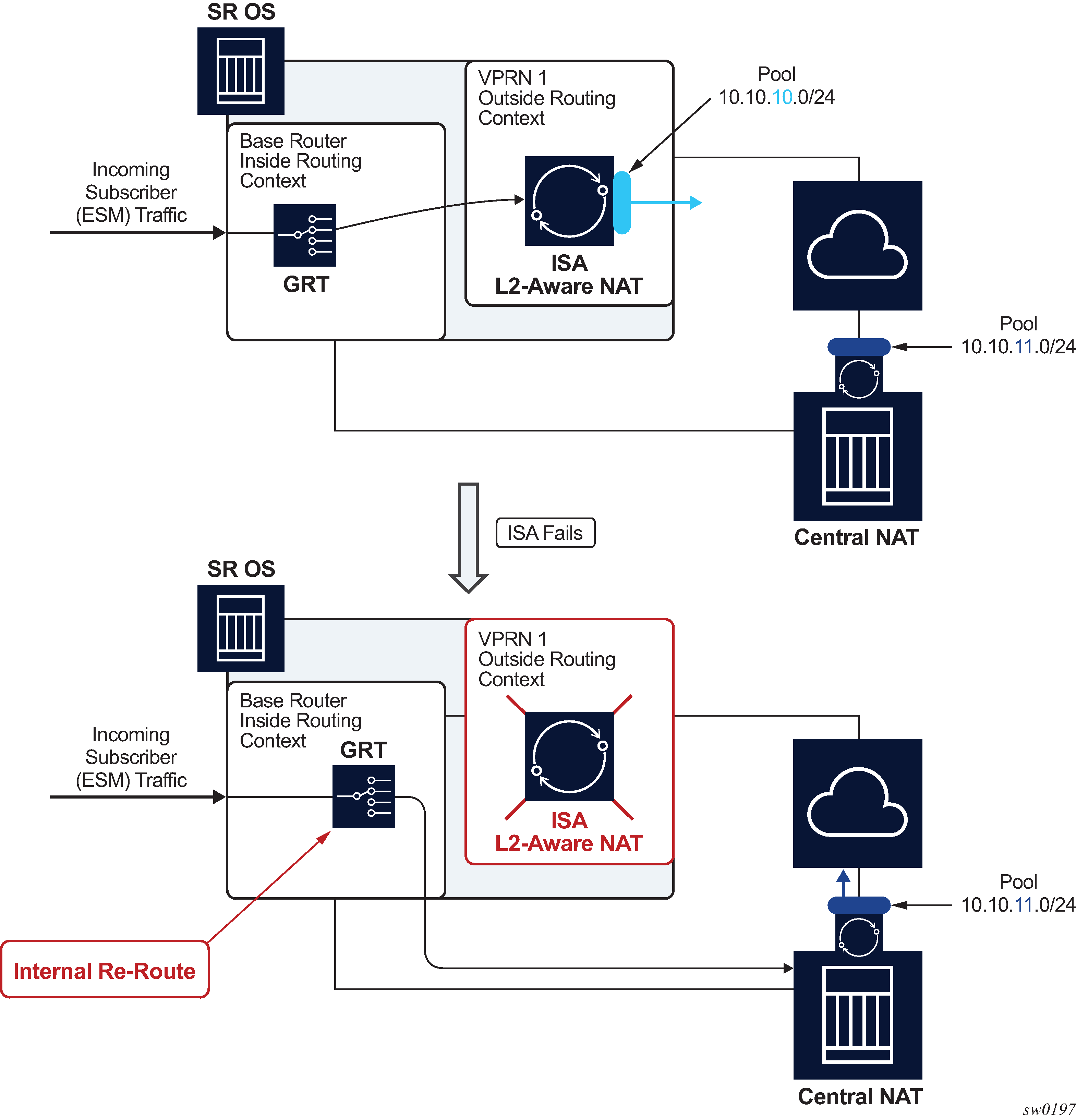
L2-Aware bypass provides the basis for traffic continuity if an MS-ISA fails. With L2-Aware bypass functionality disabled and without an intra-chassis redundancy scheme deployed (such as active/active or active/standby), the traffic to be processed by the failed MS-ISA is blackholed. This means that traffic continues to be sent to the failed MS-ISA. By enabling L2-Aware bypass, instead of being blackholed, the traffic is routed outside of the SR OS node without being NAT’d in accordance to the routing table in the inside routing context. The intent is that non-NAT’d traffic is intercepted by a central NAT node that performs the NAT function. This way, traffic served by the failed MS-ISA continues to be NAT’d by a central NAT node. The central NAT node provides redundancy for multiple SR OS nodes, therefore reducing the need to equip each individual SR OS node with multiple MS-ISAs which are normally used in an active/active or active/standby intra-chassis redundancy mode.
This concept is shown in Figure: L2-Aware bypass . The example shows the base router as an inside routing context where the global routing table (GRT) is used to decide where to send traffic if an MS-ISA is unavailable. Apart from this example, the inside routing context is not limited to the base router but instead can be an VPRN instance.
L2-Aware bypass is considered as an optional redundancy model in L2-Aware NAT which is mutually exclusive with the other two MS-ISA redundancy modes (active/active and active/standby).
L2-Aware bypass is enabled with the following CLI:
configure
isa
nat-group <id>
redundancy {active-active|active-standby|l2aware-bypass}