BGP assumes that all routers within an Autonomous System can reach destinations external to the Autonomous System using efficient, loop-free intra-AS forwarding paths. This generally requires that all the routers within the AS have a consistent view of the best path to every external destination. This is especially true when each BGP router in the AS makes its own forwarding decisions based on its own BGP routing table. The basic BGP specification does not store any intra-AS path information in the AS Path attribute so basic BGP has no way to detect routing loops within an AS that arise from inconsistent best path selections.
There are 3 solutions for dealing the issues described above.
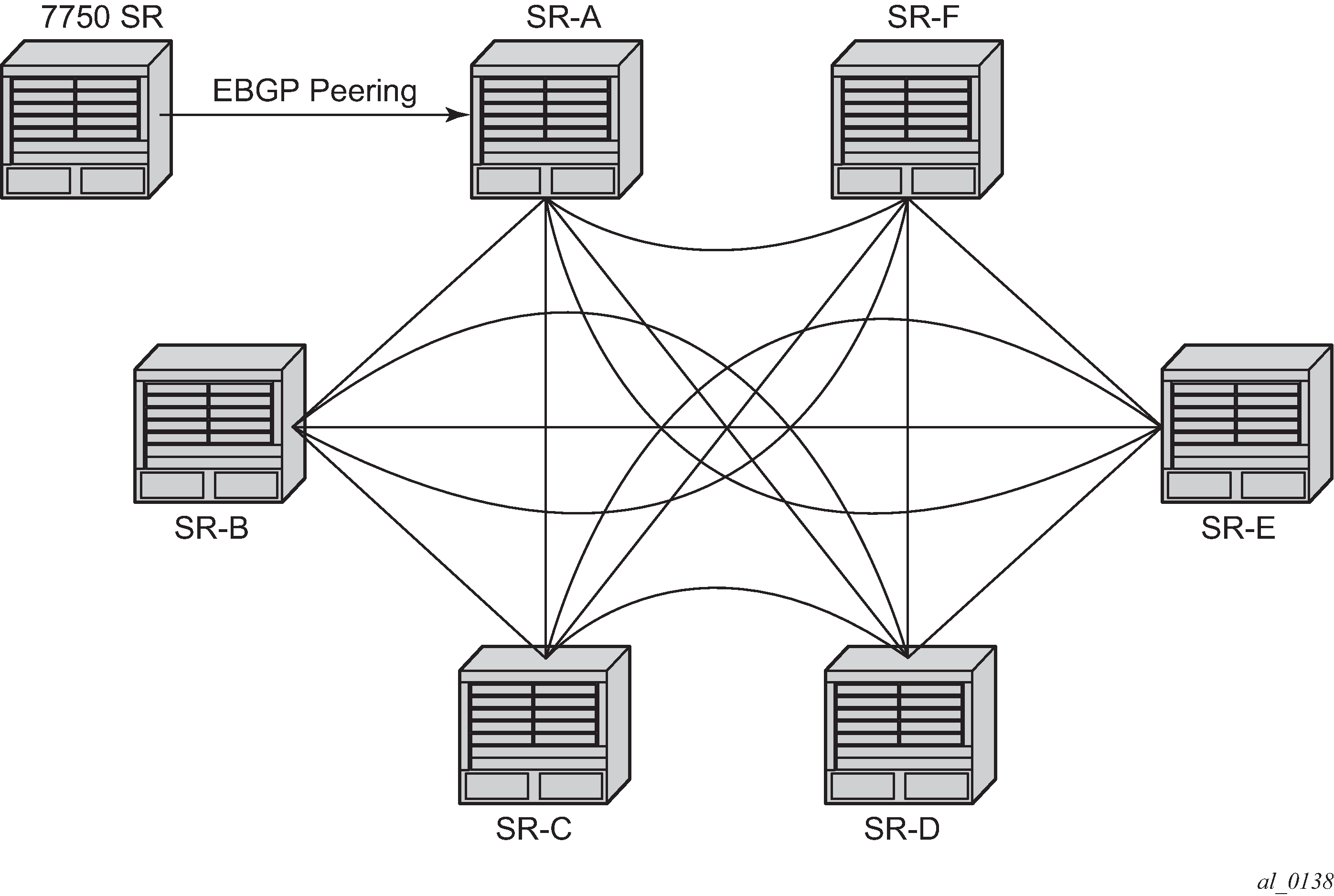
Create a full-mesh of IBGP sessions within the AS as shown in Figure: Fully meshed BGP configuration. This ensures routing consistency but does not scale well because the number of sessions increases exponentially with the number of BGP routers in the AS.
Use BGP route reflectors in the AS. Route reflection is described in the section titled Route reflection. BGP route reflectors allow for routing consistency with only a partial mesh of IBGP sessions within the AS.
-
Create a confederation of autonomous systems. BGP confederations are described in the section titled BGP confederations.