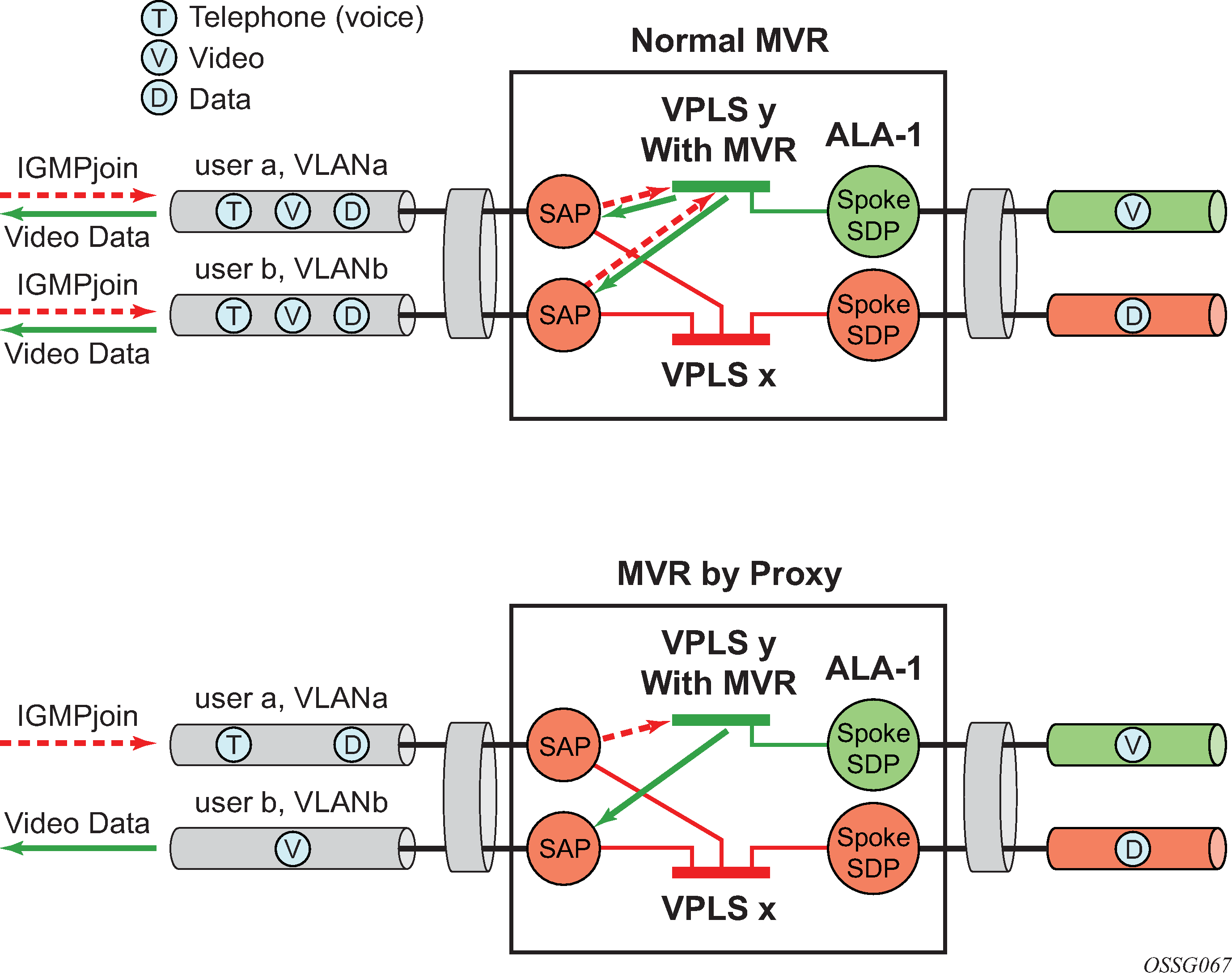
Multicast VPLS Registration (MVR) is a bandwidth optimization method for multicast in a broadband services network. MVR allows a subscriber on a port to subscribe and unsubscribe to a multicast stream on one or more network-wide multicast VPLS instances.
MVR assumes that subscribers join and leave multicast streams by sending IGMP join and leave messages. The IGMP leave and join message are sent inside the VPLS to which the subscriber port is assigned. The multicast VPLS is shared in the network while the subscribers remain in separate VPLS services. Using MVR, users on different VPLS cannot exchange any information between them, but still multicast services are provided.
On the MVR VPLS, IGMP snooping must be enabled. On the user VPLS, IGMP snooping and MVR work independently. If IGMP snooping and MVR are both enabled, MVR reacts only to join and leave messages from multicast groups configured under MVR. Join and leave messages from all other multicast groups are managed by IGMP snooping in the local VPLS. This way, potentially several MVR VPLS instances could be configured, each with its own set of multicast channels.
MVR by proxy — In some situations, the multicast traffic should not be copied from the MVR VPLS to the SAP on which the IGMP message was received (standard MVR behavior) but to another SAP. This is called MVR by proxy.
Figure: MVR and MVR by proxy shows a MVR and MVR by proxy configuration.