This section discusses IP Security (IPsec), GRE tunneling, and IP-IP tunneling features supported by the MS-ISA2/ESA-VM (ISA is used to refer to any of these hardware). In these applications, the ISA functions as a resource module for the system, providing encapsulation and (for IPsec) encryption functions. The IPsec encryption functions provided by the ISA are applicable for many applications including mobile backhaul, encrypted SDPs, video wholesale, site-to-site encrypted tunnel, and remote access VPN concentration.
Figure: 7750 SR IPsec implementation architecture shows an example of an IPsec deployment, and the way this would be supported inside a 7750 SR. GRE and IP-IP tunnel deployments are very similar. IP tunnels have two flavors GRE/IP-IP, in all but a few area the information for IP Tunnels applies to both types.
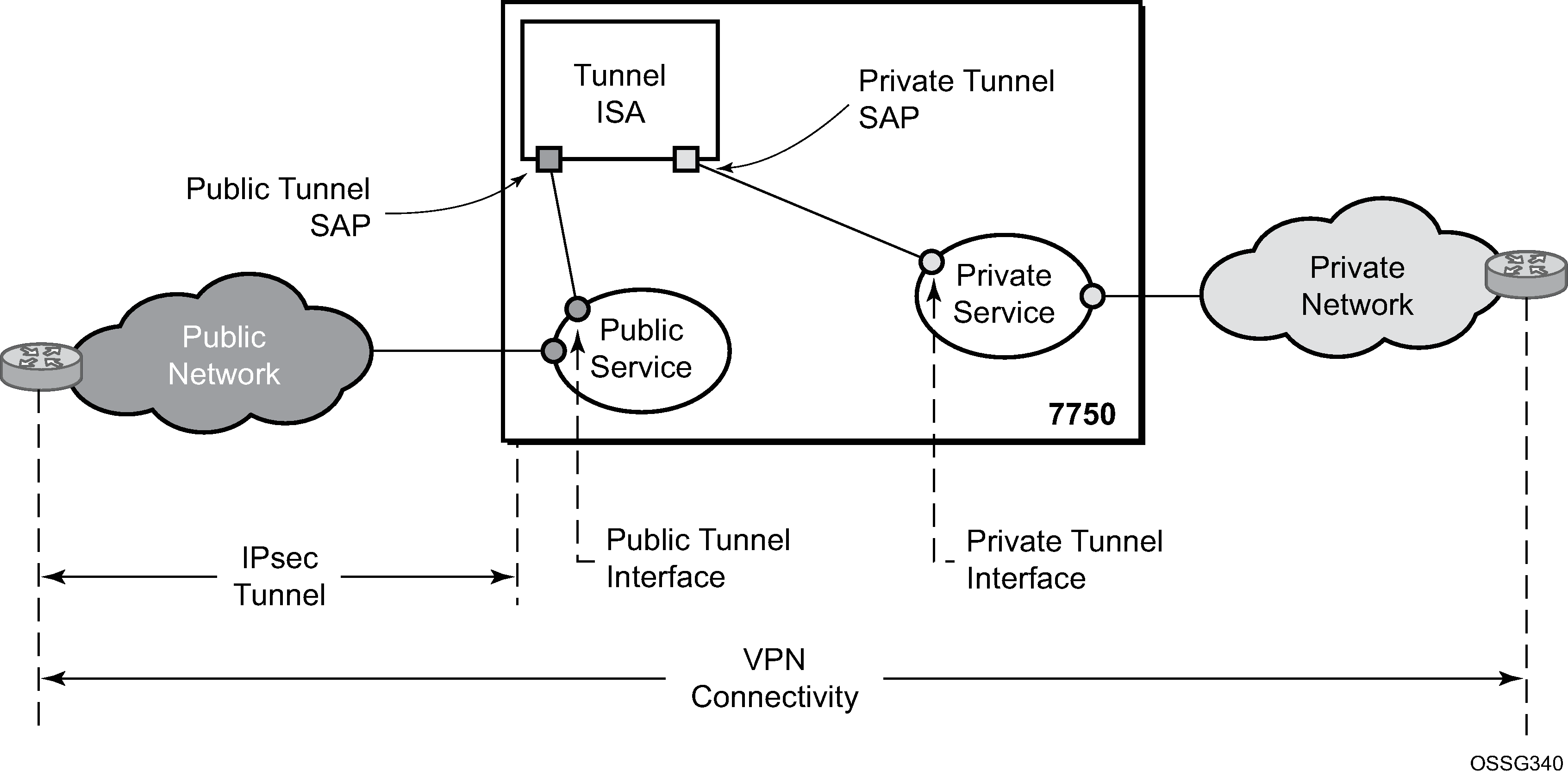
Figure: 7750 SR IPsec implementation architecture, the public network is typically an ‟insecure network” (for example, the public Internet) over which packets belonging to the private network in the diagram cannot be transmitted natively. Inside the 7750 SR, a public service instance (IES or VPRN) connects to the public network and a private service instance (typically a VPRN) connects to the private network.
The public and private services are typically two different services, and the ISA is the only ‟bridge” between the two. Traffic from the public network may need to be authenticated and encrypted inside an IPsec tunnel to reach the private network. In this way, the authenticity/confidentiality/integrity of accessing the private network can be enforced. If authentication and confidentiality are not important then access to the private network may alternatively be provided through GRE or IP-IP tunnels.
The ISA provides a variety of encryption features required to establish bidirectional IPsec tunnels including:
control plane
manual keying
dynamic keying: IKEv1/v2
IKEv1 mode: main and aggressive
authentication: Pre-Shared-Key /xauth with RADIUS support/X.509v3 Certificate/EAP
Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS)
DPD
NAT-Traversal
security policy
DH-Group: 1/2/5/14/15/19/20/21
data plane
ESP (with authentication) tunnel mode
authentication algorithm: MD5/SHA1/SHA256/SHA384/SHA512/AES-XCBC
encryption algorithm: DES/3DES/AES128/AES192/AES256/AES-GCM128/AES-GCM192/AES-GCM256/AES-GMAC128/AES-GMAC192/AES-GMAC256
anti-replay protection
N:M IPsec ISA card redundancy
SR OS uses a configured authentication algorithm for the Pseudorandom Function (PRF). IPsec features are supported on the 7750 SR, the 7450 ESS, and VSR.
There are two types of tunnel interfaces and SAPs. See Table: Tunnel interfaces and SAPs for more information.
| Tunnel interface/SAP | Association/configuration |
|---|---|
|
Public tunnel interface |
configured in the public service; outgoing tunnel packets have a source IP address in this subnet |
|
Public tunnel SAP |
associated with the public tunnel interface; a logical access point to the ISA card in the public service |
|
Private tunnel interface |
configured in the private service; can be used to define the subnet for remote access IPsec clients |
|
Private tunnel SAP |
associated with the private tunnel interface, a logical access point to the ISA card in the private service |
Traffic flows to and through the ISA card as follows:
upstream direction
The encapsulated (and possibly encrypted) traffic is forwarded to a public tunnel interface if its destination address matches the local or gateway address of an IPsec tunnel or the source address of a GRE or IP-IP tunnel. Inside the ISA card, encrypted traffic is decrypted, the tunnel header is removed, the payload IP packet is delivered to the private service, and from there, the traffic is forwarded again based on the destination address of the payload IP packet.
downstream direction
Unencapsulated/clear traffic belonging to the private service is forwarded into the tunnel by matching a route with the IPsec/GRE/IP-IP tunnel as next-hop. The route can be configured statically, learned by running OSPF on the private tunnel interface (GRE tunnels only), learned by running BGP over the tunnel (IPsec and GRE tunnels only), or learned dynamically during IKE negotiation (IPsec only). After clear traffic is forwarded to the ISA card, it is encrypted if required, encapsulated per the tunnel type, delivered to the public service, and from there, the traffic is forwarded again based on the destination address of the tunnel header.