When used together with the MD-CLI gRPC service, the remote management feature allows SR OS nodes to initiate communication with a remote NISH manager and announce to their availability to be managed using the NISH client. This provides the NISH client with a dynamic view of the available nodes that it can manage.
The remote management service does not perform or enable the actual management of the SR OS node using NISH. This communication is achieved directly from the NISH client to the SR OS node using the MD-CLI gRPC service.
This feature is particularly useful when deploying clusters of SR OS nodes that may dynamically join or leave a cluster, such as in scenarios that use the Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS) BNG application with Virtualized Service Routers (VSRs).
A working NISH manager service is required on an external server to use the remote management feature. However, in the absence of a working NISH manager, the system does not stop remote management from being enabled within SR OS, nor does it stop the SR OS node from announcing its presence to the configured IP address or addresses of the NISH manager.
When a remote NISH manager is configured, the SR OS node initiates a gRPC session with the configured manager. The SR OS node sends a message to communicate its name, IP address (IPv4 and IPv6 are supported), and gRPC port to the NISH manager. The NISH manager responds with an acknowledgment message. The SR OS node periodically checks in with the NISH manager.
Figure: Remote management service initiation shows the remote management initiation.
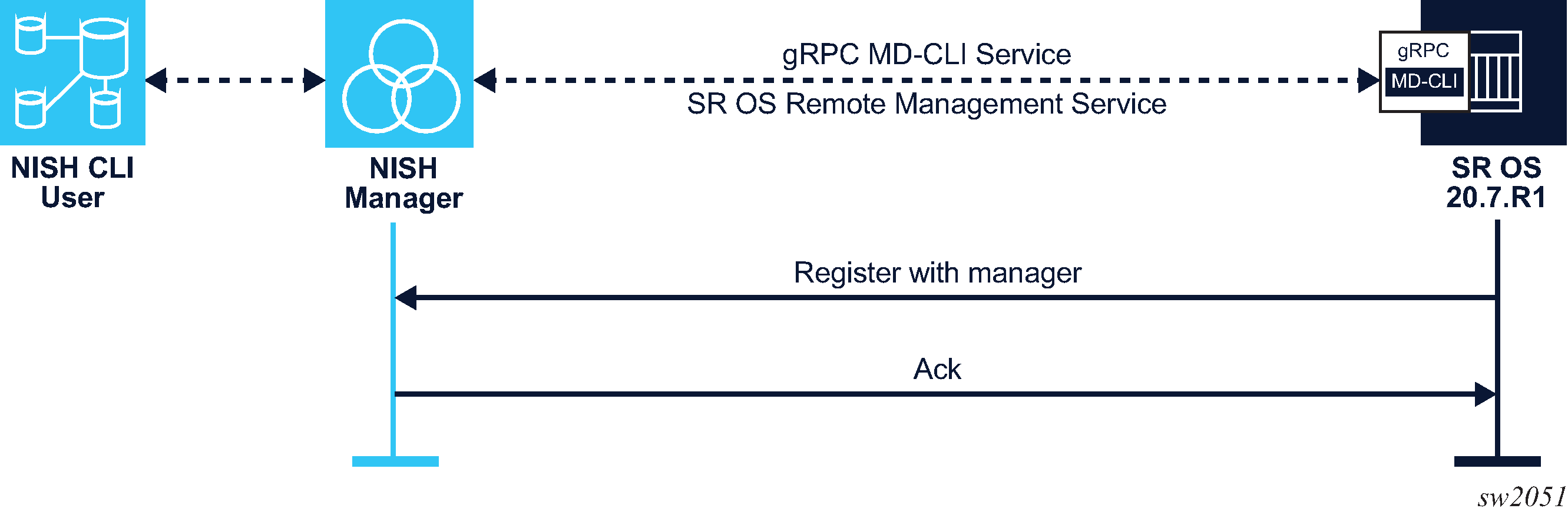
If the connection is interrupted, the SR OS node immediately attempts reconnection with the configured NISH managers.