For Inter-AS Option C, on a leaf PE, a route exists to reach root PE’s system IP and, as ASBRs can use BGP unicast routes, recursive FEC processing using BGP unicast routes, and not VPN recursive FEC processing using PMSI routes, is required.
I-PMSI and S-PMSI establishment
I-PMSI and S-PMSI functionality follows RFC 6513 section 8.1.1 and RFC 6512 Section 2. The same rules as per the GRT d-mLDP use case apply, but the VRR Route Import External community now encodes the VRF instance in the local administrator field.
Option C uses an outer opaque of type 7 and inter opaque of type 1.
Figure: Non-segmented mLDP PMSI establishment (Option C) shows the processing required for I-PMSI and S-PMSI Inter-AS establishment.
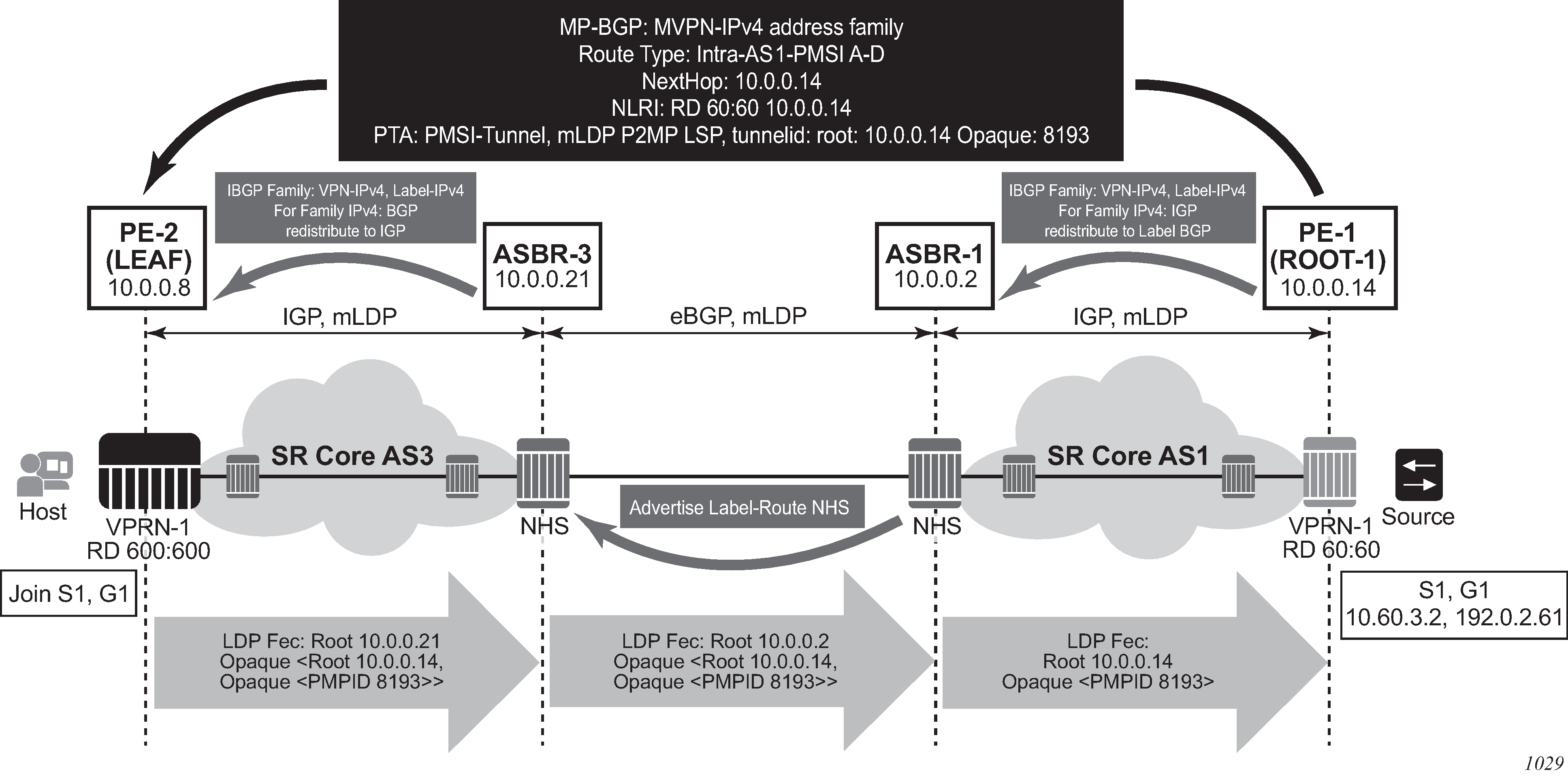
For non-segmented mLDP trees, A-D procedures follow those of the Intra-AS model, with the exception that NO EXPORT Community must be excluded; LSP FEC includes mLDP recursive FEC (and not VPN recursive FEC).
For I-PMSI on Inter-AS Option C:
-
A-D routes are not installed by ASBRs and next-hop information is not changed in MVPN A-D routes.
-
BGP-labeled routes are used to provide inter-domain connectivity on remote ASBRs.
On a receipt of an Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route, PE2 resolves PE1’s address (N-H in PMSI route) to a labeled BGP route with a next-hop of ASBR3, because PE1 is not known via IGP. PE2 sources an mLDP FEC with a root node of ASBR3, and an opaque value, shown below, containing the information advertised by PE1 in the I-PMSI A-D route.
PE-2 LEAF FEC: {root = ASBR3, opaque value: {Root: ROOT-1, opaque value: P2MP-ID xx}}
When the mLDP FEC arrives at ASBR3, it notes that it is the identified root node, and that the opaque value is a recursive opaque value. ASBR3 resolves the root node of the Recursive FEC (ROOT-1) to a labeled BGP route with the next-hop of ASBR1, because PE-1 is not known via IGP. ASBR3 creates a new mLDP FEC element with a root node of ASBR1, and an opaque value being the received recursive opaque value.
ASBR3 FEC: {root: ASBR1, opaque value: {root: ROOT-1, opaque value: P2MP-ID xx}}
When the mLDP FEC arrives at ASBR1, it notes that it is the root node and that the opaque value is a recursive opaque value. As PE-1’s address is known to ASBR1 through the IGP, no further recursion is required. Regular processing begins, using the received Opaque mLDP FEC information.
The functionality as described above for I-PMSI applies to S-PMSI and (C-*, C-*) S-PMSI.
C-multicast route processing
C-multicast route processing functionality follows RFC 6513 section 8.1.2 (BGP used for route exchange). The processing is analogous to BGP Unicast VPN route exchange. Figure: Non-segmented mLDP C-multicast exchange (Option C) shows C-multicast route processing with non-segmented mLDP PMSI details.
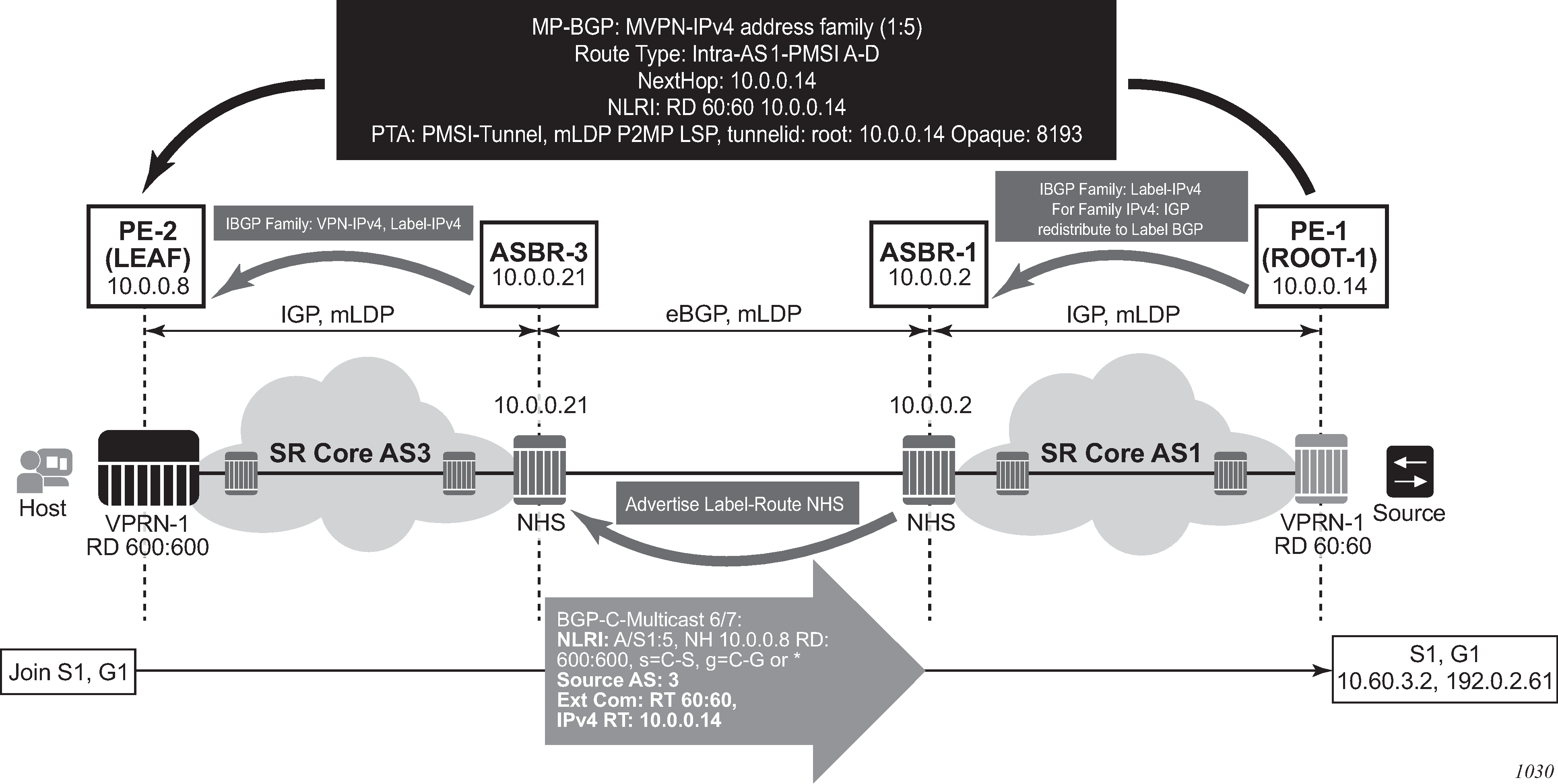
LEAF node cavities
The LEAF (PE-2) has to have the ROOT-1 system IP installed in RTM via BGP. If the ROOT-1 is installed in RTM via IGP, the LEAF does not generate the recursive opaque FEC. As such, the ASBR 3 does not process the LDP FEC correctly.