HLE allows an operator to extend the home network of the broadband user to a WAN network, such as a data center, by creating a per-home Bridge Domain (BD) on a Broadband Network Gateway (BNG). This feature provides the operator with the capability to deploy new services in a data center that have full Layer 2 reachability to the home and visibility to each individual host.
The per-home BD is created on a WLAN-GW ISA, and the system uses standard BGP EVPN VPLS services to extend the BD to remote networks.
Figure: Home LAN extension displays an example of an HLE configuration.
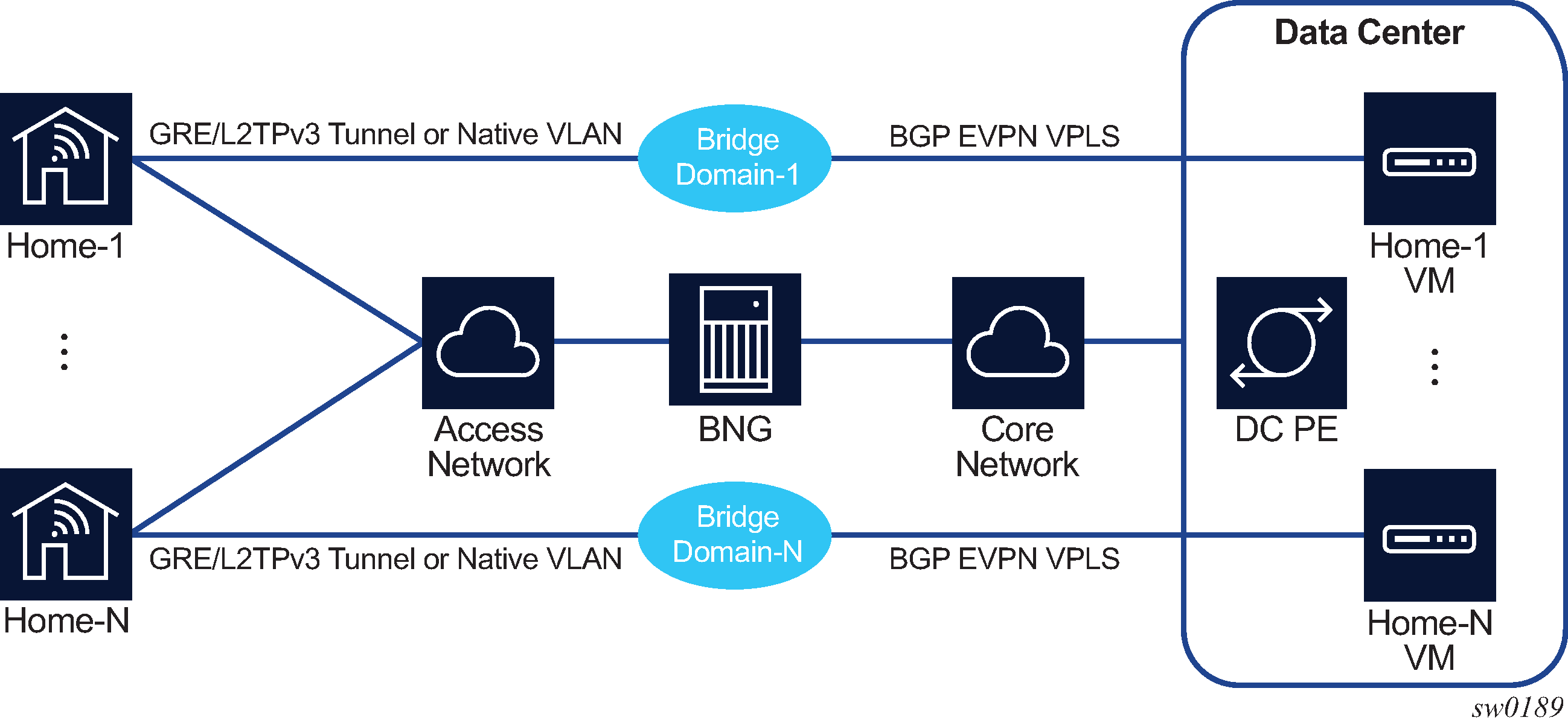
HLE requires the BNG to have Layer 2 access to the home network. The BNG supports the following types of access:
soft GRE or L2TPv3 tunnel from a home gateway, which encapsulates Ethernet traffic from the host into a GRE/L2TPv3 tunnel
native VLAN access that is terminated on the WLAN-GW group ISA using L2-AP access
A unique BD is created on the ISA for each home. The BD bridges traffic between the following connections:
access-facing connection (for example, home)
GRE/L2TPv3/L2-AP
network-facing connection (for example, DC)
BGP EVPN tunnel
ESM SAP-facing connection
each home has its own ESM SAP
Each BD has a unique ID, which is a number returned by the RADIUS server as the Alc-Bridge-Id attribute during home authentication.
With HLE services, each home host is a WLAN-GW UE object and an ESM host object. Each network host (such as a VM in a data center) is a WLAN-GW UE object but not a ESM host. This means that a network host cannot use the BNG as the default router for other non-home-facing traffic.
HLE relies on SR OS vRGW functions, which means that the vRGW BRG in the same VLAN range of the WLAN-GW group interface must be enabled for HLE.