Auto-provisioning is used to provision a node using an external DHCP server and file server. It is used to obtain a configuration file and an image file from an external server using an in-band mechanism. Auto-provisioning is not compatible with an out-of-band management port.
Before using auto-provisioning, the SR OS must be booted up and running the application image. In addition, it needs to have some minimum configuration before the auto-provision script is executed by the operator.
After the auto-provision application is triggered using a tools command, SR OS checks all operationally up ports without IP addresses and send DHCP discovery to these interfaces. The DHCP server needs to be configured with Option 67 and the user must provide the SR OS with the URL of a file server and the corresponding directory for the image.
Figure: Example of a network with no DHCP relay to Figure: Example of a network with multiple subnets describe scenarios in which auto-provisioning are used.
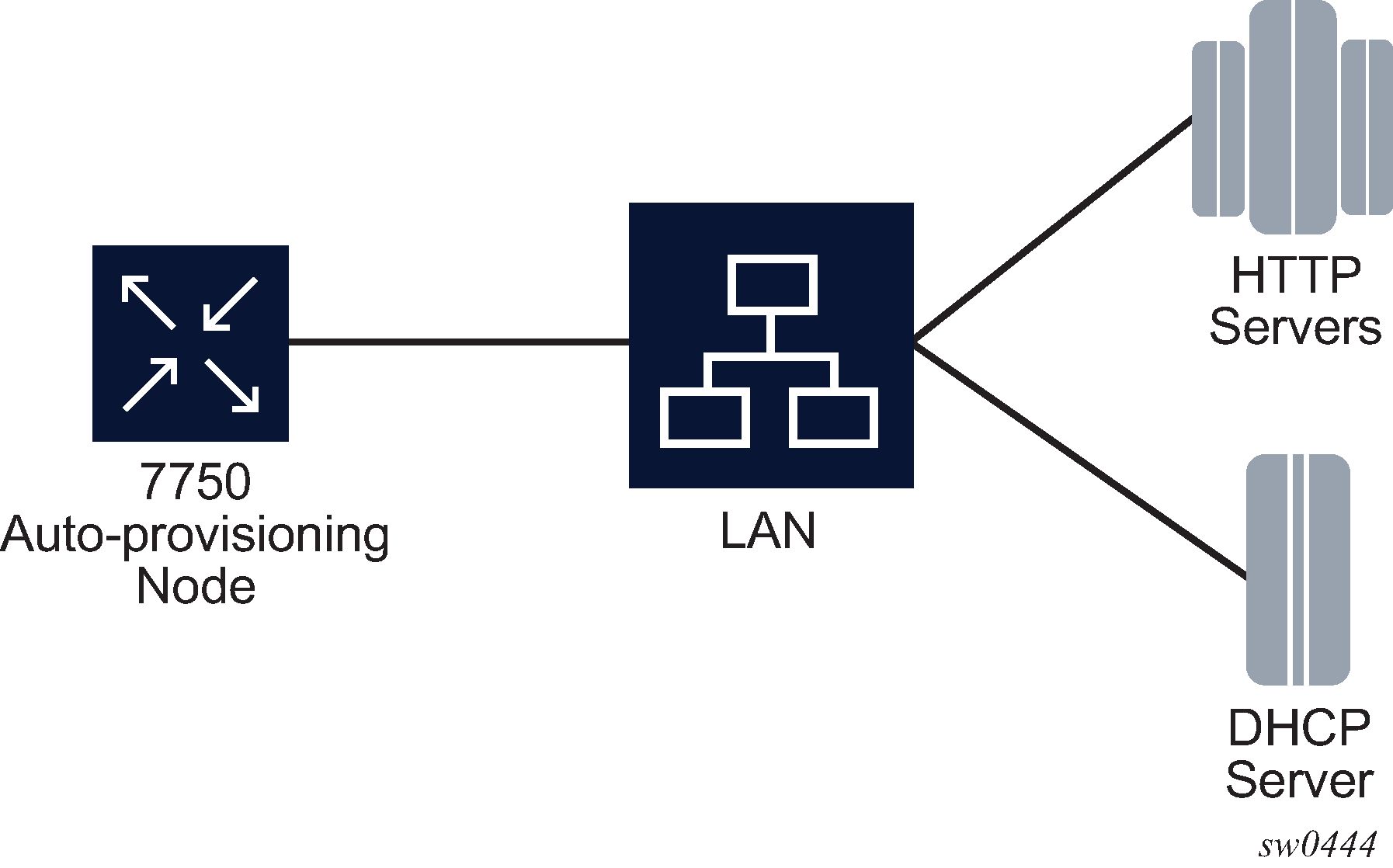
In Figure: Example of a network with no DHCP relay, there is no DHCP relay and all IP addresses are assigned from a single pool.
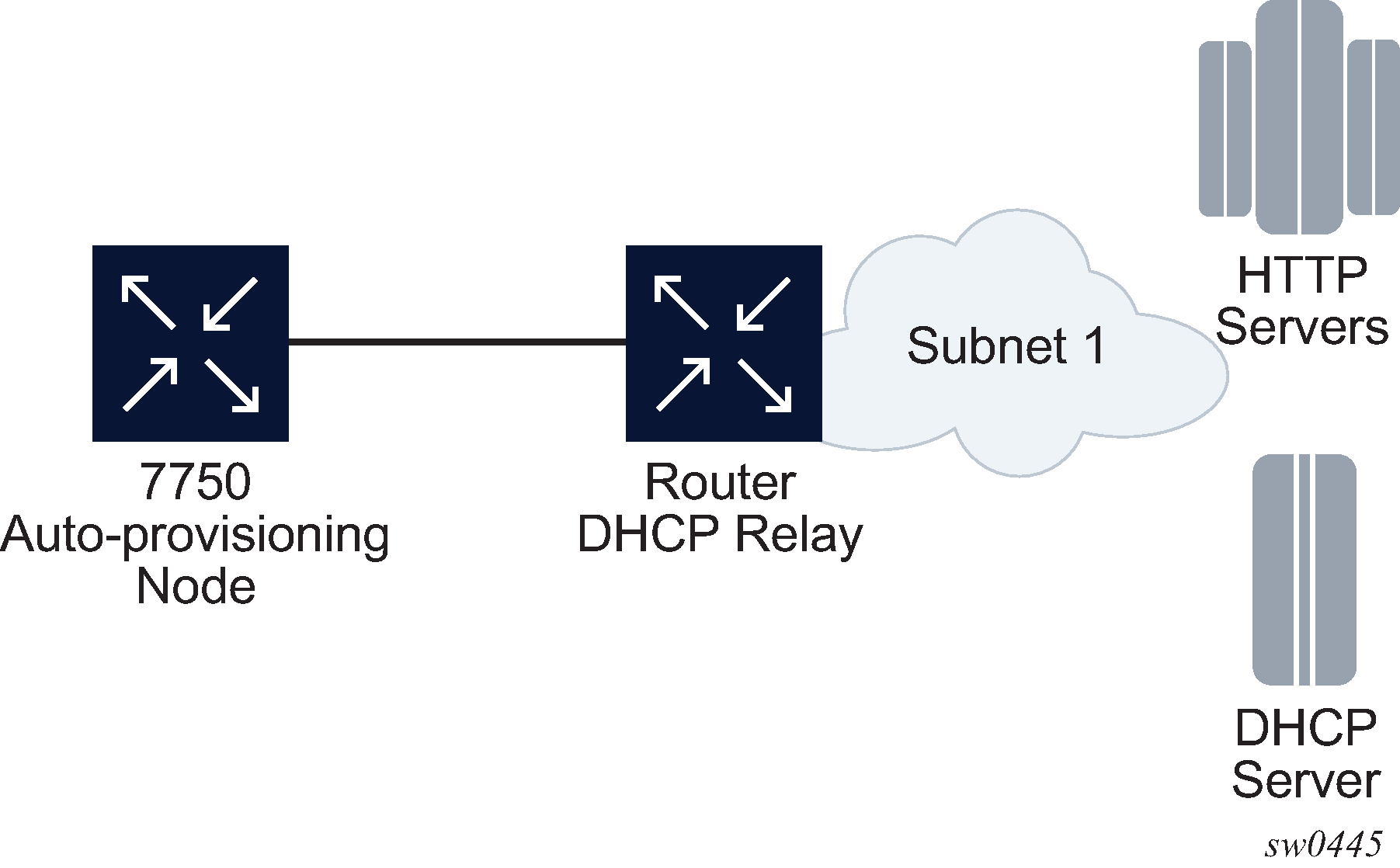
In Figure: Example of a network with a DHCP relay, there is a DHCP relay which injects the Option 82 as a gateway address. The DHCP server is assigned the IP address from the pool dictated by the gateway address option 82. The DHCP server and HTTP server are in the same subnet. The DHCP offer has option 3 "router" which is used for a default gateway creation on the 7750 SR.
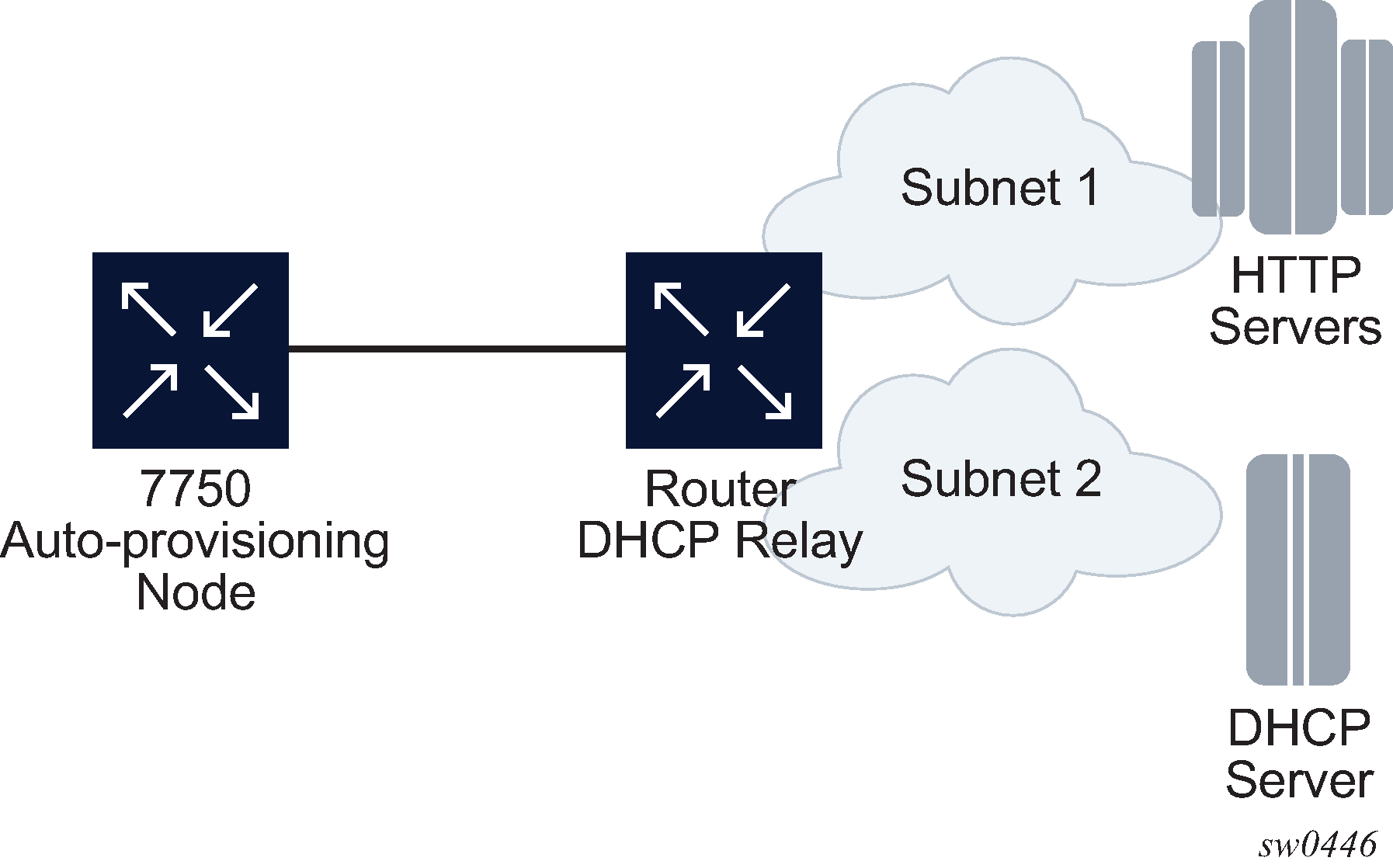
In Figure: Example of a network with multiple subnets, all components are in different subnets. The DHCP relay adds Option 82 to the DHCP request as the gateway address which is used for pool selection. The DHCP server must add option 3 configured with the gateway address of the HTTP server.