Multiple deployment models are supported for integrating AA in the various subscriber edge and VPN PE network topologies (Figure: AA deployment topologies). In all cases, AA can be added by in-service upgrade to the installed base of equipment instead of needing to deploy and integrate a whole new set of equipment and vendors into the network for Layer 4-7 awareness.
Integrating Layer 4-7 application policy with the 7750 SR or 7450 ESS subscriber edge policy context is the primary solution to address both residential broadband edge and Layer 2/Layer 3 application aware business VPN. Placement of Layer 4-7 analysis at the distributed subscriber edge policy point simplifies AA deployments in the following ways:
For residential markets, CO-based deployment allows deployment-driven scaling of resources to the amount of bandwidth needed and the amount of subscribers requiring application-aware functionality.
For AA business VPNs, a network deployment allows large scale application functionality at a VPN provider edge access point, vastly reducing complexity, cost, and time-to-market required to offer application-aware VPN services.
Traffic asymmetry is avoided. Any subscriber traffic usually passes through one CO subscriber edge element so there is no need for flow paths to be recombined for stateful analysis.
PE integration provides a single point of policy enforcement.
SeGW integration provides firewall protection for NMS, MME and SGW.
Figure: AA deployment topologies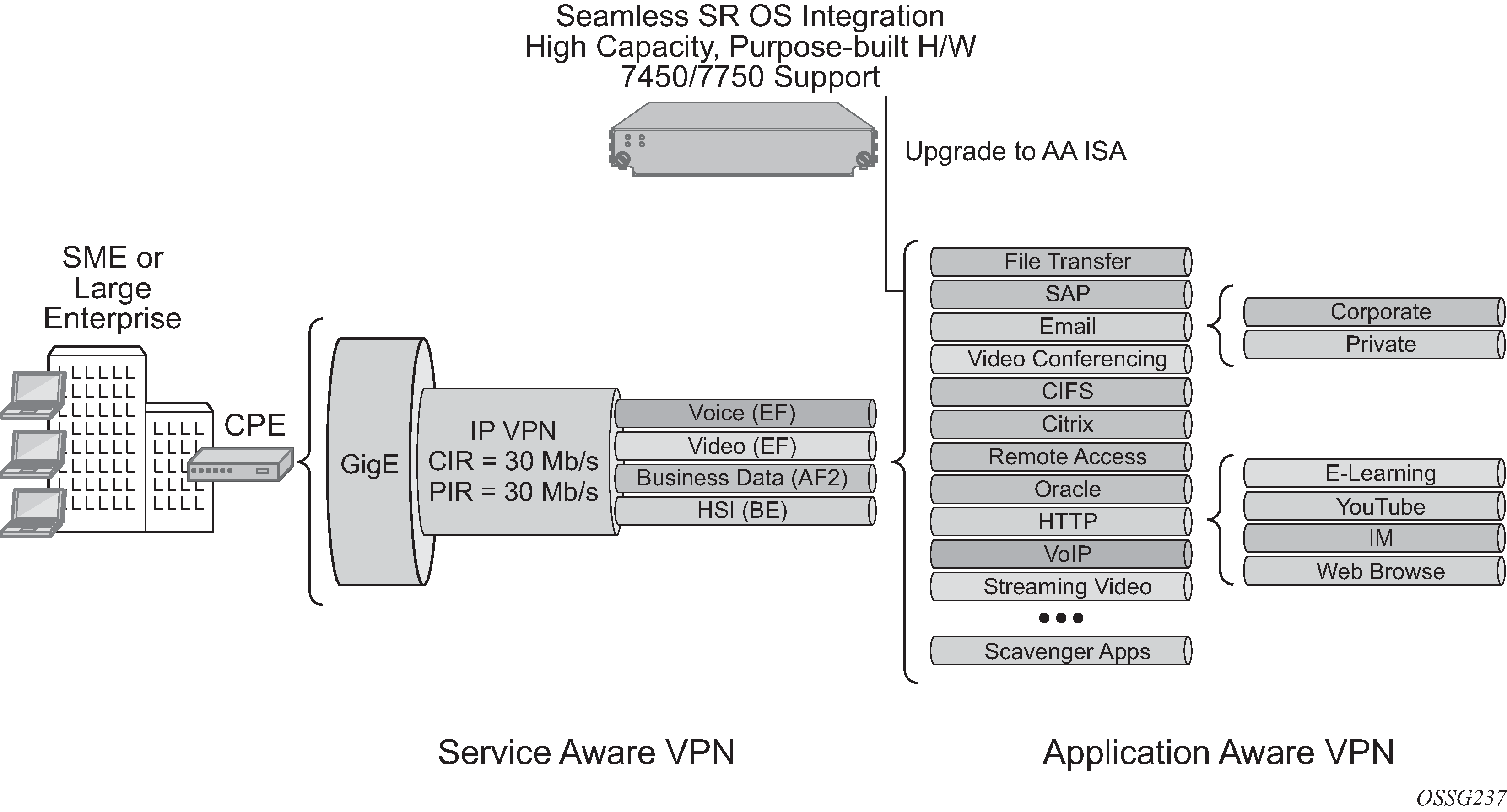
There are residential topologies where it is not possible or practical to distribute ISAs into the same network elements that run ESM, including for legacy edge BRASs that still need AA policy (reporting and control) for the same Internet services, and which needs to be aligned and consistent with the ESM AA policy. This is supported using transit AA subscribers, typically in the first routed element behind the legacy edge.
AA enables per AA subscriber (a residential subscriber, or a Layer 2/Layer 3 SAP or spoke SDP), per application policy for all or a subset of AA subscriber's applications. This provides the ability to:
implement Layer 4-7 identification of applications using a multitude of techniques from a simple port-based/IP address based identification to behavioral techniques used to identify, for example, encrypted or evasive applications
when identified, apply a QoS policy on either an aggregate or a per-AA subscriber, per-application basis
provide reports on the identification made, the traffic volume and performance of the applications, and policies implemented
An integrated AA module allows the SR and ESS product families to provide application-aware functions that previously required standalone devices (either in residential or business environment) at a fraction of the cost and operational complexity that additional devices in a network required.
A key benefit of integrating AA in the existing IP/MPLS network infrastructure (as opposed to an in-line appliance) is the ability to select traffic for treatment on a granular, reliable basis. Only traffic that requires AA treatment is simply and transparently diverted to the ISA. Other traffic from within the same service or interface follows the normal forwarding path across the fabric. In the case of ISA failure, ISA redundancy is supported and in the case where no backup ISAs are available, the AA traffic reverts to the normal fabric matrix forwarding, also known as ‟fail to fabric”.
Table: Traffic diversion to the ISA lists ISA traffic diversion information.
| Deployment case | System divert ID | AA subscriber type | App-profile on: |
|---|---|---|---|
Residential Edge (BNG) |
ESM Sub-ID |
ESM |
ESM sub (All IPs, not per-host) |
vRGW Bridged Residential Gateway (BRG) subscriber |
ESM Sub-ID |
ESM |
ESM sub (All IPs, not per-host) |
vRGW BRG session |
ESM-MAC |
ESM-MAC |
ESM-MAC (by device, for any hosts assigned to a device |
Wireless LAN GW |
ESM or DSM |
ESM or DSM |
ESM or DSM |
Business Edge |
L2/L3 SAP |
SAP |
SAP (Aggregate) |
Residential Transit |
Parent L3 SAP or spoke SDP |
Transit AA |
Transit Sub |
Spoke Attached Edge |
Spoke SDP |
Spoke SDP |
Spoke SDP (Aggregate) |
SeGW |
Parent SAP or spoke SDP or L2/L3 SAP |
Transit AA SAP |
Transit AA SAP |