See Figure: Logical networks using multi-instance IGP for an operational example of logical networks using Multi-Instance IGP.
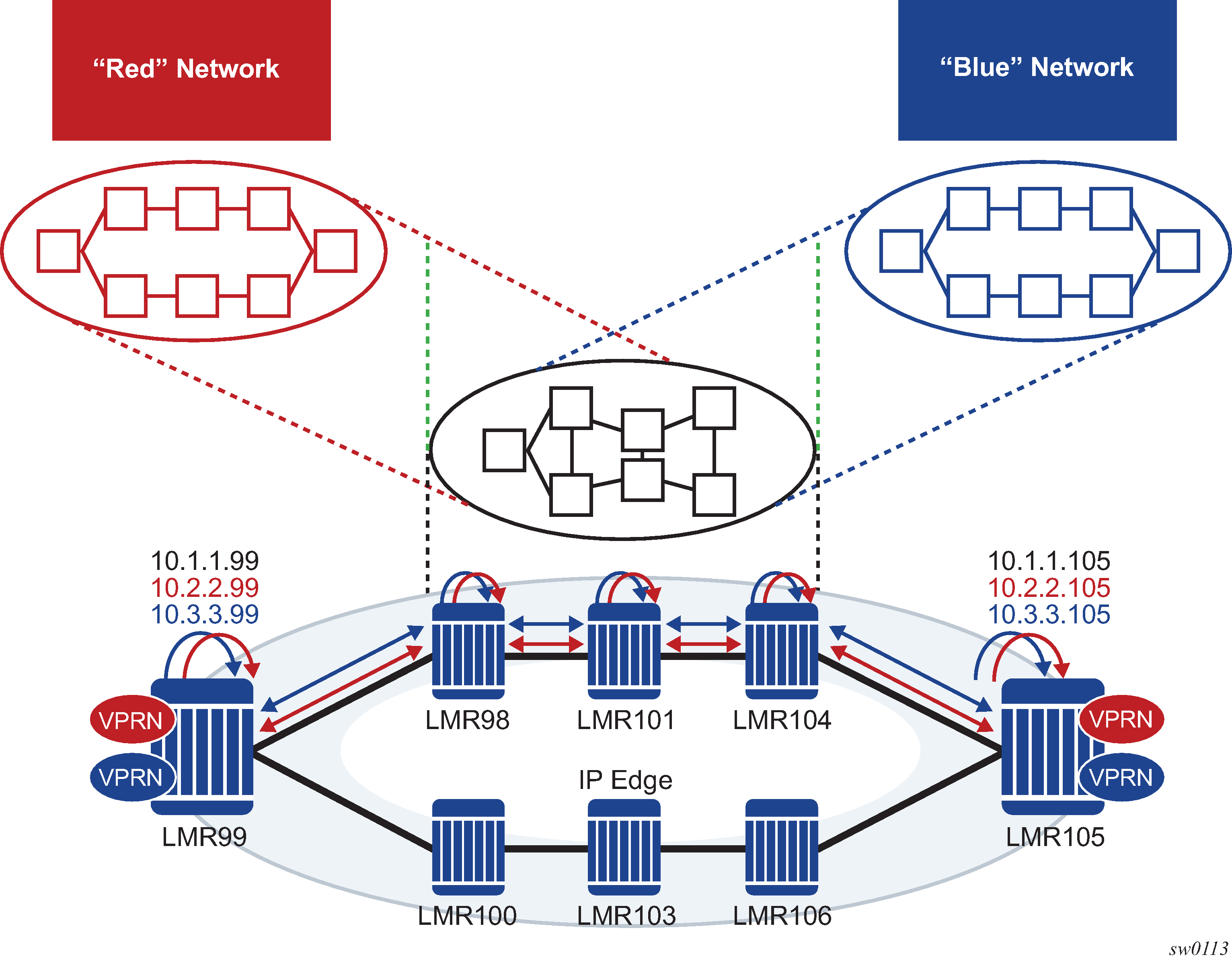
SR OS is being positioned in multi-instance IGP as a virtualization or migration strategy in numerous cases. One specific application is as a virtual LSR core whereby various topologies are created using separate IGP instances. Specifically, the migration to SR solutions requires the deployment of multi-instance IGP with service migrations. The objective is to more cleanly segregate protocols and service bindings to specific routing instances. NG-MVPN does not currently allow non-system loopbacks to be used for PMSI (for example, MVPN address family).
The ability to support binding MVPN with mLDP tunnels to different loopback interfaces is one of the main requirements. In addition, assigning these loopback interfaces to different IGP instances creates parallel NG-MVPN services, each running over a separate IGP instance.
This feature has two main components to it:
-
The ability of advertising a MVPN route, via a loopback interface, and generating an mLDP FEC with that loopback interface.
-
The ability of creating multiple IGP instances and assigning a loopback to each IGP instance. This, combined with the component above, creates parallel NG-MVPN services on different IGP instances.