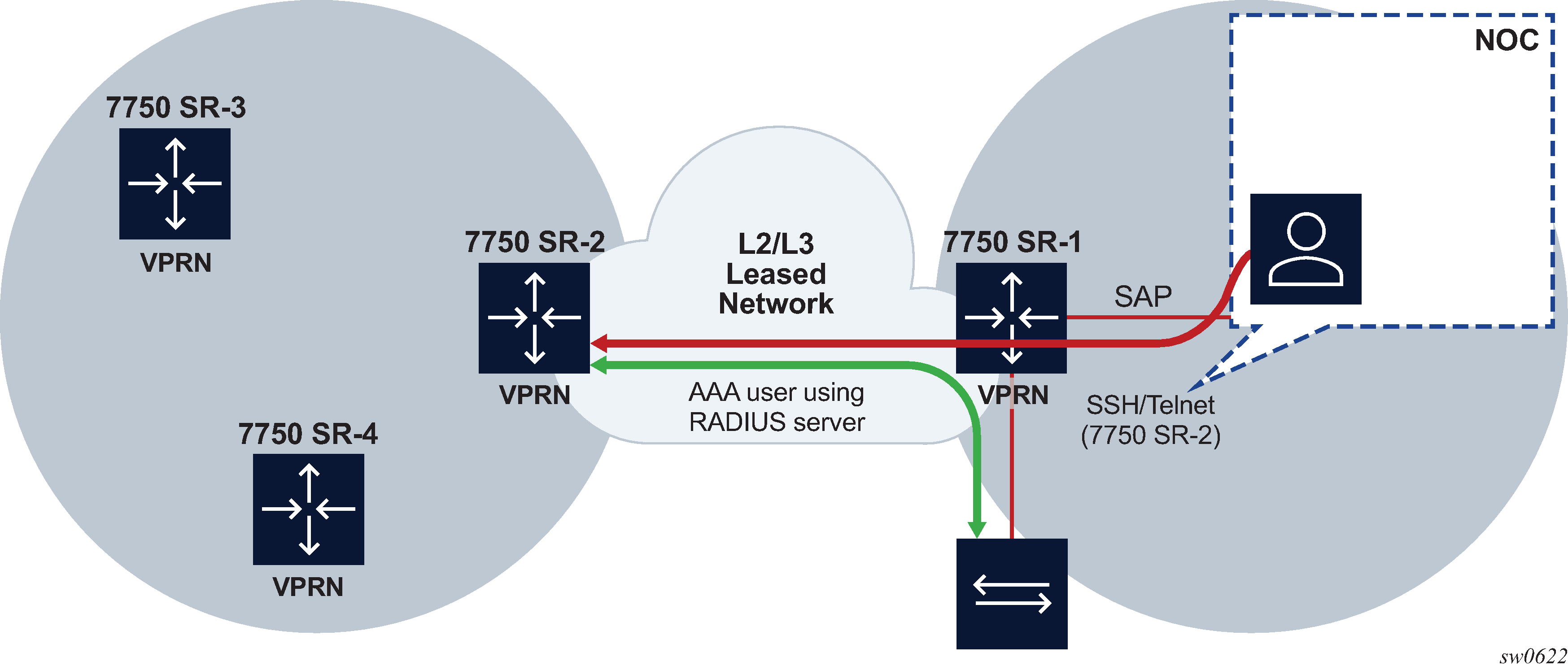
There are two basic approaches that can be used to manage a node using a VPRN. In both cases, management traffic is received and sent in the VPRN router instance:
- Management traffic can target the IP address of a VPRN interface
- Management traffic can target the system address in the base router instance (using grt-leaking)
In the first approach, node management can be enabled using the local interface of any VPRN service. A management VPRN is separated from other traffic using an MPLS transport tunnel. This provides IP domain separation and security for the management domain. The management domain supports IPv4 and IPv6 address families and the AAA server is connected to the same VPRN for authentication, authorization, and accounting. The SR OS allows management using a VPRN as long the management packet is destined for a local interface of the VPRN, in addition it allows configuration of the AAA servers within a VPRN; see Figure: VRF network example.
In the second approach, node management is achieved using GRT leaking. In this case the management traffic uses an IP address in the Base routing context. See Management via VPRN using GRT leaking for details on this method.
The remainder of this section describes node management using the local VPRN interfaces (non grt-leaking).