As mentioned in the previous section, LFI on LNS is implemented only on MLPPPoX bundles with a single LCP session.
There are two major tasks (Most of this is also applicable to non-lfi case. The only difference between lfi and non-lfi is that there is no artificial delay performed in non-lfi case) associated with LFI on the LNS:
Executing subscriber QoS in the carrier IOM based on the last mile conditions. The subscriber QoS rates are the last mile on-the-wire rates. After traffic is QoS conditioned, it is sent to the BB-ISA for further processing.
Fragmentation and artificial delay (queuing) of the fragments so that high priority packets can be injected in-between low priority fragments (interleaved). This operation is performed by the BB-ISA.
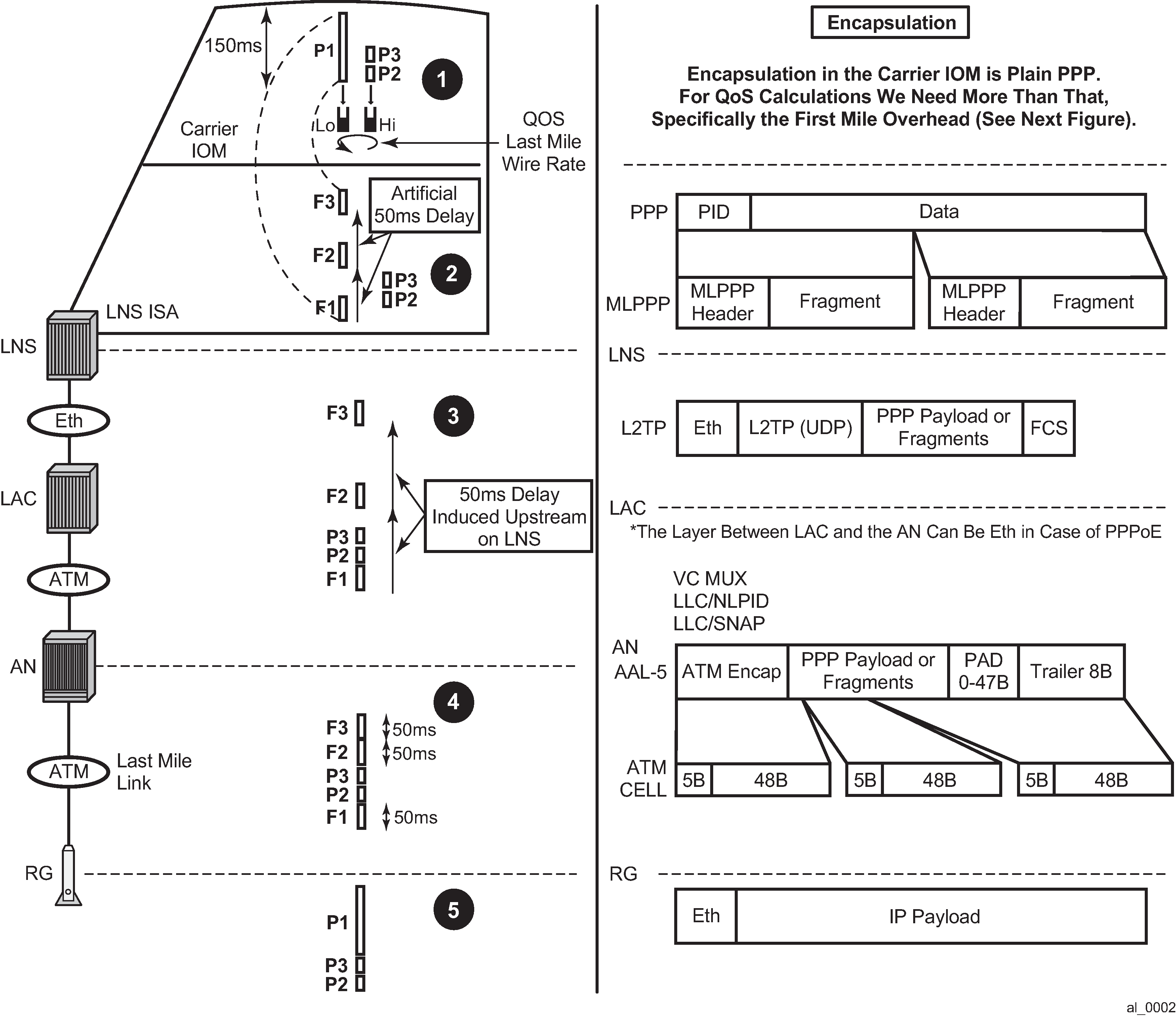
Examine an example to further clarify functionality of LFI. The parameters, conditions and requirements that are used in the example to describe the wanted behavior are the following:
High priority packets must not be delayed for more than 50ms in the last mile because of the transmission delay of the large low priority packets. Considering that tolerated end-to-end VoIP delay must be under 150ms, limiting the transmission delay to 50ms on the last mile link is a reasonable option.
The link between the LNS and LAC is 1Gb/s Ethernet.
The last mile link rate is 256 kb/s.
Three packets arrive back-to-back on the network side of the LNS (in the downstream direction). The large 5000B low priority packet P1 arrives first, followed by two smaller high priority packets P2 and P3, each 100B.
Note:Packets P1, P2 and P3 can be originated by independent sources (PCs, servers, and so on) and therefore can theoretically arrive in the LNS from the network side back-to-back at the full network link rate (10Gb/s or 100Gb/s).
The transmission time on the internal 10G link between the BB-ISA and the carrier IOM for the large packet (5000B) is 4us while the transmission time for the small packet (100B) is 80ns.
The transmission time on the 1G link (LNS->LAC) for the large packet (5000B) is 40us while the transmission time for the small packet (100B) is 0.8us.
The transmission time in the last mile (256 kb/s) for the large packet is ~150ms while the transmission time for the small packet on the same link is ~3ms.
Last mile transport is ATM.
To satisfy the delay requirement for the high priority packets, the large packets are fragmented into three smaller fragments. The fragments are carefully sized so that their individual transmission time in the last mile does not exceed 50ms. After the first 50ms interval, there is an opportunity to interleave the two smaller high priority packets.
This entire process is further clarified by the five points (1-5) in the packet route from the LNS to the Residential Gateway (RG) as depicted in Figure: Packet route from the LNS to the RG.
The five points are:
-
Figure: Packet route from the LNS to the RG