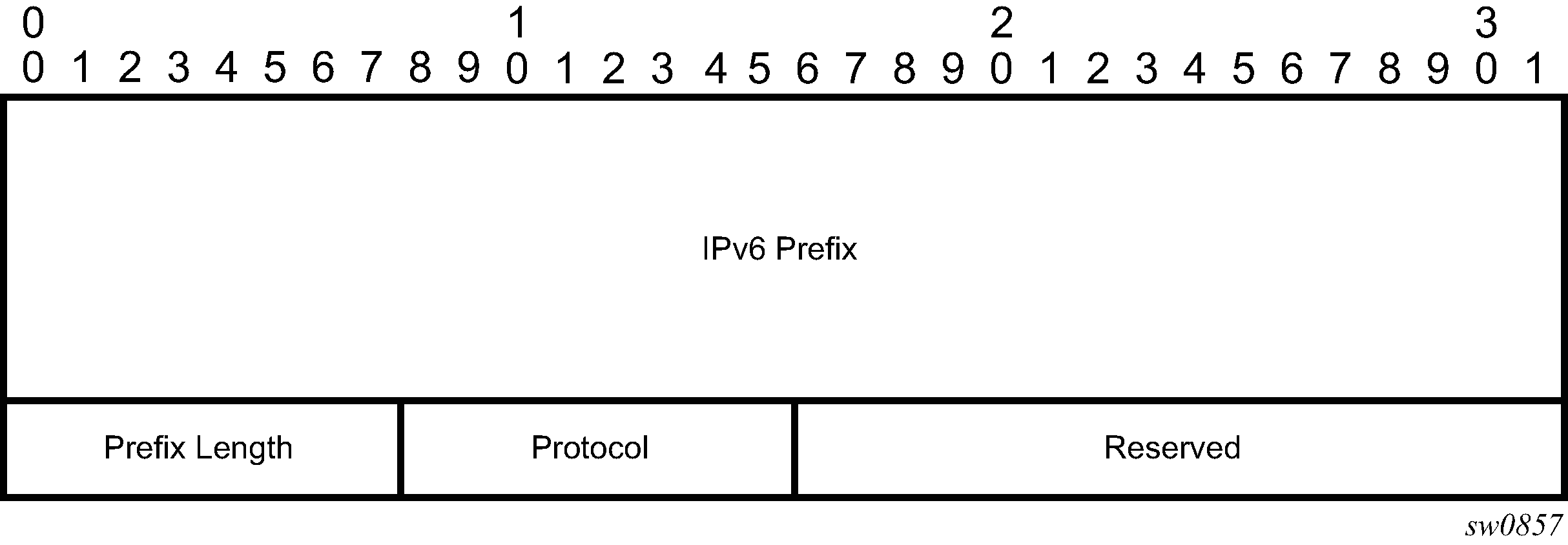
In this format, the fields are as follows:
IPv6 Prefix
This field carries the IPv6 prefix to which the segment ID is assigned. For anycast segment ID, this field carries the IPv4 anycast address. If the prefix is shorter than 128 bits, trailing bits must be set to zero.
Prefix Length
The Prefix Length field is one octet, it gives the length of the prefix in bits (values can be 1 to 128).
Protocol
This field is set to 1 if the IGP protocol is OSPF and is set to 2 if the IGP protocol is IS-IS.
An SR-TE LSP, as a hierarchical LSP, uses the Target FEC Stack TLV, which contains a FEC element for each node SID and for each adjacency SID in the path of the SR-TE LSP. Because the SR-TE LSP does not instantiate state in the LSR other than the ingress LSR, MPLS OAM is just testing a hierarchy of node SID and adjacency SID segments toward the destination of the SR-TE LSP. The format of the node-SID is as illustrated above. Figure: IGP-Adjacency segment ID illustrates the format for the IGP-Adjacency segment ID is as follows:
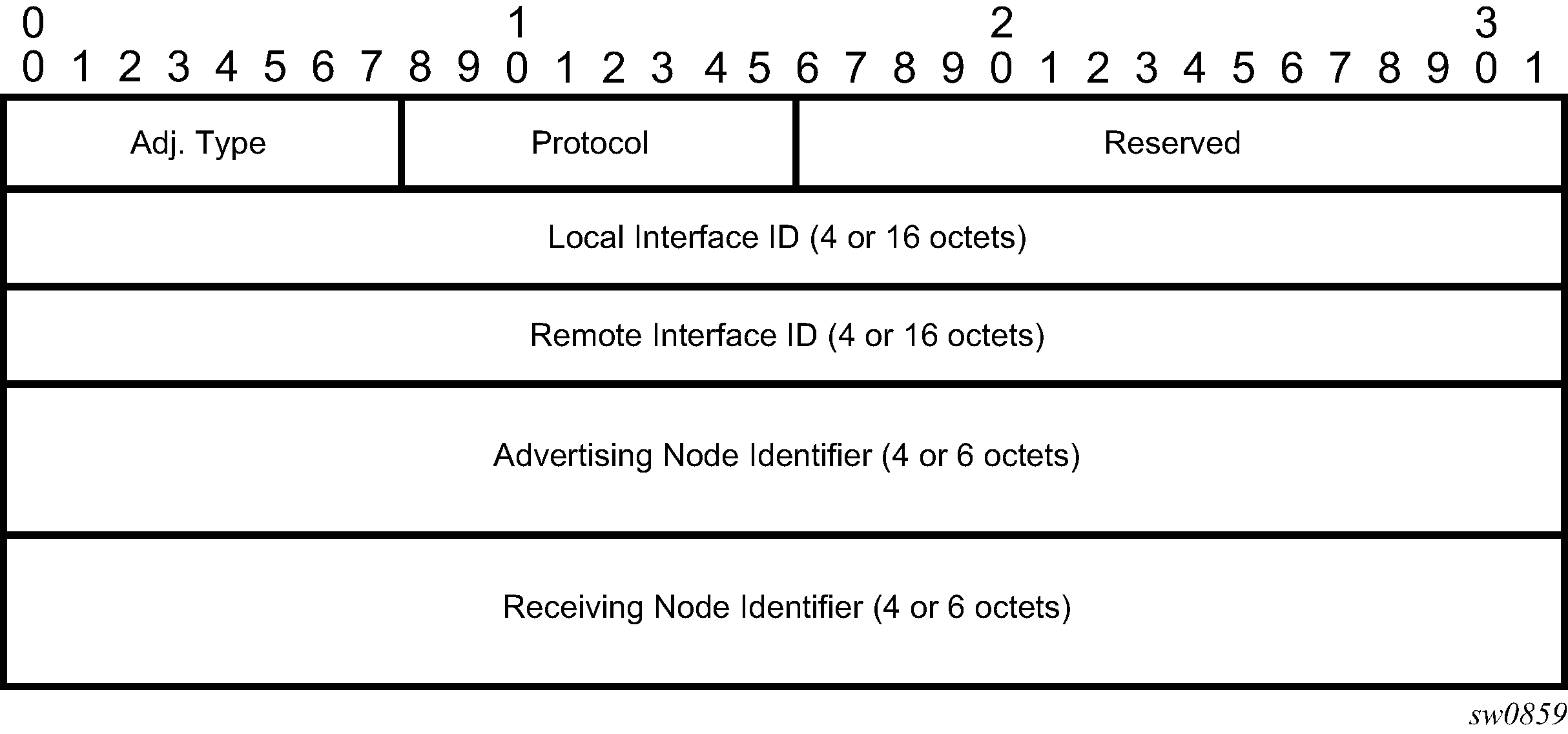
In this format, the fields are as follows:
Adj. Type (Adjacency Type)
This field is set to 1 when the adjacency segment is parallel adjacency as defined in section 3.5.1 of I-D.ietf-spring-segment-routing. This field is set to 4 when the adjacency segment is IPv4-based and is not a parallel adjacency. This field is set to 6 when the adjacency segment is IPv6-based and is not a parallel adjacency.
Protocol
This field is set to 1 if the IGP protocol is OSPF and is set to 2 if the IGP protocol is IS-IS.
Local Interface ID
This field is an identifier that is assigned by local LSR for a link on which the adjacency segment ID is bound. This field is set to local link address (IPv4 or IPv6). If unnumbered, the 32-bit link identifier defined in RFC 4203 and RFC 5307 is used. If the adjacency segment ID represents parallel adjacencies, as described in section 3.5.1 of I-D.ietf-spring-segment-routing, then this field must be set to zero.
Remote Interface ID
This field is an identifier that is assigned by remote LSR for a link on which adjacency segment ID is bound. This field is set to the remote (downstream neighbor) link address (IPv4 or IPv6). If unnumbered, the 32-bit link identifier defined in RFC 4203 and RFC 5307 is used. If the adjacency segment ID represents parallel adjacencies, as described in section 3.5.1 of I-D.ietf-spring-segment-routing. This field must be set to zero.
Advertising Node Identifier
This field specifies the advertising node identifier. When the Protocol field is set to 1, then the 32 rightmost bits represent the OSPF router ID. If the Protocol field is set to 2, this field carries the 48-bit IS-IS system ID.
Receiving Node Identifier
This field specifies the downstream node identifier. When the Protocol field is set to 1, then the 32 rightmost bits represent OSPF router ID. If the Protocol field is set to 2, this field carries the 48-bit IS-IS system ID.
Both lsp-ping and lsp-trace apply to the following contexts:
SR-ISIS or SR-OSPF shortest path IPv4 tunnel
SR-ISIS or SR-OSPF3 (OSPFv3 instance ID 0-31) shortest path IPv6 tunnel
IS-IS SR-TE IPv4 LSP and OSPF SR-TE IPv4 LSP
IS-IS SR-TE IPv6 LSP
SR-ISIS IPv4 tunnel stitched to an LDP IPv4 FEC
BGP IPv4 LSP or BGP IPv6 LSP (with an IPv4 or an IPv4-mapped-IPv6 next-hop) resolved over an SR-ISIS IPv4 tunnel, an SR-OSPF IPv4 tunnel, or an SR-TE IPv4 LSP. This includes support for BGP LSP across AS boundaries and for ECMP next-hops at the transport tunnel level.
BGP IPv4 LSP (with an IPv6 next-hop) or a BGP IPv6 LSP resolved over an SR-ISIS IPv6 tunnel, an SR-OSPF3 IPv6 tunnel, or an SR-TE IPv6 LSP; including support for BGP LSP across AS boundaries and for ECMP next-hops at the transport tunnel level.
SR-ISIS or SR-OSPF IPv4 tunnel resolved over IGP IPv4 shortcuts using RSVP-TE LSPs
SR-ISIS IPv6 tunnel resolved over IGP IPv4 shortcuts using RSVP-TE LSPs
LDP IPv4 FEC resolved over IGP IPv4 shortcuts using SR-TE LSPs