An AR-L is configured as shown in the following example.
A:PE-3>config>service>vpls# info
----------------------------------------------
vxlan instance 1 vni 4000 create
assisted-replication leaf replicator-activation-time 30
bgp
exit
bgp-evpn
evi 4000
vxlan bgp 1 vxlan-instance 1
no shutdown
exit
mpls
shutdown
exit
exit
stp
shutdown
exit
sap 1/1/1:4000 create
no shutdown
exit
no shutdown
----------------------------------------------
In this example configuration, the BGP advertises a new inclusive multicast route with a tunnel-type = IR, type (T) = AR-L and tunnel-id = originating-ip = next-hop = IR-IP (IP address terminating VXLAN normally, either system-ip or vxlan-src-vtep address).
The AR-L builds a single flooding list per service but controlled by the BM and U flags. These flags are displayed in the following show service id vxlan command example output.
A:PE-3# show service id 4000 vxlan
===============================================================================
Vxlan Src Vtep IP: N/A
===============================================================================
VPLS VXLAN, Ingress VXLAN Network Id: 4000
Creation Origin: manual
Assisted-Replication: leaf Replicator-Activation-Time: 30
RestProtSrcMacAct: none
===============================================================================
VPLS VXLAN service Network Specifics
===============================================================================
Ing Net QoS Policy : none Vxlan VNI Id : 4000
Ingress FP QGrp : (none) Ing FP QGrp Inst : (none)
===============================================================================
Egress VTEP, VNI
===============================================================================
VTEP Address Egress VNI Num. MACs Mcast Oper L2
State PBR
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
10.2.2.2 4000 0 BM Up No
10.4.4.4 4000 0 - Up No
192.0.2.2 4000 0 U Up No
192.0.2.5 4000 0 U Up No
192.0.2.6 4000 0 U Up No
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of Egress VTEP, VNI : 5
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
===============================================================================
The AR-L creates the following VXLAN destinations when it receives and selects a Replicator-AR route or the Regular-IR routes:
A VXLAN destination to each remote PE that sent an IR route. These bindings have the U flag set.
A VXLAN destination to the selected AR-R. These bindings have only the BM flag set; the U flag is not set.
The non-selected AR-Rs create a binding with flag ‟-” (in the CPM) that is displayed by the show service id vxlan command. Although the VXLAN destinations to non-selected AR-Rs do not carry any traffic, the destinations count against the total limit and must be considered when accounting for consumed VXLAN destinations in the router.
The BM traffic is only sent to the selected AR-R, whereas the U (unknown unicast) traffic is sent to all the destinations with the U flag.
The AR-L performs per-service load-balancing of the BM traffic when two or more AR-Rs exist in the same service. The AR Leaf creates a list of candidate PEs for each AR-R (ordered by IP and VNI; candidate 0 being the lowest IP and VNI). The replicator is selected out of a modulo function of the service-id and the number of replicators, as shown in the following example output.
A:PE-3# show service id 4000 vxlan assisted-replication replicator
===============================================================================
Vxlan AR Replicator Candidates
===============================================================================
VTEP Address Egress VNI In Use In Candidate List Pending Time
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
10.2.2.2 4000 yes yes 0
10.4.4.4 4000 no yes 0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of entries : 2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
===============================================================================
A change in the number of Replicator-AR routes (for example, if a route is withdrawn or a new route appears) affects the result of the hashing, which may cause a different AR-R to be selected.
The following list summarizes other aspects of the AR-L behavior:
When a Leaf receives a BM packet on an AC, it sends the packet to its flood list that includes access SAP or SDP bindings and VXLAN destinations with BM or BUM flags. If a single AR-R is selected, only a VXLAN destination includes the BM flags.
Control plane-generated BM packets, such as ARP/ND (when proxy-ARP/ND is enabled) or Eth-CFM, follow the behavior of regular data plane BM packets.
When a Leaf receives an unknown unicast packet on an AC, it sends the packet to the flood-list, skipping the AR destination because the U flag is set to 0. To avoid packet re-ordering, the unknown unicast packets do not go through the AR-R.
When a Leaf receives a BUM packet on an overlay tunnel, it forwards the packet to the flood list, skipping the VXLAN tunnels (that is, the packet is sent to the local ACs and never to a VXLAN tunnel). This is the default IR behavior.
When the last Replicator-AR route is withdrawn, the AR-L removes the AR destination from the flood list and falls back to ingress replication.
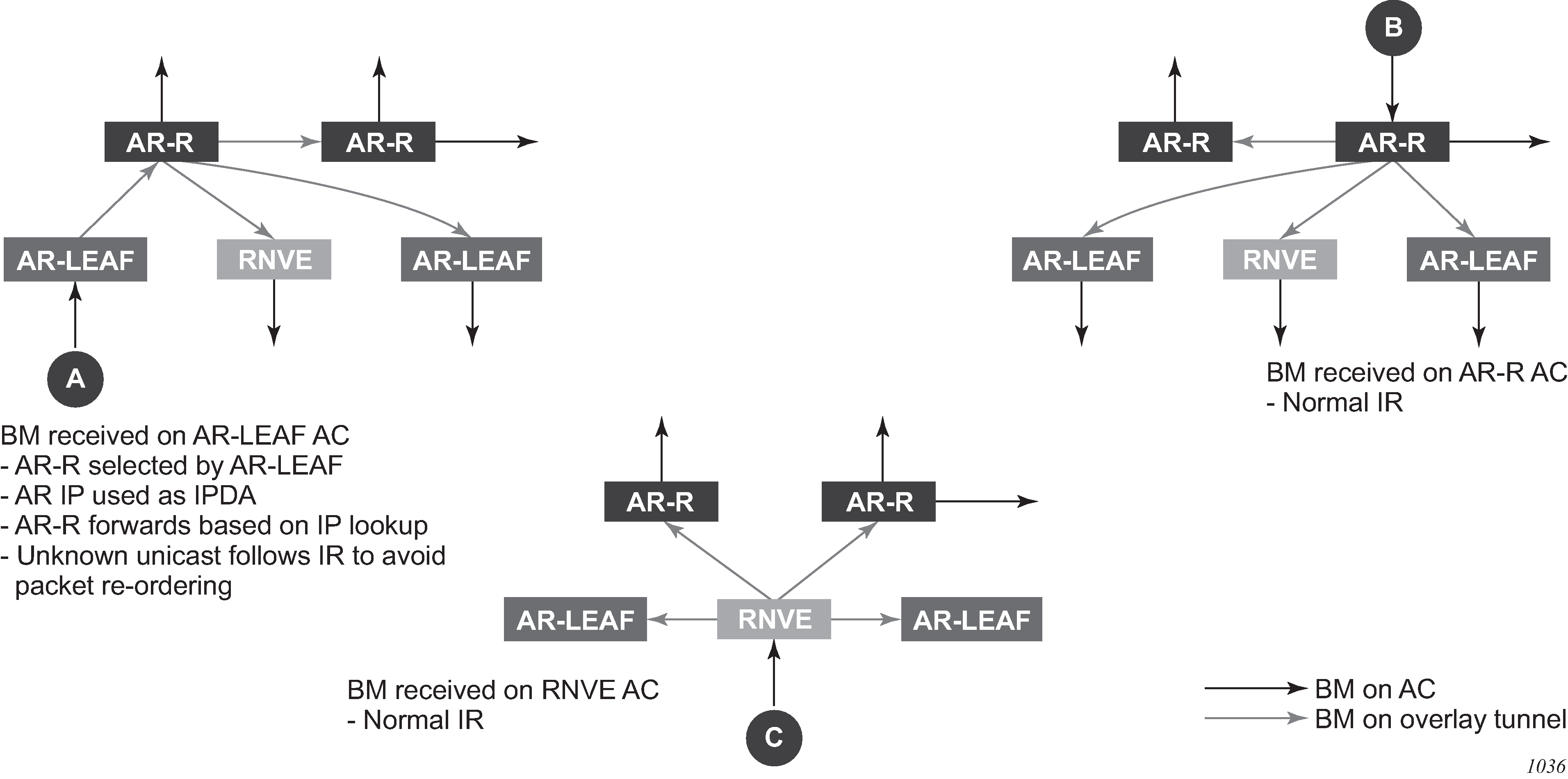
Figure: AR BM replication behavior for a BM packet shows the expected replication behavior for BM traffic when received at the access on an AR-R, AR-L, or RNVE router. Unknown unicast follows regular ingress replication behavior regardless of the role of the ingress node for the specific service.