Applications for multicast over subscriber interfaces in Routed CO ESM model can be divided in two main categories:
Residential customers where the driver applications are:
IPTV in an environment with legacy non-multicasting DSLAMs
Internet multicast where users connect to a multicast stream sourced from the Internet.
For the business customers, the main drivers are enterprise multicast and Internet multicast applications.
On multicast-capable ANs, a single copy of each multicast stream is delivered over a separate regular IP interface. AN would then perform the replication. This is how multicast would be deployed in Routed CO environment with the 7750 SR and 7450 ESS.
On legacy, non-multicast ANs, or in environments with low volume multicast traffic where it is not worth setting up a separate multicast topology (from BNG to AN), multicast replication is performed with subscriber-interfaces in the 7750 SR and 7450 ESS. There are differences in replicating multicast traffic on IPoE vs PPPoX which are described in subsequent sessions.
An example of a business connectivity model is shown in Figure: Typical business connectivity model.
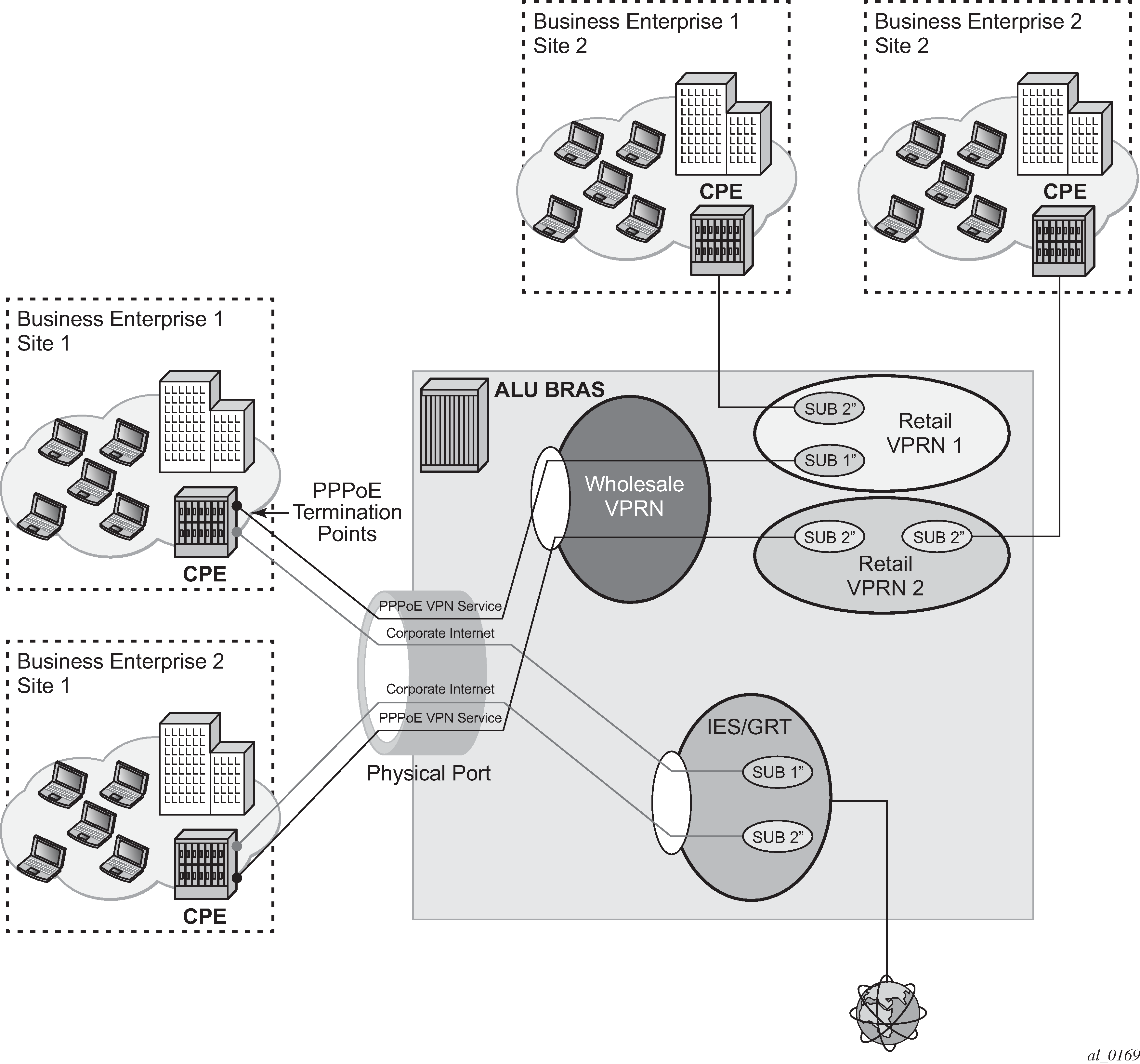
In this example, HSI is terminated in a Global Routing Table (GRT) whereas VPRN services are terminated in Wholesale/Retail VPRN method, with each customer using a separate VPRN.
The actual connectivity model that is deployed depends on many operational aspects that are present in the customer environment.
Multicast over subscriber-interfaces in a Routed CO model is supported for both types of hosts, IPoE and PPPoE which can be simultaneously enabled on a shared SAP.
There are some fundamental differences in multicast behavior between two host types (IPoE and PPPoX). The differences are discussed further in the next sections.