Wholesale providers can deliver Internet access to directly connected PPP users through third party ISPs. This involves the users connecting to an L2TP Access Concentrator (LAC) with their traffic being tunneled to and from an L2TP Network Server (LNS) in their ISP.
If there is a requirement to support per-ISP (and per-subscriber host) QOS control for downstream traffic on the LAC toward the users based on the DSCP marking in the L2TP header, the use-ingress-l2tp-dscp command must be configured within the sla-profile selected for the users. An example topology is shown in Figure: ISP Internet access through wholesale provider.
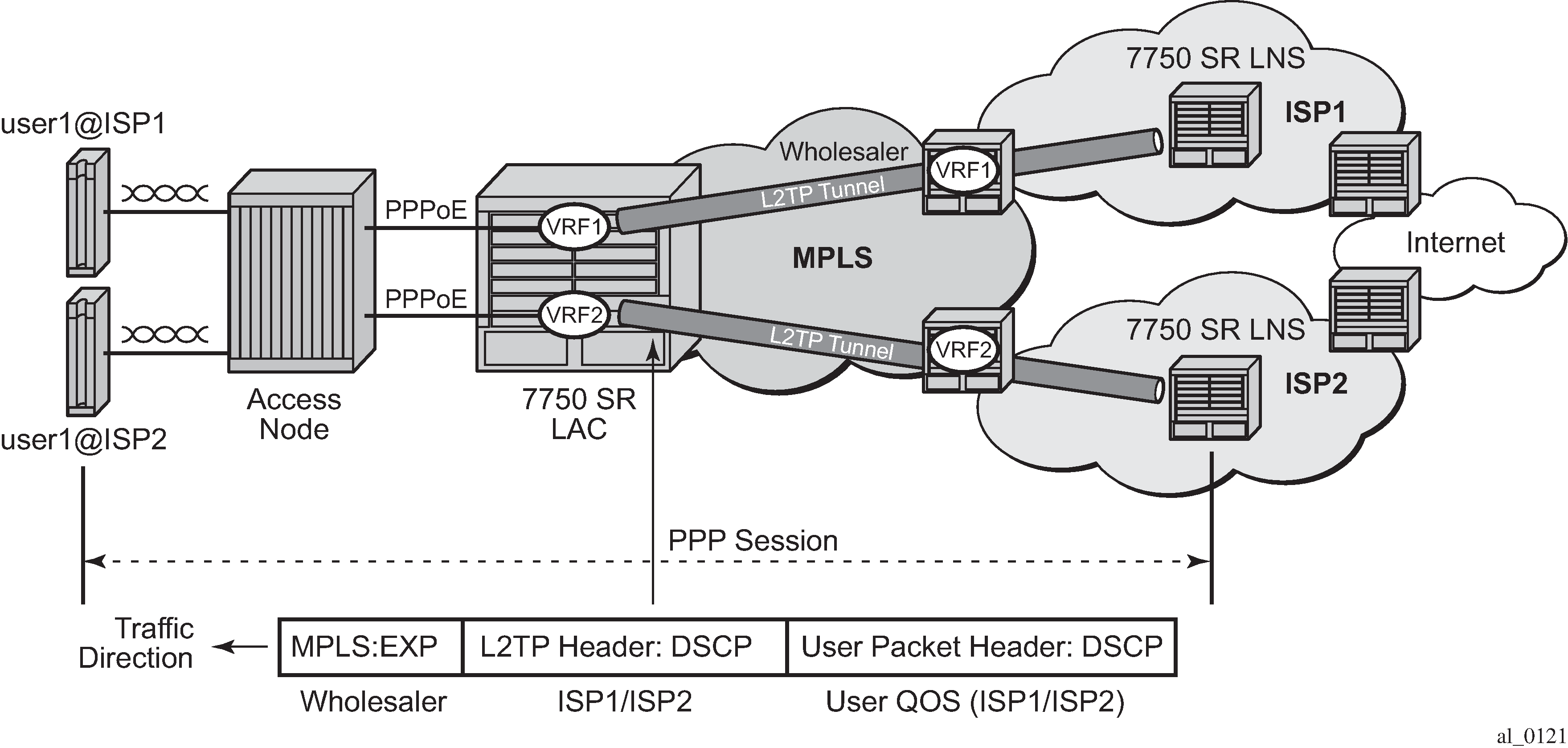
The downstream traffic arrives at the LAC with:
An MPLS header (because of the VRF encapsulation). This contains EXP bits which are set based on the wholesale provider’s QOS scheme.
An L2TP header (because of the L2TP tunnel to the ISP). This contains DSCP bits in its IP header which are set by the originating ISP.
A user IP packet header. This contains DSCP bits which could be set by the ISP or by the originating Internet application.
The network ingress on the LAC would normally use the MPLS EXP bits for traffic QoS classification, however, this matches the wholesale provider’s QoS scheme.
It is possible to apply the ler-use-dscp parameter at the LAC network ingress to classify based on the L2TP header DSCP, but this would require the QoS schemes used by all ISPs, and the wholesale provider, to have a consistent interpretation of the DSCP bits.
If the standard egress IP reclassification is used, the QOS would be dependent on the DSCP in the user packet.
Configuring the use-ingress-l2tp-dscp parameter in the sla-profile of the ISP1 and ISP2 users forces the egress QoS control to be based on the DSCP from the L2TP header received on the LAC (which is set by ISP1/ISP2). This provides per-ISP (and per-subscriber host) QoS control for downstream traffic on the LAC toward the users.