The concept of a logical tunnel carrying many unique and individual services has been deployed in many networks on QinQ encapsulated access ports where the outer VLAN represents the common transports and the inner VLAN represents the specific service. Typically, the tunnel transparently passes frames from multiple services through some common network. Tunnel MEPs are logically configured on the Port or LAG and outer VLAN for access ports use QinQ Ethernet encapsulation. Service processing is done after the tunnel MEP. This means that any service-based MEPs are required to be a higher level than that of the tunnel MEP. Tunnel MEPs are only supported on LAGs that are configured with QinQ encapsulation and must specify the outer VLAN.
The Tunnel MEP must validate connectivity between the tunnel end points. As with all facility MEPs, this is a point-to-point relationship between the local MEP and one remote MEP. By default, the MEP configured at the tunnel level performs only alarming functions. Actionable functions such as AIS, SAP transition, and fault propagation requires the operator to enable these functions.
The tunnel MEP must first be configured to take action when the MEP enters a fault state, similar to all other facilities MEPs. For the individual services to share the fate of the tunnel, each service must accept the facility MEP state. This is service-dependent and depends on the needed goals. Services share the tunnel fate based on the lag-id and the outer VLAN.
Epipe services support the ais-enable configuration option on the SAP. Enabling this option generates AIS in the event the tunnel MEP has entered a fault state as a result of ETH-CC failure, similar to other facility MEPs. However, because the individual SAPs configured within the different services are not directly affected by the tunnel MEP, an additional configuration is necessary to perform local SAP transitions, in the case of VPLS, IES and VPRN services and OAM mapping functions for Epipe services.
The tunnel-fault service-level command configured on an Epipe allows SAP flags to be set and fault propagation and OAM mapping functions between technology. The operational state of the SAP remains up. The operator needs to determine if the AIS generation of fault propagation is the best approach in their specific network. It is possible to configure both ais-enable and tunnel-fault accept within the Epipe service. However, this may generate multiple ETH-CFM packets, or multiple actions as a result of a single failure.
The tunnel-fault accept service level option is also available under Epipe, VPLS and IES services hierarchy level within the CLI. This allows for a tunnel fault to share fate with these service SAPs. For the non-Epipe services, the SAP enters an operationally down state, and normal processing occurs as a result of the SAP transition. To generate any ETH-CC based fault propagation, suspend-cmm or use-int-stat-tlv, this requires service-based MEPs that are actively running CCM with a peer.
The tunnel-fault configuration options occur in two levels of the CLI hierarchy: service level and SAP level. Both of the levels within a service and within the SAP (whose underlying port and outer tag has a tunnel MEP) must be set to accept, in order to have the function enabled. By default the tunnel-fault is set to ignore at the service level and accept at the SAP level. This means that a single tunnel-fault accept at the service level enables fault operations for all SAPs in the service. The operator is free to enable and disable on specific SAPs by choosing the ignore option under the individual SAP. The combination of accept at the service level and ignore at the SAP level prevents that specific SAP from recognizing fault. AIS generation for Epipe services is not controlled by the tunnel-fault configuration options.
Specific to tunnel MEPs, reception of AIS on the tunnel MEP causes AIS to be cut through to all Epipe services that have the ais-enabled command configured under the SAP. During a fault condition, it is important that the AIS configuration under the tunnel MEP not be modified. This causes increased network element CPU processing requirements and in scaled environments transitioning this command during a heavily loaded fault condition, where highly scaled SAPs are linked to the fate of the tunnel MEP, may cause the system to spend more than normal processing time to be spent dealing with this artificially induced clear and fault situation. It is not expected that operators perform these types of tasks in production networks. Reception of AIS does not trigger a fault condition or AIS to be cut through when sub second CCM intervals have been configured on the Tunnel MEP.
Service-based MEPs may also be configured as normal for all services. They perform normal processing tasks, including service-based MEP with fault propagation.
As with all other facility MEPs, use only ETH-CFM functions to cause the Tunnel MEP to enter the fault state. Tunnel MEPs support sub second ccm-intervals on selected hardware. Tunnel MEPs must be configured with a direction of down. UP MEPs are not supported as part of the facility MEP concept.
LAG-based MEPs and LAG-based tunnel MEPs cannot be configured on the same LAG. Port-based MEPs may be configured on the LAG member ports of a tunnel MEP as long as they follow the requirements for port-based MEPs on LAG member ports. All those consideration are applicable here, including nesting and port-level control only without propagation.
Port-based MEPs and port-based tunnel MEPs cannot be configured on the same port.
LAG-based tunnel MEPs are supported in Multi-Chassis LAG (MC-LAG) configuration. However, sub second CCM enabled intervals should not be configured when the LAG-based tunnel MEP uses the transport of an MC-LAG. Only one second and above CCM intervals should be used. Not all platforms support sub second CCM enable tunnel MEPs.
Tunnel MEPs are meant to propagate fault from one segment to the other for Epipe services. Figure: Tunnel concepts and encapsulation shows how individual Epipes have SAPs connecting to a legacy network. A MEP is configured at the tunnel level and peers with a single remote peer MEP.
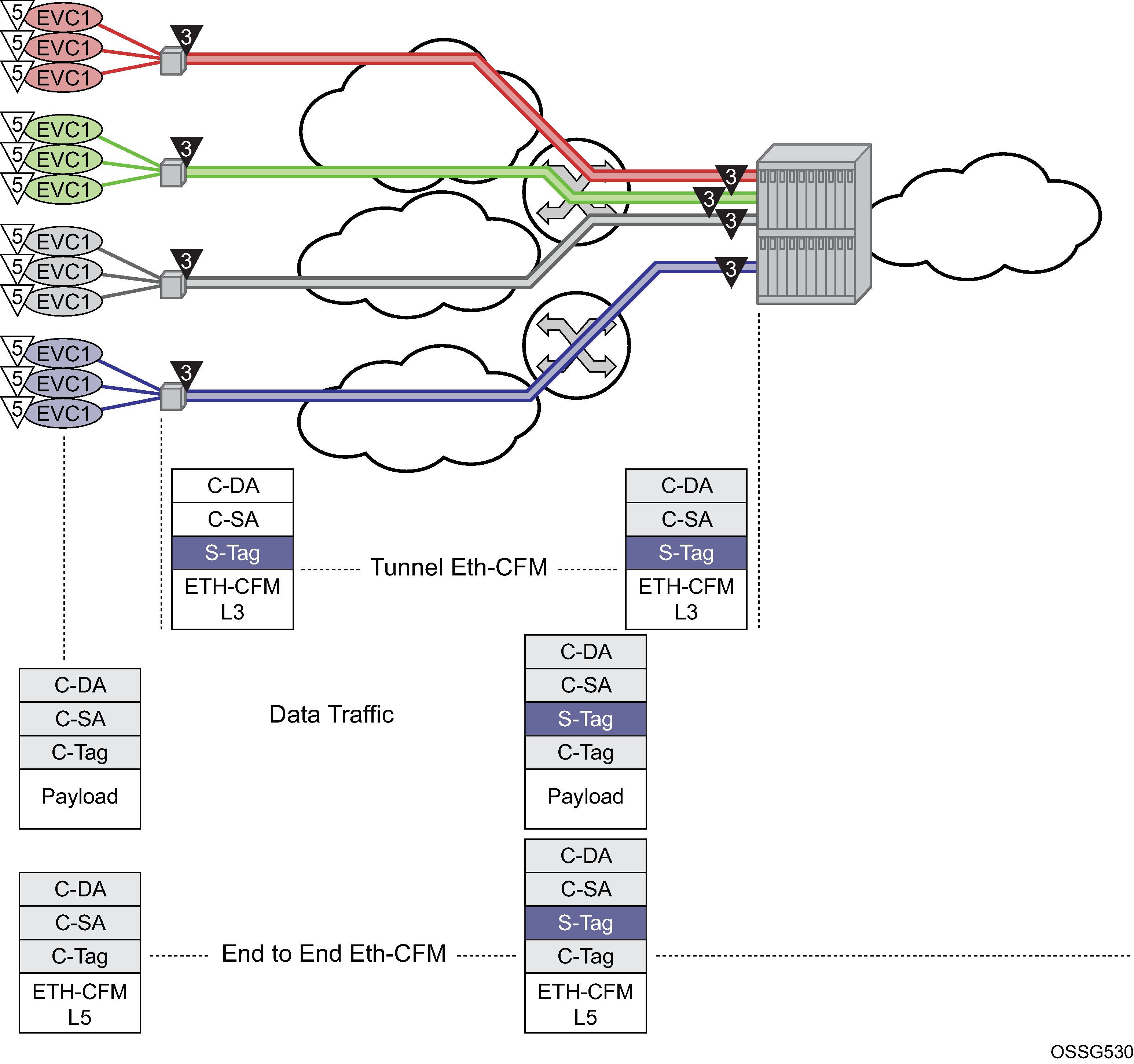
This is only one example of a tagged service. The principles of a tunnel MEP may be applied to other service as applicable. Remember that tunnel MEPs are only supported on LAGs that are configured with QinQ encapsulation and must have an outer VLAN.
Individual services can be monitored end-to-end by placing a MEP on the service endpoint at the CPE, denoted by the MEP at level 5 on the individual EVC (customer levels 5-7). The Network Interface Demarcation (NID) typically places a single tag, outer or only, on the customer traffic. This is cross connected to the correct connection in the access network and eventually arrive on the Ethernet Aggregation Switch. The connection between the legacy or access network and the aggregation switch must be either a LAG bundle or MC-LAG in order for tunnel MEPs to be configured.
Because there can be a large number of services transported by a single tunnel, the MEP executing at the tunnel-level reduces network overhead and simplifies the configuration.
A SAP is needed in order for the Tunnel MEP to extract the tunnel MEP ETH-CFM packets at the appropriate level. No SAP record is created by default. A service must already exist that includes a SAP in the form lag-id:vid.* or lag-id:vid.0 where the vid matches the outer VLAN in which the tunnel is to monitor. Because the ETH-CFM traffic arrives at the Ethernet aggregation node as a single outer tag with no inner tag, the operator may want to consider the ability to configure the lag-id:vid.0 to accept untagged only frames with the matching outer tag and no inner tag. The global command config>system->ethernet>new-qinq-untagged-sap is available to enable this functionality. By default both the vid.* and vid.0 accepts all packets that match the outer vid and any inner vid. If no SAP record exists for this VLAN, one must be created manually. Manually creating this SAP requires a service context. Nokia recommends that an Epipe service be configured with this single SAP, preventing any flooding of packets. It is possible to use a VPLS instance and combine many tunnel SAP records into a single service instance. However, configuration errors may result in leakage because of the multipoint nature of a VPLS service. Regardless of the service type chosen, it should be in a shutdown state. Also, normal ETH-CFM rules apply. ETH-CFM packets arriving on the SAP passes all ETH-CFM packets at and below the tunnel MEP to the ETH-CFM application for processing.
The goal of a Tunnel MEP is to validate an attachment circuit and relate the state to services that share the same LAG and outer VLAN to other services across the network. Tunnel MEPs are not intended for propagating fault between two endpoints that share the same LAG and outer VLAN. For this reason, locally switched circuits that share the same LAG and the same outer tag must not use the ais-enable function under those SAPs. As an example, lag-1 may have two SAPs associated with it: lag-1:1.1 and lag-1:1.2. These two SAP represent two different endpoints on the same LAG using the same outer VLAN. In this case, if the ais-enable is configured under both SAPs, AIS functionality does not work properly. Normal fault propagation could be used in this case instead. Because the tunnel MEP is validating the common physical path and these two MEPs share the common physical path, there is no reason to propagate fault. Service-based MEPs could be configured on the endpoints to validate the connectivity between the two endpoints when this type of model is deployed. However, two SAPs that are connected to different LAGs is a supported configuration. An example of this would be lag-1:1.1 and lag-2:1.1.
Sub second Tunnel MEPs are monitored for every three seconds to ensure that they are not continuously bouncing and consuming an unfair allocation of ETH-CFM resources. A sub second MEP is only allowed three operational status changes in a three second window before holding the state for the remaining time in that window. Messages are paced from Tunnel MEPs. Fault propagation depends on factors such as how busy the node is, or how scaled the node configuration is.
Five percent of the operational/negotiated port speed not physical speed is available for Tunnel MEP control traffic. When applying this to the LAG-based Tunnel MEPs the five percent is derived from the lowest speed of a single member port in the bundle. If this bandwidth percentage required for ETH-CFM is exceeded the ETH-CFM packets are not able to be sent and failures occur. As an example, a physical port of 1Gb/s that has negotiated an operational speed of 100 Mb/s with a peer is allowed to send up to a maximum of 5 Mb/s of Tunnel MEP control traffic.
Figure: Tunnel MEP example shows how fate can be shared between the Tunnel MEP and the services configured on the same LAG and outer VLAN.
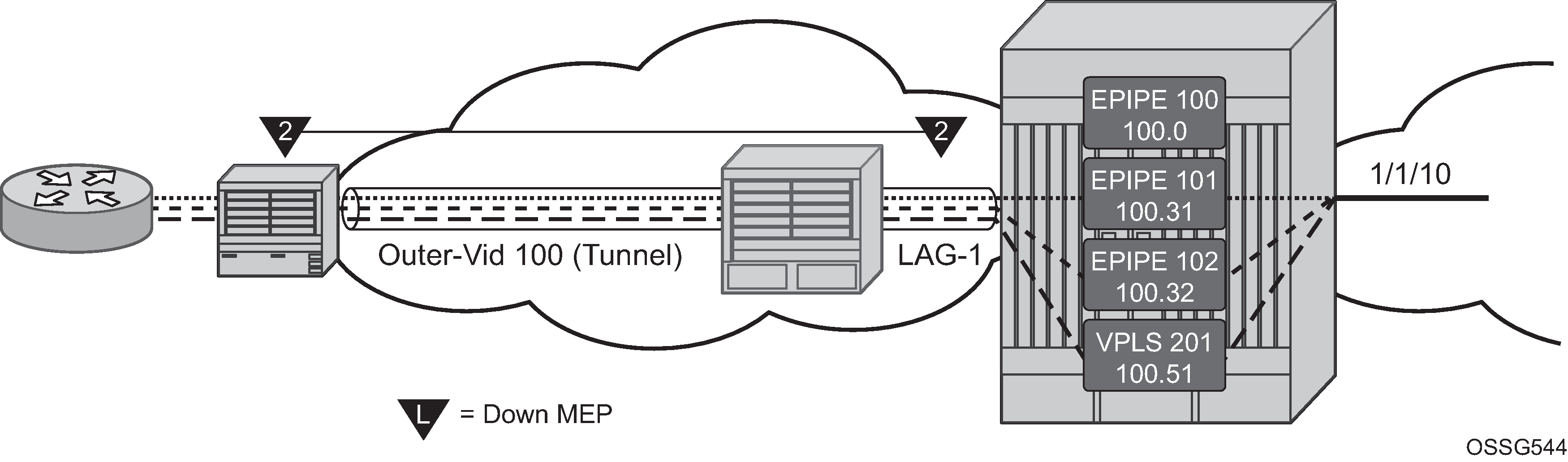
In this example, a single Tunnel, LAG-1 outer VLAN 100, carries three services. Epipe 101, Epipe 102 and VPLS 201 are the service extraction points on the aggregation node. Epipe 100 is the extraction point for the Tunnel MEP eth-cfm traffic. This is a single SAP Epipe that is operationally shutdown. One common configuration error when using Tunnel MEPs is the lack extraction on the aggregation node, causing unidirectional failures. The aggregation node is sending eth-cfm traffic to the NID, but is not extracting the eth-cfm traffic that the NID is sending.
Epipe 101 is configured to accept the tunnel MEP fate and generate AIS.
Epipe 102 is configured to accept the tunnel MEP state and apply fault propagation rules. If the network-side mate were an SDP binding, then the applicable setting of the LDP status bits are in the header. Because this example uses an Ethernet SAP as the mate, and only tunnel fault-accept is configured with no ais-enable, only the SAP flag is set to indicate an error.
VPLS 201 also shares the fate of the tunnel MEP. The tunnel-fault accept transitions the SAP to operationally down. Any configured event that occurs because of a SAP down for the VPLS also occur.
Only the configuration for the aggregation node is shown below. The NID configuration is not required to show how this function works.
Aggregation node
config>eth-cfm# info
----------------------------------------------
domain 2 format none level 2
association 1 format icc-based name "FacilityTun01"
ccm-interval 1
remote-mepid 101
exit
exit
----------------------------------------------
config>lag# info
----------------------------------------------
mode access
encap-type qinq
eth-cfm
mep 100 domain 2 association 1 vlan 100
description "Tunnel Facility MEP - Do NOT Delete"
ais-enable
client-meg-level 5
exit
facility-fault
ccm-enable
low-priority-defect allDef
no shutdown
exit
exit
port 1/1/2
no shutdown
----------------------------------------------
config>service# info
----------------------------------------------
customer 1 create
description "Default customer"
exit
epipe 100 customer 1 create
shutdown
description "Tunnel Extraction Service"
sap lag-1:100.0 create
exit
exit
epipe 101 customer 1 create
description "Customer Service 100.31"
sap 1/1/10:100.31 create
exit
sap lag-1:100.31 create
eth-cfm
ais-enable
exit
exit
no shutdown
exit
epipe 102 customer 1 create
description "Customer Service 100.32"
eth-cfm
tunnel-fault accept
exit
sap 1/1/10:100.32 create
exit
sap lag-1:100.32 create
exit
no shutdown
exit
vpls 201 customer 1 create
description "Customer Service 100.51"
stp
shutdown
exit
eth-cfm
tunnel-fault accept
exit
sap 1/1/10:100.51 create
exit
sap lag-1:100.51 create
exit
no shutdown
exit
----------------------------------------------
# show eth-cfm mep 100 domain 2 association 1
===============================================================================
Eth-Cfm MEP Configuration Information
===============================================================================
Md-index : 2 Direction : Down
Ma-index : 1 Admin : Enabled
MepId : 100 CCM-Enable : Enabled
Port : lag-1 VLAN : 100
Description : Tunnel Facility MEP - Do NOT Delete
FngState : fngReset ControlMep : False
LowestDefectPri : allDef HighestDefect : none
Defect Flags : None
Mac Address : 90:f3:ff:00:01:41 ControlMep : False
CcmLtmPriority : 7
CcmTx : 3958 CcmSequenceErr : 0
Fault Propagation : disabled FacilityFault : Notify
MA-CcmInterval : 1 MA-CcmHoldTime : 0ms
Eth-1Dm Threshold : 3(sec) MD-Level : 2
Eth-Ais: : Enabled Eth-Ais Rx Ais: : No
Eth-Ais Tx Priorit*: 7 Eth-Ais Rx Interv*: 1
Eth-Ais Tx Interva*: 1 Eth-Ais Tx Counte*: 175
Eth-Ais Tx Levels : 5
Eth-Tst: : Disabled
Redundancy:
MC-LAG State : n/a
CcmLastFailure Frame:
None
XconCcmFailure Frame:
None
===============================================================================
# show eth-cfm cfm-stack-table facility all-tunnel-meps
===============================================================================
CFM Stack Table Defect Legend:
R = Rdi, M = MacStatus, C = RemoteCCM, E = ErrorCCM, X = XconCCM, A = AisRx
===============================================================================
CFM Facility LAG Stack Table
===============================================================================
Lag Tunnel Lvl Dir Md-index Ma-index MepId Mac-address Defect
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
lag-1 100 2 Down 2 1 100 90:f3:ff:00:01:41 ------
===============================================================================
# show service sap-using eth-cfm facility
===============================================================================
Service ETH-CFM Facility Information
===============================================================================
SapId SvcId SAP AIS SAP Tunnel SVC Tunnel
Fault Fault
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
lag-1:100.0 100 Disabled Accept Ignore
lag-1:100.31 101 Enabled Accept Ignore
lag-1:100.32 102 Disabled Accept Accept
lag-1:100.51 201 Disabled Accept Accept
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
No. of Facility SAPs: 4
===============================================================================
When the tunnel MEP enters a fault state:
-
Epipe 101 starts to generate AIS out the mate sap.
-
Epipe 102 SAP flag is set.
-
VPLS 201 SAP goes down.
Output from one of the nodes is included below. Because both react in the same manner output from both nodes is not required.
Aggregation node
# show eth-cfm cfm-stack-table facility all-tunnel-meps
===============================================================================
CFM Stack Table Defect Legend:
R = Rdi, M = MacStatus, C = RemoteCCM, E = ErrorCCM, X = XconCCM, A = AisRx
===============================================================================
CFM Facility LAG Stack Table
===============================================================================
Lag Tunnel Lvl Dir Md-index Ma-index MepId Mac-address Defect
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
lag-1 100 2 Down 2 1 100 90:f3:ff:00:01:41 --C---
===============================================================================
# show service sap-using eth-cfm facility tunnel 100
===============================================================================
Service ETH-CFM Facility Information
===============================================================================
SapId SvcId SAP AIS SAP Tunnel SVC Tunnel
Fault Fault
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
lag-1:100.0 100 Disabled Accept Ignore
lag-1:100.31 101 Enabled Accept Ignore
lag-1:100.32 102 Disabled Accept Accept
lag-1:100.51 201 Disabled Accept Accept
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
No. of Facility SAPs: 4
===============================================================================
# show eth-cfm mep 100 domain 2 association 1
===============================================================================
Eth-Cfm MEP Configuration Information
===============================================================================
Md-index : 2 Direction : Down
Ma-index : 1 Admin : Enabled
MepId : 100 CCM-Enable : Enabled
Port : lag-1 VLAN : 100
Description : Tunnel Facility MEP - Do NOT Delete
FngState : fngDefectReported ControlMep : False
LowestDefectPri : allDef HighestDefect : defRemoteCCM
Defect Flags : bDefRemoteCCM
Mac Address : 90:f3:ff:00:01:41 ControlMep : False
CcmLtmPriority : 7
CcmTx : 4211 CcmSequenceErr : 0
Fault Propagation : disabled FacilityFault : Notify
MA-CcmInterval : 1 MA-CcmHoldTime : 0ms
Eth-1Dm Threshold : 3(sec) MD-Level : 2
Eth-Ais: : Enabled Eth-Ais Rx Ais: : No
Eth-Ais Tx Priorit*: 7 Eth-Ais Rx Interv*: 1
Eth-Ais Tx Interva*: 1 Eth-Ais Tx Counte*: 215
Eth-Ais Tx Levels : 5
Eth-Tst: : Disabled
Redundancy:
MC-LAG State : n/a
CcmLastFailure Frame:
None
XconCcmFailure Frame:
None
===============================================================================
show service id 101 base
===============================================================================
Service Basic Information
===============================================================================
Service Id : 101 Vpn Id : 0
Service Type : Epipe
Name : (Not Specified)
Description : Customer Service 100.31
Customer Id : 1
Last Status Change: 02/04/2010 15:53:12
Last Mgmt Change : 02/04/2010 16:31:00
Admin State : Up Oper State : Up
MTU : 1514
Vc Switching : False
SAP Count : 2 SDP Bind Count : 0
Per Svc Hashing : Disabled
Force QTag Fwd : Disabled
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Service Access & Destination Points
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Identifier Type AdmMTU OprMTU Adm Opr
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sap:1/1/10:100.31 qinq 1522 1522 Up Up
sap:lag-1:100.31 qinq 1522 1522 Up Up
===============================================================================
# show service id 102 base
===============================================================================
Service Basic Information
===============================================================================
Service Id : 102 Vpn Id : 0
Service Type : Epipe
Name : (Not Specified)
Description : Customer Service 100.32
Customer Id : 1
Last Status Change: 02/04/2010 15:45:07
Last Mgmt Change : 02/04/2010 16:30:43
Admin State : Up Oper State : Up
MTU : 1514
Vc Switching : False
SAP Count : 2 SDP Bind Count : 0
Per Svc Hashing : Disabled
Force QTag Fwd : Disabled
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Service Access & Destination Points
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Identifier Type AdmMTU OprMTU Adm Opr
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sap:1/1/10:100.32 qinq 1522 1522 Up Up
sap:lag-1:100.32 qinq 1522 1522 Up Up
===============================================================================
# show service id 102 sap lag-1:100.32
===============================================================================
Service Access Points(SAP)
===============================================================================
Service Id : 102
SAP : lag-1:100.32 Encap : qinq
QinQ Dot1p : Default
Description : (Not Specified)
Admin State : Up Oper State : Up
Flags : OamTunnelMEPFault
Multi Svc Site : None
Last Status Change : 02/04/2010 15:45:07
Last Mgmt Change : 02/04/2010 15:44:26
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ETH-CFM SAP specifics
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tunnel Faults : accept AIS : Disabled
MC Prop-Hold-Timer : n/a
===============================================================================
*A:PE-6# show service id 1 base
===============================================================================
Service Basic Information
===============================================================================
Service Id : 1 Vpn Id : 0
Service Type : VPLS
Name : 1
Description : (Not Specified)
Customer Id : 1 Creation Origin : manual
Last Status Change: 05/08/2018 09:40:32
Last Mgmt Change : 05/08/2018 09:40:24
Etree Mode : Disabled
Admin State : Up Oper State : Up
MTU : 1514
SAP Count : 1 SDP Bind Count : 1
Snd Flush on Fail : Disabled Host Conn Verify : Disabled
SHCV pol IPv4 : None
Propagate MacFlush: Disabled Per Svc Hashing : Disabled
Allow IP Intf Bind: Disabled
Fwd-IPv4-Mcast-To*: Disabled Fwd-IPv6-Mcast-To*: Disabled
Mcast IPv6 scope : mac-based
Def. Gateway IP : None
Def. Gateway MAC : None
Temp Flood Time : Disabled Temp Flood : Inactive
Temp Flood Chg Cnt: 0
SPI load-balance : Disabled
TEID load-balance : Disabled
Src Tep IP : N/A
Vxlan ECMP : Disabled
VSD Domain : <none>
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Service Access & Destination Points
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Identifier Type AdmMTU OprMTU Adm Opr
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sap:1/1/c1/1:1 q-tag 9000 9000 Up Up
sdp:65:1 S(192.0.2.5) Spok 0 8974 Up Down
===============================================================================
* indicates that the corresponding row element may have been truncated.