AA ISA supports modifications of the HTTP header for traffic going to specific user configured sites (URLs/IPs) to add network-based information, such as subscriber ID, to the HTTP header. These sites use this information to authenticate the user or present the user with user-specific information and services.
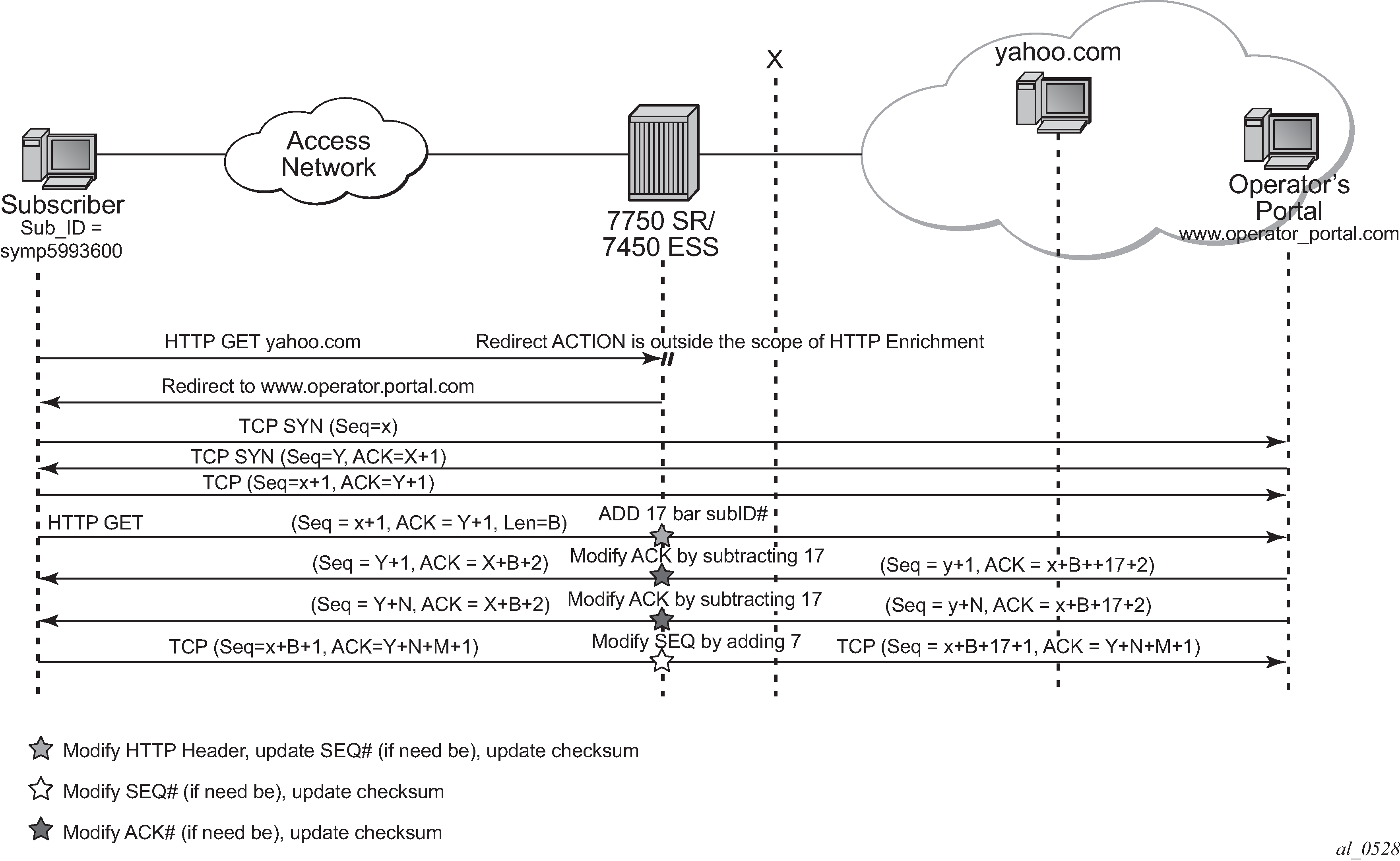
In Figure: HTTP enrichment, the operator configures the AA ISA to insert the subscriber ID into the HTTP header for all the HTTP traffic destined for the operator portal (designated by server IP or HTTP hostname). Traffic going to other destinations, such as yahoo.com, does not get enriched. To support this, AA introduces a new AQP action called HTTP_enrich that allows the operator to enrich traffic that satisfies the AQP-matching conditions.
The operator can configure multiple HTTP enrichment policies that are applied to traffic going to different destinations. For example, HTTP traffic destined for xyz.com, gets the user's IP inserted into the header, while traffic going to billing.xyz.com gets enriched with the subscriber ID and the user's IP address.
The AA ISA supports the insertion of one or more fields listed in Table: HTTP header enrichment fields and formats into the HTTP header.
| Field | Format | Supported in all deployments | Supported in FWA mode only |
|---|---|---|---|
|
apn |
Complete APN string |
— | ✓ |
|
apn-ni |
APN Network Identifier (APN-NI) or the complete APN if AA cannot decode the APN properly |
— | ✓ |
|
billing-type |
4-byte value IE: 0001 |
— | ✓ |
|
dynamic-acr |
Dynamic Anonymous Customer Reference (ACR)1 |
— | ✓ |
|
imei-hyphenated2 |
Subscriber's IMEI with format AABBBBBB-CCCCCC-EE |
— | ✓ |
|
imei-sv |
Subscriber's IMEI with format AABBBBBBCCCCCCEE |
— | ✓ |
|
imsi2 |
Subscriber’s IMSI |
— | ✓ |
|
msisdn |
Subscriber’s MSISDN |
— | ✓ |
|
msisdn-ts |
Subscriber's MSISDN appended with the UNIX timestamp |
— | ✓ |
|
msisdn-without-cc |
Subscriber's MSISDN without the country code |
— | ✓ |
|
pgw_ggsn_address |
PGW IP Address in IPv4 or IPv6 format, if the user is not in 5G UPF IP Address, if the user is in 5G |
— | ✓ |
|
plmin-id |
MCC/MNC values as defined in 3GPP 24.301 |
— | ✓ |
|
rat-type |
4-byte value as defined in 3GPP 29.212 |
— | ✓ |
|
static-acr |
Static ACR1 |
— | ✓ |
|
static-string2 |
As configured by the operator |
✓ | — |
|
subscriber-id |
Subscriber’s ID |
✓ | — |
|
subscriber-ip |
Subscriber’s IP address in IPv4 or IPv6 format |
✓ | — |
|
timestamp |
8-byte UNIX timestamp when enrichment took place |
— | ✓ |
|
user-location |
— | ✓ | |
|
user-location-3gpp |
ULI encoded as defined in 3GPP TS2.061 |
— | ✓ |
|
user-location-raw2 |
ULI in raw format: <uli-type1>[+<uli-type2>]= <ULI data in hex> Example: x-locinfo: TAI+ECGI= 1300622c46130062014adf16 |
— | ✓ |
Table: User-location encoding and enrichment examples lists user-location encoding and enrichment examples.
| Identity-type format | Enrichment example3 |
|---|---|
|
CGI mcc-mnc-lac-ci |
x-user-loc: CellId=310-053-01a1-100a |
|
SAI mcc-mnc-lac-sac |
x-user-loc: ServiceId=310-054-01a2-200b |
|
RAI mcc-mnc-lac-rac |
x-user-loc: RoutingId=310-066-01a3-300c |
|
TAI mcc-mnc-tac |
x-user-loc: TrackingId=310-220-01a4 |
|
ECGI mcc-mnc-eci |
x-user-loc: EutranCellId=623-01-1234567 |
|
LAI mcc-mnc-lac |
Not supported |
|
Not-available |
x-user-loc: User Location unavailable |
-
The ULI type can change and when it does, the mobile gateway reports it as a change to the AA-sub. AA stores and uses the latest ULI for enrichment. If the ULI type changes between the original packet transmission and the TCP retransmission, the latest ULI type is used on retransmission (that is, the ULI for retransmission is not cached).
-
The mcc-mnc values of the ULI are decimal digits (BCD), while the trailing portion of the ULI are hexadecimal values.
-
There can be more than one ULI identity type specified for an AA-sub, in which case the ECGI format is used. The only combination ULI supported by the mobile gateway is TAI + ECGI.
-
LAI is not supported, therefore this value is not used for enrichment.
-
The ULI is an optional parameter and may not be reported for an AA-sub. In this case, when enrichment is requested, the header is enriched with "User Location Unavailable".
The text preceding an inserted field is fully configurable. For example, sub-ID = 1243534666 or x-sub-ID = 1243534666.
AA supports enrichment of all HTTP methods, such as GET, POST, and so on. AA enriches HTTP traffic without having to terminate the TCP session (for example, it does not act as a proxy). In this way, the AA enrichment function does not intervene with other TCP acceleration functions or appliances that could be deployed by the operator.
For configured enriched fields, operators can optionally configure AA ISA to perform MD5 hashing, RC4 encryption, AES encryption, and anti-spoofing. When hashing is configured, the operator can optionally configure a string which is appended to the parameter before being hashed.
To perform encryption, the operator can configure an encryption key, which is used to encrypt the header values using the RC4 or AES algorithm, or install a certificate and configure the header enrichment to use that certificate. In the case of certificate-based header enrichment, the system uses the key contained in the HTTP header and performs encryption using the RSA algorithm. The system supports a maximum of 20 certificate profiles per group.
Anti-spoofing, if enabled, ensures that only the fields enriched by AA are valid. Anti-spoofing is applicable only to the subscriber ID field.
AA statistics reflect post header enrichment packet sizes.