This feature allows a downstream LSR to send a label binding to a couple of upstream LSR nodes but only accept traffic from the ILM on the interface to the primary next-hop of the root LSR for the P2MP FEC in normal operation, and accept traffic from the ILM on the interface to the backup next-hop under failure. A candidate upstream LSR node must either be an ECMP next-hop or a Loop-Free Alternate (LFA) next-hop. This allows the downstream LSR to perform a fast switchover and source the traffic from another upstream LSR while IGP is converging because of a failure of the LDP session of the upstream peer which is the primary next-hop of the root LSR for the P2MP FEC. In a sense it provides an upstream Fast-Reroute (FRR) node-protection capability for the mLDP FEC packets.
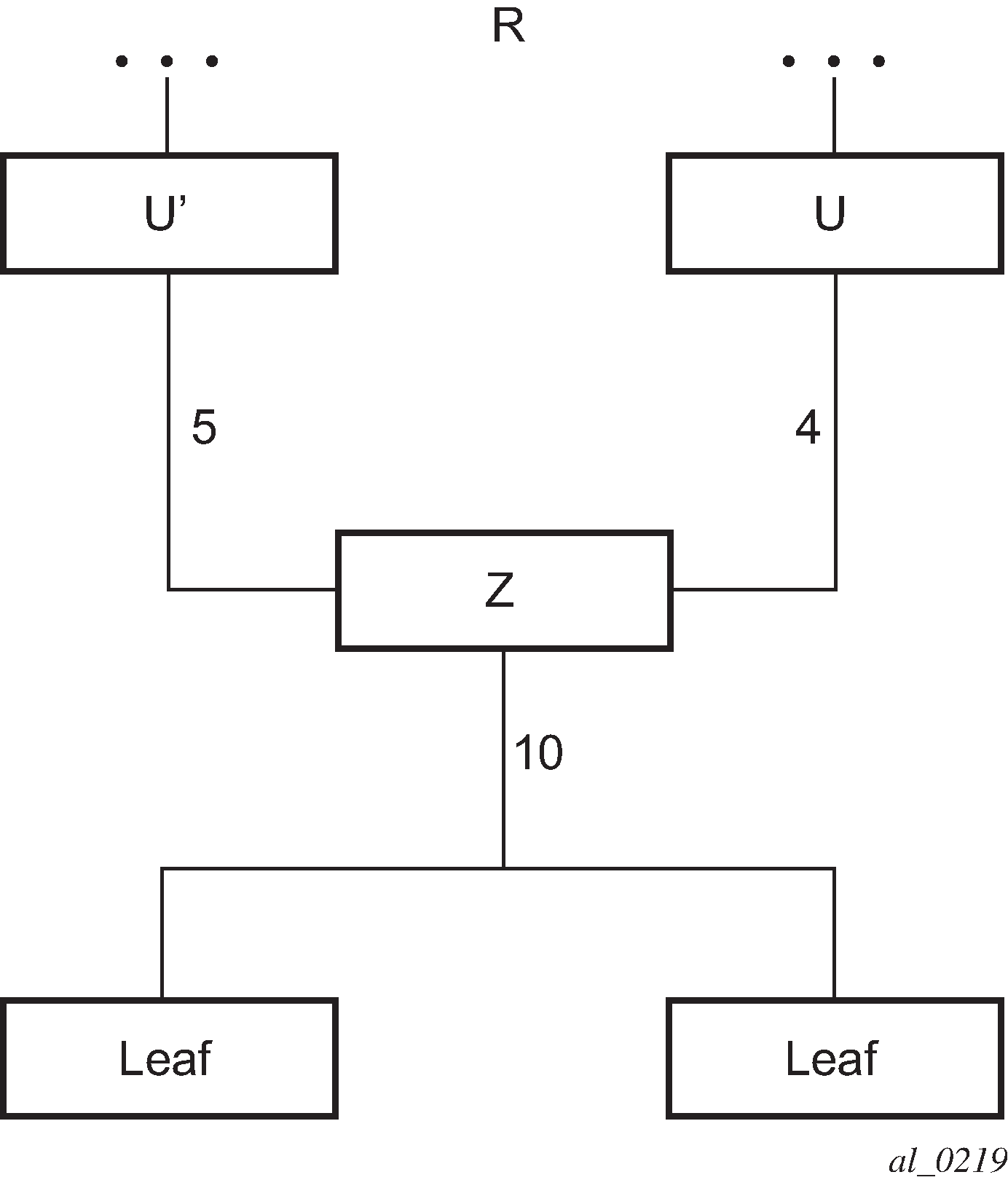
Upstream LSR U in Figure: mLDP LSP with backup upstream LSR nodes is the primary next-hop for the root LSR R of the P2MP FEC. This is also referred to as primary upstream LSR. Upstream LSR U’ is an ECMP or LFA backup next-hop for the root LSR R of the same P2MP FEC. This is referred to as backup upstream LSR. Downstream LSR Z sends a label mapping message to both upstream LSR nodes and programs the primary ILM on the interface to LSR U and a backup ILM on the interface to LSR U’. The labels for the primary and backup ILMs must be different. LSR Z therefore attracts traffic from both of them. However, LSR Z blocks the ILM on the interface to LSR U’ and only accepts traffic from the ILM on the interface to LSR U.
In case of a failure of the link to LSR U or of the LSR U itself causing the LDP session to LSR U to go down, LSR Z detects it and reverses the ILM blocking state and immediately starts receiving traffic from LSR U’ until IGP converges and provides a new primary next-hop, and ECMP or LFA backup next-hop, which may or may not be on the interface to LSR U’. At that point LSR Z updates the primary and backup ILMs in the data path.
The LDP uses the interface of either an ECMP next-hop or a LFA next-hop to the root LSR prefix, whichever is available, to program the backup ILM. ECMP next-hop and LFA next-hop are however mutually exclusive for a specified prefix. IGP installs the ECMP next-hop in preference to an LFA next-hop for a prefix in the Routing Table Manager (RTM).
If one or more ECMP next-hops for the root LSR prefix exist, LDP picks the interface for the primary ILM based on the rules of mLDP FEC resolution specified in RFC 6388:
-
The candidate upstream LSRs are numbered from lower to higher IP address.
-
The following hash is performed: H = (CRC32(Opaque Value)) modulo N, where N is the number of upstream LSRs. The Opaque Value is the field identified in the P2MP FEC Element right after 'Opaque Length' field. The 'Opaque Length' indicates the size of the opaque value used in this calculation.
-
The selected upstream LSR U is the LSR that has the number H.
LDP then picks the interface for the backup ILM using the following new rules:
if (H + 1 < NUM_ECMP) {
// If the hashed entry is not last in the next-hops then pick up the next as backup.
backup = H + 1;
} else {
// Wrap around and pickup the first.
backup = 1;
}
In some topologies, it is possible that no ECMP or LFA next-hop is found. In this case, LDP programs the primary ILM only.