Similar to the non-L2-Aware ping command, understanding how the ICMP Echo Request packets are sourced in L2-Aware ping is crucial for the correct execution of this command and the interpretation of its results. The ICMP Echo Reply packets must be able to reach the source IP address that was used in ICMP Echo Request packets on the SR OS node on which the L2-Aware ping command was executed. See Figure: L2-Aware ping.
The return packet (the ICMP Echo reply sent by the targeted host) is subject to L2- Aware NAT routing executed in the MS-ISA. The L2-Aware NAT routing process looks at the destination IP address of the upstream packet and then directs the packet to the correct outside routing context. The result of this lookup is a NAT policy that references the NAT pool in an outside routing context. This outside routing context must be the same as the one from which the L2-Aware ping command was sourced. Otherwise, the L2-Aware ping command fails.
The L2-Aware ping command can be run in two modes:
basic mode (ping ip-address subscriber subscriber-id) in which the subscriber-id is a required field to differentiate subscriber hosts that assigned the same IP address (although each host has its own instantiation of this IP address)
-
extended mode where additional parameters can be selected. The two most important being the source IP address (source) and the routing context (router):
ping ip-address subscriber subscriber-id source ip-address router router-id
Figure: L2-Aware ping shows the traffic flow for an L2-Aware ping command targeting the subscriber’s IP address 10.2.3.4, sourced from the Base routing context using an arbitrary source IP address of 10.6.7.8 (it is not required that this IP address belong to the L2-Aware ping originating node).
When the host 10.2.3.4 replies, the incoming packets with the destination IP address of 10.6.7.8 are matched against the destination-prefix 10.6.7.0/24 referencing the nat-policy-1. nat-policy-1 contains the Pool B which resides in the Base routing context. Hence, the loop is closed and the execution of the L2-Aware ping command is successful.
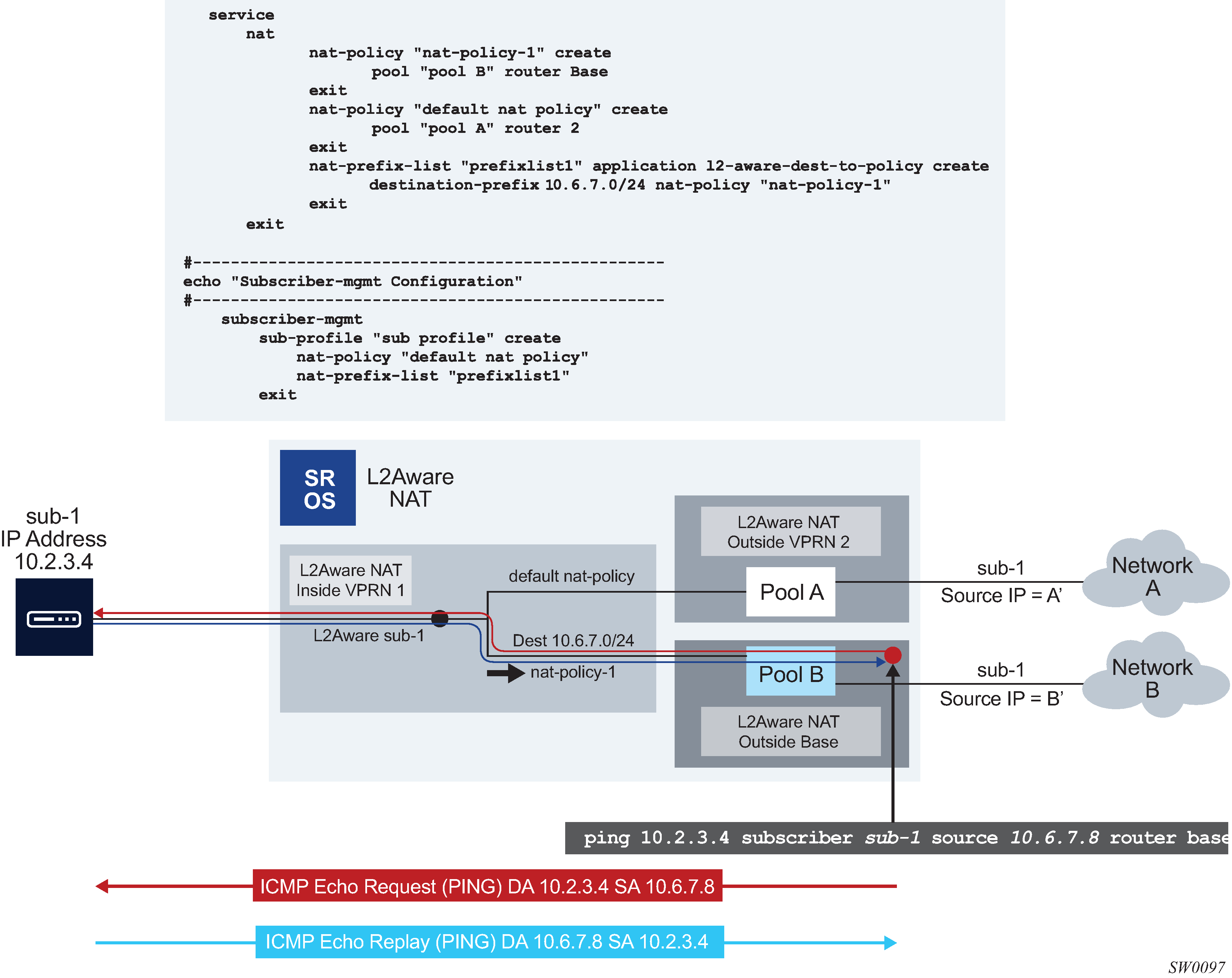
L2-Aware ping is always sourced from the outside routing context, never from the inside routing context. If the router is not specifically configured as an option in the L2-Aware ping command, the Base routing context is selected by default. If that the Base routing context is not one of the outside routing contexts for the subscriber, the L2-Aware ping command execution fails with the following error message:
‟MINOR: OAM #2160 router ID is not an outside router for this subscriber.”