2. ISA and ESA Hardware
2.1. In This Section
This section provides an overview of Nokia’s implementation of the ISA and ESA hardware.
| Note: Cards must be configured using the commands described in the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR Interface Configuration Guide. |
2.2. MS-ISA2 Overview
The MS-ISA2 (or ISA2-MS in CLI) is a second generation Integrated Services Adapter for multiservice processing, as a resource module within the router system providing packet buffering and packet processing.
The MS-ISA2 fits in an MDA/ISA slot on an IOM4-e and has no external ports, so all communication passes through the Input/Output Module (IOM), making use of the network processor complex on the host IOM for queuing and filtering functions like other MDAs and ISAs.
The actual ingress and egress throughput will vary depending on the buffering and processing demands of a specific application, but the MS-ISA2 hardware can support 40 Gb/s of throughput processing. The processed rate (up to 40 Gb/s) is the sum of the upstream and downstream rates (for example, 10 Gb/s up and 30 Gb/s down, or 20 Gb/s up and 20 Gb/s down).
2.3. MS-ISM Overview
The Multiservice Integrated Services Module (MS-ISM) card contains two ISA2 processing modules providing increased packet processing throughput and scale compared to the MS-ISA platform. Each ISA2 processing module supports a 40G datapath for packet processing; as with ISA1 the actual throughput varies by function. The processed rate (up to 40 Gb/s) is the sum of the upstream and downstream rates (for example, 10 Gb/s up and 30 Gb/s down, or 20 Gb/s up and 20 Gb/s down).
The IOM base card is an imm-2pac-fp3 with two embedded positions for ISA2s. Hot swap or field replacement of the ISA2s within an MS-ISM assembly is not supported. IMM cards offering 10x10GE media plus one ISA2, or 1x100GE media plus one ISA2.
Figure 1 shows the ISA2 processing modules in the MG-ISM card.
Figure 1: MS-ISM with ISA2s
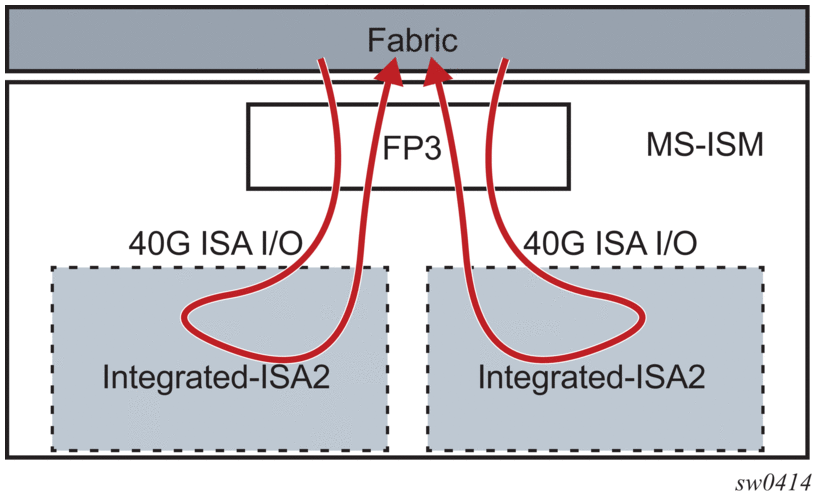
The MS-ISA2 remains as a common base hardware assembly to be used as a generic CPU processing platform for multiple applications. The functions supported on the MS-ISA2 and MS-ISM include the following software based capabilities:
- Application Assurance (AA)
- Tunnel (IPsec, GRE)
- Broadband (NAT, LNS)
- Video (FCC, RET)
2.4. ESA Overview
An Extended Services Appliance (ESA) is a server that attaches to a host 7750 SR over standard SR system interface ports, and which has one to four Virtual Machine (VM) instances to perform multiservice processing. The ESA provides packet buffering and processing and is logically part of the router system. The ESA 100G includes a 24-core Intel Cascade Lake 6252 processor and 192 GB of memory. The ESA 400G includes two 32-core Intel Ice Lake 6338N processors and 512 GB of memory.
The ESA processing rate is the sum of the upstream and downstream rates (for example, 80 Gb/s up and 20 Gb/s down, or 50 Gb/s up and 50 Gb/s down).
The ESA 100G hardware can support up to 100 Gb/s of throughput processing, and the ESA 400G up to 400 Gb/s of processing. However, the maximum ESA ingress and egress throughput varies depending on the buffering and processing demands of a specific application.
Figure 2 shows an ESA connected to a 7750 SR.
Figure 2: ESA Connection to 7750 SR
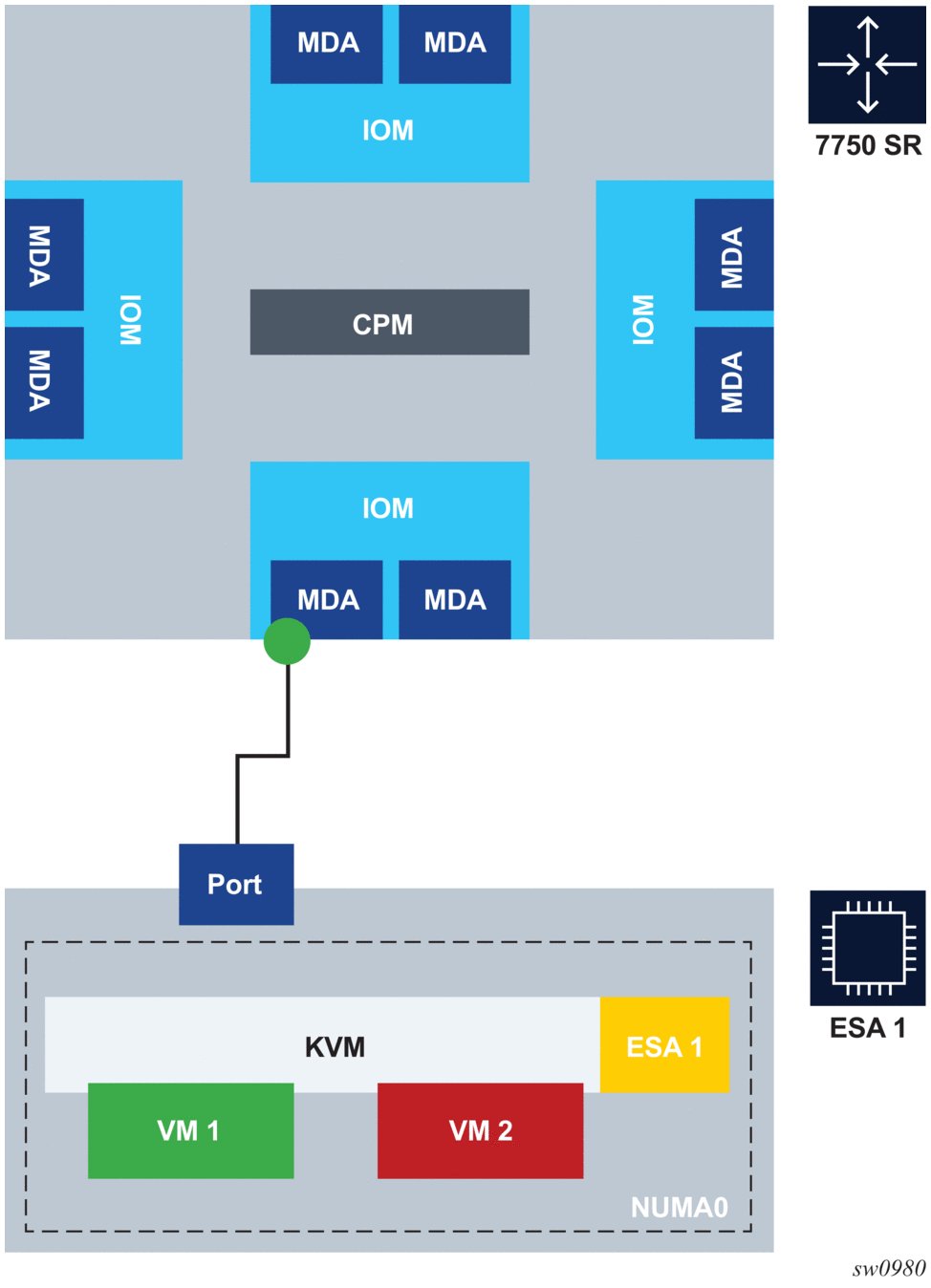
A direct local fiber connection must be used to connect an ESA port to a 7750 SR port. As with other MDAs and ISAs, all communication passes through the 7750 SR Input/Output Module (IOM), making use of the network processor complex on the host IOM for queuing and filtering functions. The ESA 100G includes a Mellanox Connect X5 2-port 100 Gb/s NIC with QSFP28 optics connectors. Either one or both of the ESA NIC ports can be used to connect to the 7750 SR within the maximum 100 Gb/s throughput per NIC.
The ESA 400G includes two Mellanox Connect X6 2-port 100 Gb/s NIC with QSFP28 optics connectors. Each NIC has a maximum 200 Gb/s throughput per NIC, and any of the four ESA NIC ports can be used to connect to the 7750 SR port.
The following SR to ESA port speeds are supported:
- 100GE — using QSFP28 optics in both the SR and ESA
- 40GE — using QSFP+ optics in both the SR and ESA
- 25GE — using a QSFP28 - SFP28/SFP+ Adapter and SFP28 optics in both SR and ESA
- 10GE — using a QSFP28 - SFP28/SFP+ Adapter and SFP+ optics in both SR and ESA
Ports for an ESA may be from same or different IOMs, XMAs, or MDAs. Any combination of supported port speeds may be used on an ESA. If at least one host-port between the SR and the ESA is up, the ESA instance will stay up.
An ESA-VM must be associated with one specific 7750 SR port. One physical 7750 SR port can be used by multiple VMs within an ESA. ESA-VMs may be configured as different types or the same type.
As each ESA-VM may only be associated to one 7750 SR port, LAG cannot be used between ports to an ESA. ESA-to-SR link resilience is handled by provisioning more VM instances than the processing requires (using the ISA group N+1 redundancy model). Functional sparing capacity is also handled by provisioning more VM instances than required.
Each ESA is managed by one 7750 SR. The ESA software (hypervisors.tim file, located on the active CPM from the 7750 SR host) can only be instantiated by a 7750 SR and cannot be instantiated in any other virtualized environment. Creation, configuration, deletion, resource allocation, and upgrade of a ESA-VM are all controlled by the 7750 SR CPM.
SR system LLDP must be enabled for ESA use, as LLDP is used to verify connectivity between the configured SR ESA host-ports and the matching configured ESA port for an ESA-VM. To set up an ESA in a 7750 SR system, the following actions must be completed in any order:
- install the ESA hardware in a rack, then apply power to the ESA hardware
- connect the ESA hardware to a compatible 7750 SR chassis, IOM, or MDA using the appropriate optics
- from the 7750 SR, configure ESA host and ESA-VM ports; see Configuring an ESA with CLI
For more information about the first two items in this list refer to the 7750 SR ESA 100G Chassis Installation Guide.
| Note: After the ESA host-port is assigned, the port defaults are automatically modified. The new port defaults cannot be changed by the operator until the port is unassigned as an ESA host-port. |
The ESA hardware is then booted by the 7750 SR CPM and available resources are discovered by the 7750 SR. ESA-VMs are configured as a desired type and size (number of cores and amount of memory). ESA-VM types include services that also run on ISAs, thereby providing a virtualized ISA function as an ESA-VM within the SR system and as part of an ISA group. An ISA group can only contain physical ISAs or ESA-VMs. Traffic for an ESA-VM enters the 7750 SR and is forwarded to the ESA-VM in a manner identical to that of a traditional ISA.
Multiple ESAs may be configured per IOM and per system as needed for scale.
2.5. Application Assurance Hardware Features
2.5.1. AA System Support
The Application Assurance Integrated Services Adapter (AA ISA) is a resource adapter, which means that there are no external interface ports on the AA ISA itself. Similarly, ESAs only do processing functions for traffic on the ESA interconnect ports to the SR system. Traffic on the SR system is forwarded to ISAs or ESA from any other IOMs on a system in which the AA ISA or ESA is installed, with a divert mechanism used to switch traffic internally to the AA ISA or ESA-VM.
Refer to the SR OS 22.x.Rx Software Release Notes for information about the ESA platform support.
Table 4 describes Application Assurance support on the 7750 SR and 7450 ESS.
Table 4: AA System Support
System | AA on MS-ISM | AA on MS-ISA2 |
7750 SR-12 | Yes | Yes |
7750 SR-12e | Yes | Yes |
7750 SR-7 | Yes | Yes |
7750 SRe-1 | No | Yes |
7750 SRe-2 | No | Yes |
7750 SRe-3 | No | Yes |
7450 ESS-12 | Yes | Yes |
7450 ESS-7 | Yes | Yes |
2.5.2. Host IOM Support for AA on ISAs
The AA MS-ISA2 is supported on IOM3-XP and on the IOM4-e. The MS-ISM versions contain one or two ISA2s embedded on a IMM card.
Each IOM can support a maximum of two AA ISA2 modules. To maximize AA ISA redundancy, deployment of AA ISAs on separate host IOMs is recommended as it provides IOM resilience. Traffic from any supported IOM (for example, IOM3-XP, a fixed port IOM (IMM)) can be diverted to an AA ISA host IOM.
The MS-ISA2 is field replaceable and supports hot insertion and removal. An SR system can support up to 15 active ISA2s for AA, each providing up to 40 Gb/s processing and 600 Gb/s total per system.
AA ISA software upgrades are part of the ISSU functionality. Upgrades to AA ISA software, for example to activate new protocol signatures, do not impact the second MDA slot for the IOM carrying the AA ISA, nor do upgrades impact the router itself (for example a new AA ISA software image can be downloaded without a need to upgrade other software images).
2.5.3. Host IOM Support for AA on ESAs
ESA port connectivity is supported on most FP3-based IOMs and all FP4-based cards. For a list of supported platforms or cards, contact your Nokia representative.
An SR system can support up to 15 active and one standby ESA-VMs for AA.
AA ESA-VM software upgrades are part of the ISSU functionality. Upgrades to AA software, for example to activate new protocol signatures, do not impact other ESA-VMs on the same ESA or on other traffic on the same IOM, nor do upgrades impact the router itself (for example, a new AA software image can be downloaded to an ESA-VM without a need to upgrade other software images).
The ESA version must match the build release version of the host IOM.