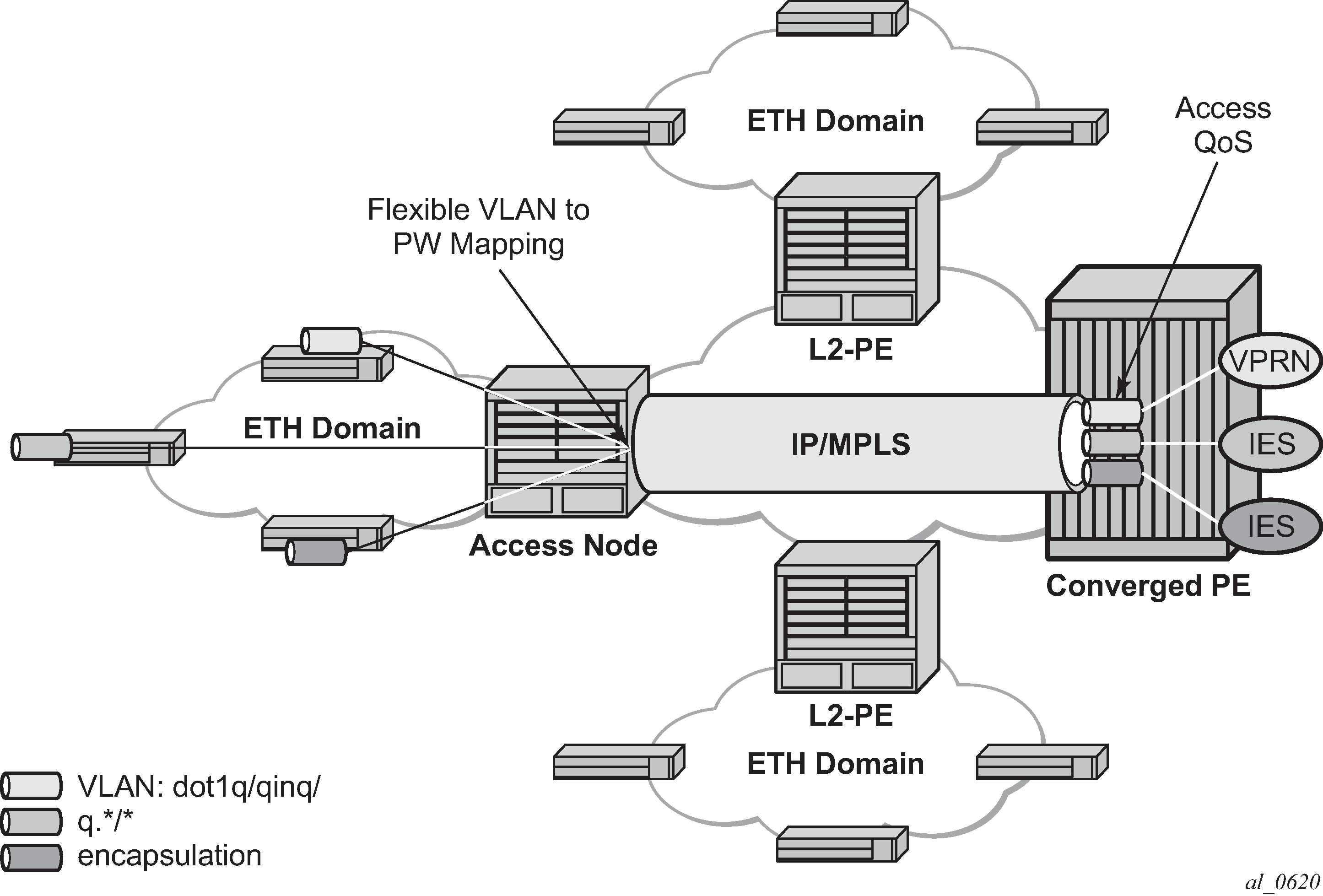
This feature allows customers of an IES, VPRN, or Epipe VLL service and connected to an Ethernet SAP on an Access PE to be backhauled through an Ethernet aggregation network using MPLS pseudowires terminating directly on a converged PE hosting the IES, VPRN, or Epipe VLL service. If Enhanced Subscriber Management over PW is also used, then the converged PE may also act as a BNG. This service is different from VLL Spoke-SDP termination on an IES or VPRN because access QoS policies can be applied directly at a centralized PE hosting the IES or VPRN instance. This feature uses the same concepts of pseudowire ports and pseudowire SAPs that are used for ESM over MPLS pseudowires, described in the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, and VSR Triple Play Service Delivery Architecture Guide.
The MPLS pseudowire originates from the first hop aggregation PE (referred to as access PE) upstream of the Access-Node (or directly from a multi-service AN), and terminates on the converged PE. Multiple customers from a specific access-port on the Access-PE can be backhauled over a single MPLS pseudowire toward the converged PE. This capability allows the network to scale and does not require an MPLS pseudowire per customer between the Access-PE and the converged PE. The access-port on the Access-PE can be dot1q, q-in-q or NULL encapsulated. The converged PE terminates the MPLS pseudowire, decapsulates the received frames, and provides access QoS functions including HQoS, without requiring an internal or external loopback. Each MPLS pseudowire is represented on the BNG as a ‟PW-port” for which SAPs are created. These SAPs are termed ‟PW SAPs”, and must be statically configured on IES or VPRN interfaces or under the VLL service (unlike the ESM case where a capture SAP can be configured). The underlying Ethernet port must be in hybrid mode. Pseudowire SAPs are supported on Ethernet MDAs.
Figure: Network architecture using pseudowire SAPs illustrates the architecture of an aggregation network that uses pseudowire SAPs.