The DEM technology allows the DEM-GW to detect congestion within the access network.
If congestion is detected at any point, DEM-GW can employ policies per application, per application group, or per subscriber to limit the impact of low-priority traffic on QoE-sensitive applications. See Figure: DEM-GW multi-point congestion control.
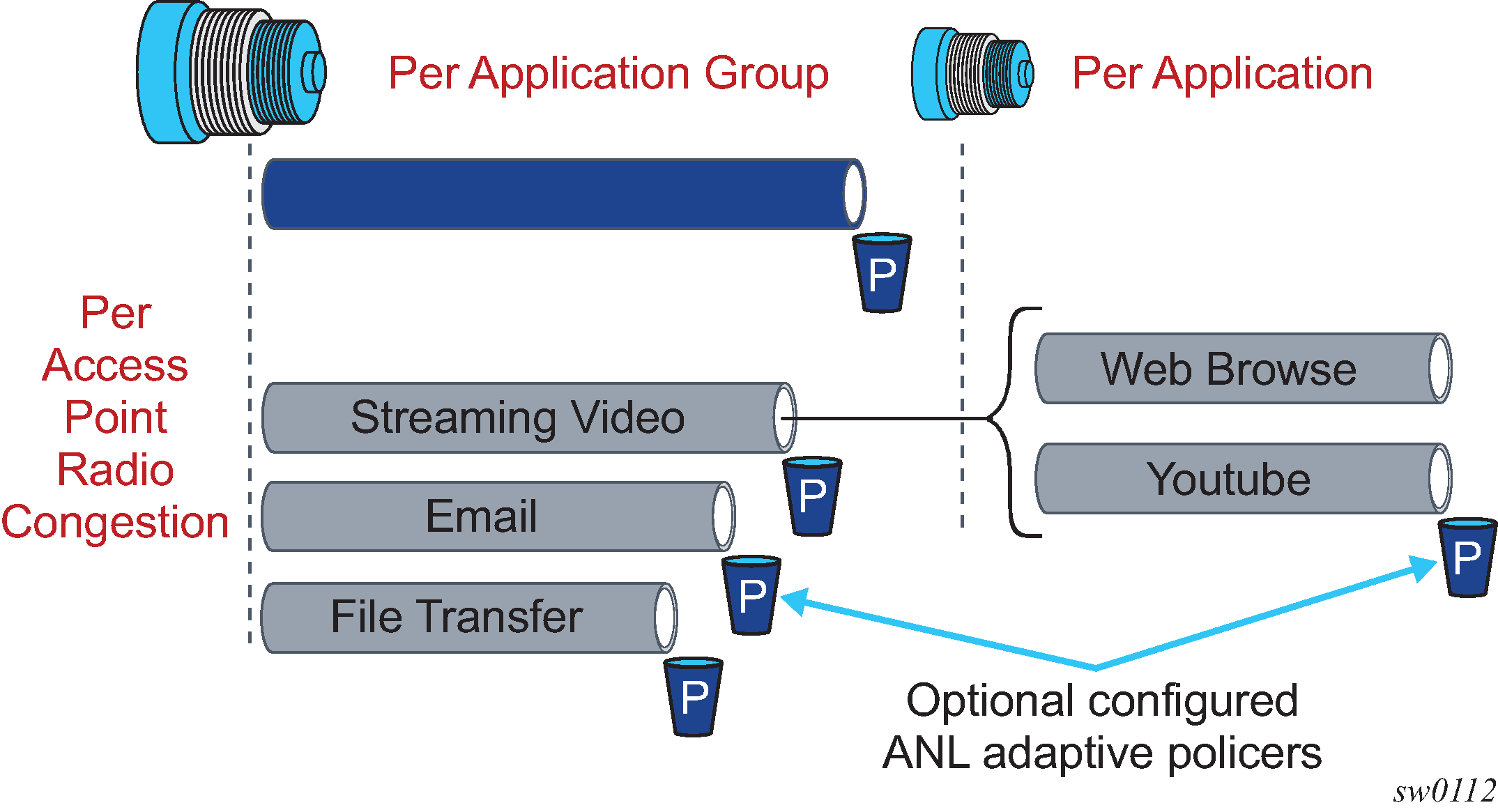
A DEM-GW is integrated directly into the WLGW using AA. The DEM-GW models the congestion points, called ANLs, that it learns from the WLGW subscriber attributes, and manages them accordingly to achieve the configured QoE/QoS target.
The DEM-GW achieves congestion control by:
running DPI to classify flows into applications, including encrypted traffic
dynamically learning access network congestion points and estimating their maximum capacity:
through real-time detection, sniffing, measurements and profiling
continuous monitoring of UEs locations and associating them to the right access point radio congestion points
QoE enforcement (efficient access point radio congestion detection, localization and management provided via configurable adaptive policers)
The DEM-GW actively runs intelligent congestion control. It relies on location information relayed by WLGW sub management for Access Point MAC and VLAN.
For AP congestion detection, the DEM-GW runs an algorithm-based on measurements of Round Trip Time (RTT) to determine congestion state.
The DEM-GW uses location-awareness of all UEs to apply traffic management at specific impacted access sites, while unrestricting users during times of non-congestion. This ensures different applications within an AP radio get fair share of available resources, while controlling low-value traffic during times of congestion.
The inherited subscriber or application awareness at the DEM-GW (SSG/PGW/GGSN), when integrated with AA application detection and control, results in entitlement-based enforcements of specific applications for specified users or UEs, allowing the operators to provide differentiated services.
The end-to-end DEM solution can involve PCRF for opt-in policy control and off-line reporting platforms to facilitate some additional value-add use-cases.