IPv6 multicast support in SR OS allows operators to offer customers IPv6 multicast MVPN service. An operator uses IPv4 mLDP or RSVP-TE core to carry IPv6 c-multicast traffic inside IPv4 mLDP or RSVP-TE provider tunnels (p-tunnels). The IPv6 customer multicast on a specific MVPN can be blocked, enabled on its own or in addition to IPv4 multicast per PE or per interface. When both IPv4 and IPv6 multicast is enabled for a specific MVPN, a single tree is used to carry both IPv6 and IPv4 traffic. Figure: IPv6 MVPN example shows an example of an operator with IPv4 MPLS backbone providing IPv6 MVPN service to Customer 1 and Customer 2.
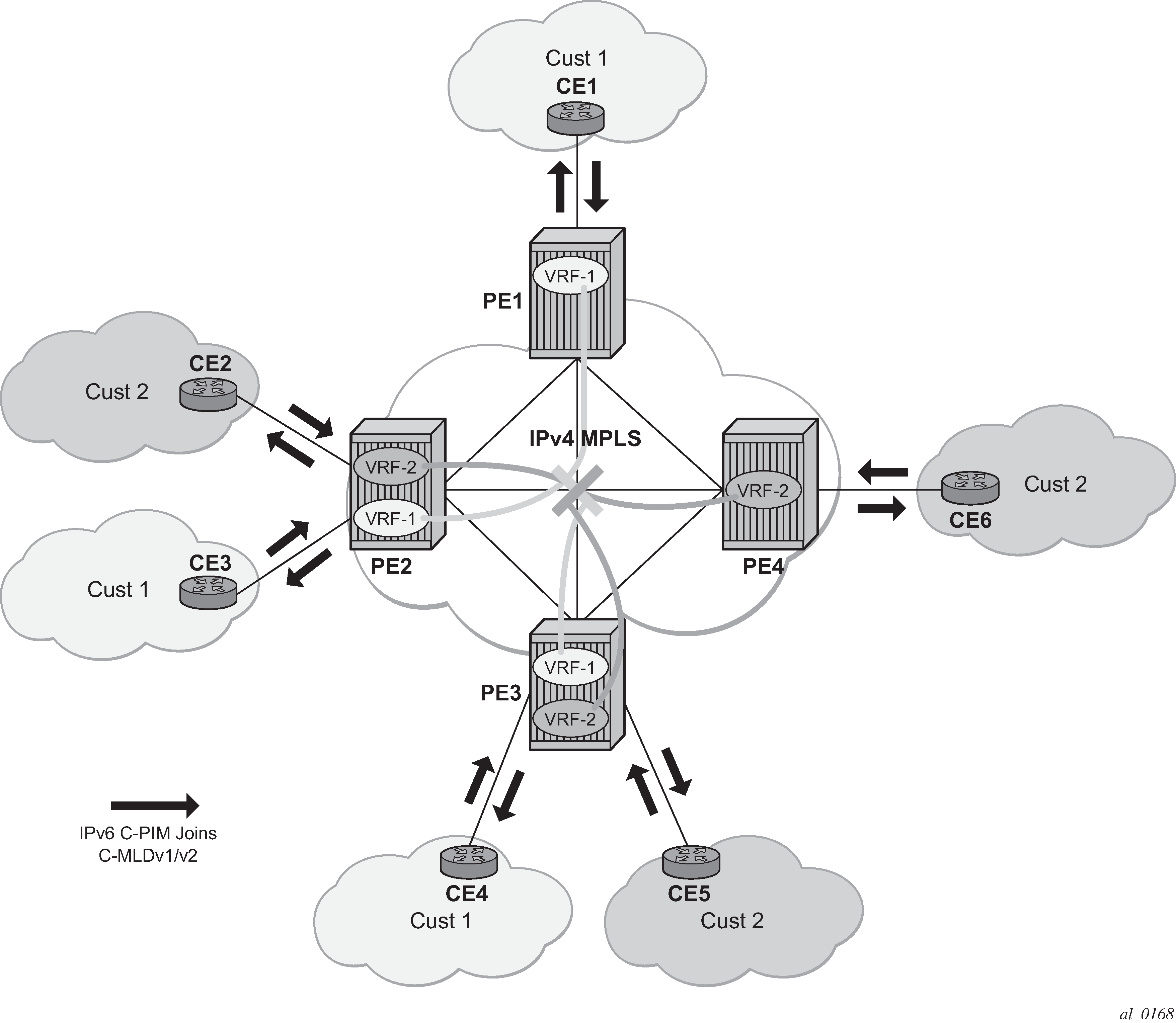
SR OS IPv6 MVPN multicast implementation provides the following functionality:
IPv6 C-PIM-SM (ASM and SSM)
MLDv1 and MLDv2
SSM mapping for MLDv1
I-PMSI and S-PMSI using IPv4 P2MP mLDP p-tunnels
I-PMSI and S-PMSI using IPv4 P2MP RSVP p-tunnels
BGP auto-discovery
PE-PE transmission of C-multicast routing using BGP mvpn-ipv6 address family
IPv6 BSR/RP functions on functional par with IPv4 (auto-RP using IPv4 only)
Embedded RP
Inter-AS Option A
The following known restrictions exist for IPv6 MVPN support:
Non-congruent topologies are not supported.
IPv6 is not supported in MCAC.
If IPv4 and IPv6 multicast is enabled, per-MVPN multicast limits apply to entire IPv4 and IPv6 multicast traffic as it is carried in a single PMSI. For example IPv4 AND IPv6 S-PMSIs are counted against a single S-PMSI maximum per MVPN.
IPv6 Auto-RP is not supported.