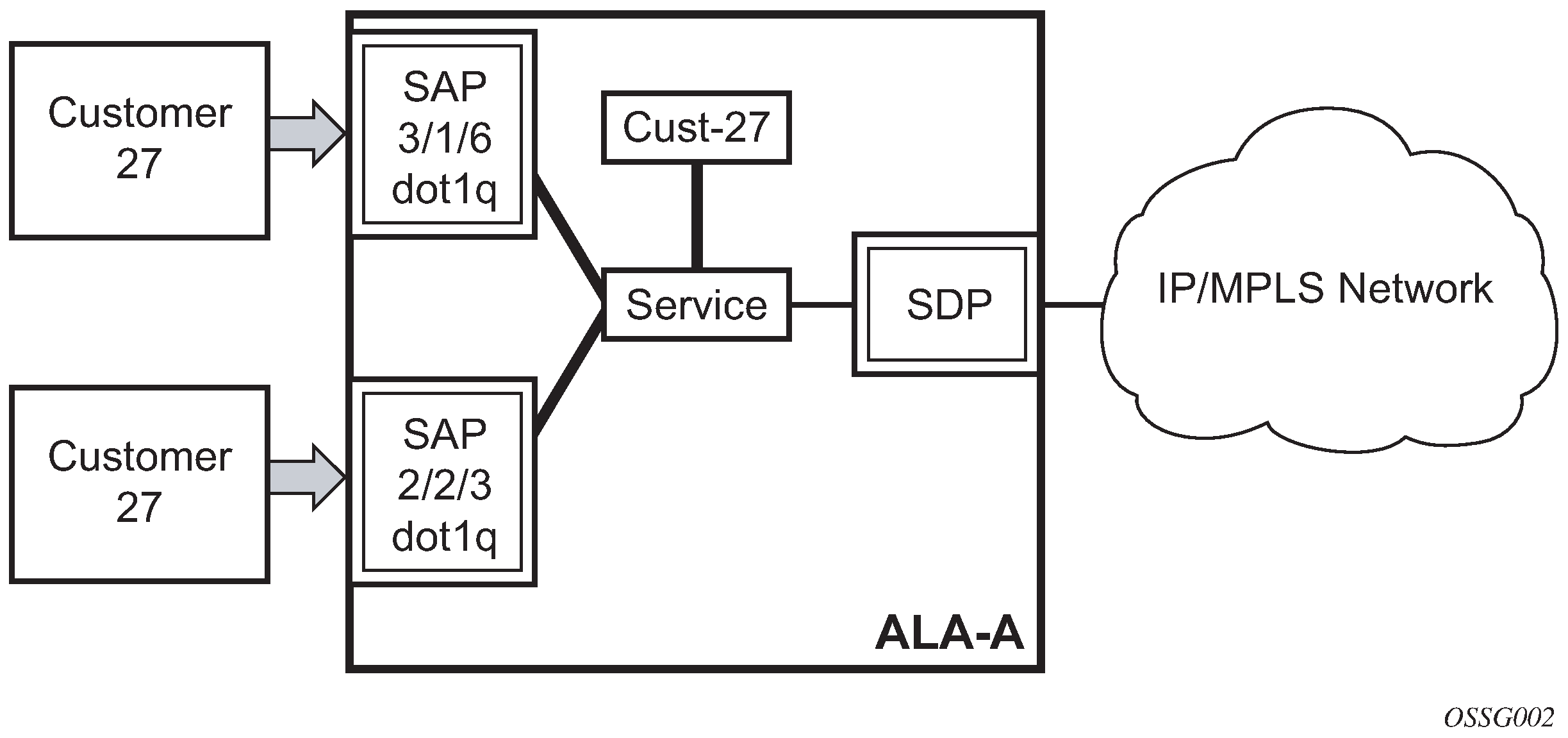
Each subscriber service type is configured with at least one service access point (SAP). A SAP identifies the customer interface point for a service on a router (for example Figure: 7750 SR/7950 XRS service access point (SAP)). The SAP configuration requires that slot, XMA or MDA, and port/channel information be specified. The slot, XMA or MDA, and port/channel parameters must be configured before provisioning a service (See the XMAs, Cards, MDAs, and Ports sections of the SR OS Interface Configuration Guide).
A SAP is a local entity to the router and is uniquely identified by:
the physical Ethernet port or SONET/SDH port or TDM channel
the encapsulation type
the encapsulation identifier (ID)
Depending on the encapsulation, a physical port or channel can have more than one SAP associated with it. SAPs can only be created on ports or channels designated as ‟access” in the physical port configuration. SAPs cannot be created on ports designated as core-facing ‟network” ports as these ports have a different set of features enabled in software.
A SAP can also be associated with a pseudowire port instead of an access port. Such SAPs are called pseudowire SAPs. This is only applicable to IES, VPRN, and Epipe services. Pseudowire ports represent pseudowires in enhanced subscriber management (ESM). For a description of pseudowire ports, see the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, and VSR Triple Play Service Delivery Architecture Guide.